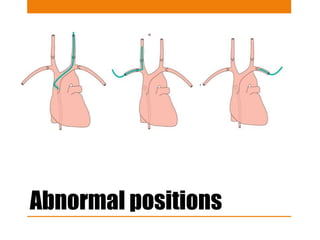
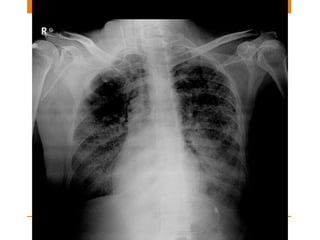
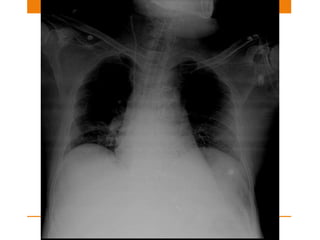
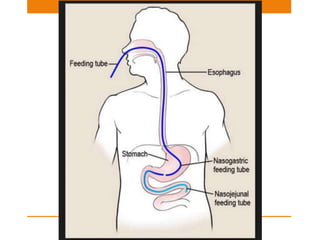
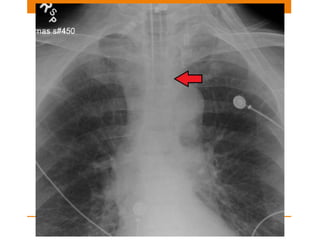
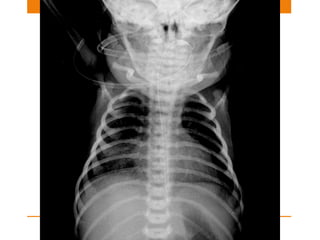
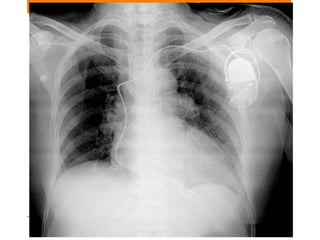
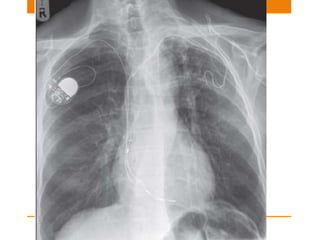
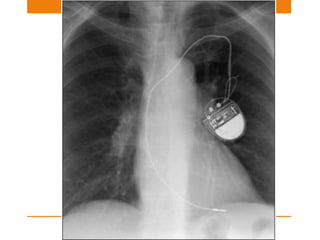
Central lines and tubes seen on chest x-rays include central venous catheters, pulmonary artery catheters, nasogastric tubes, endotracheal tubes, and tracheostomy tubes. Correct positioning is important to avoid complications. A central venous catheter's tip should be in the superior vena cava or brachiocephalic vein. A pulmonary artery catheter is used to assess pressures but is now less common. A nasogastric tube's tip should be past the stomach. An endotracheal tube should be 5-7cm above the carina. Tracheostomy tubes lie parallel to the trachea above the carina.