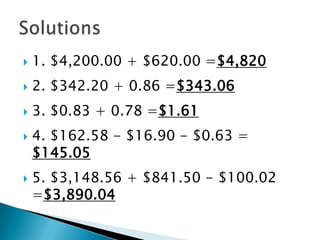
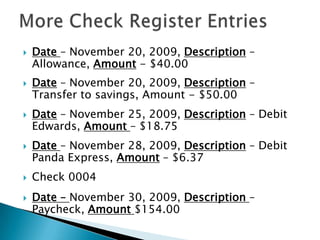
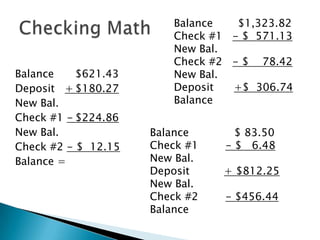
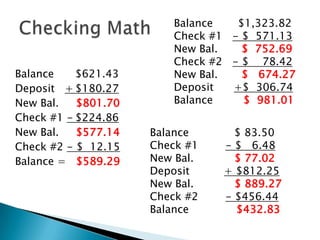
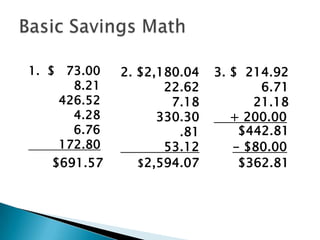This document provides information and instructions on opening and managing bank savings and checking accounts. It defines key terms related to accounts, describes different types of savings accounts and services banks offer, and provides examples and instructions for completing tasks like deposits, writing and recording checks, and reconciling a bank statement. The goal is to teach readers how to properly open and manage their bank accounts.