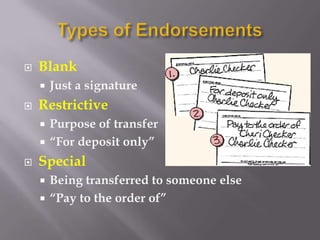
This document provides information about checking accounts and how they work. It defines key terms like checks, checkbooks, deposits, withdrawals, fees, endorsements, bounced checks, and fraud protection. It also outlines best practices for using a checking account, such as how to properly fill out and safeguard checks, how transactions are tracked in a check register, and the benefits of direct deposits and safety deposit boxes.