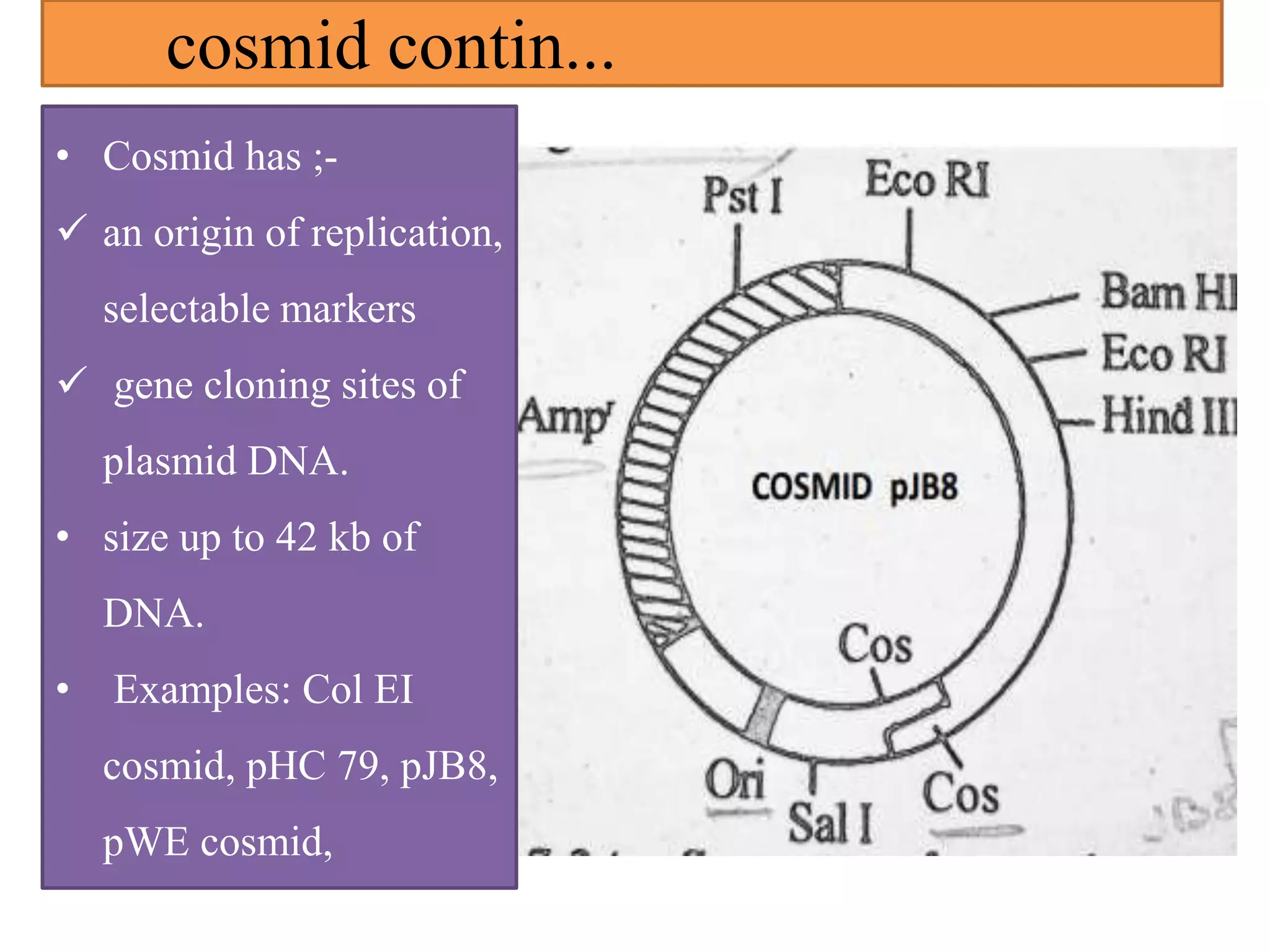
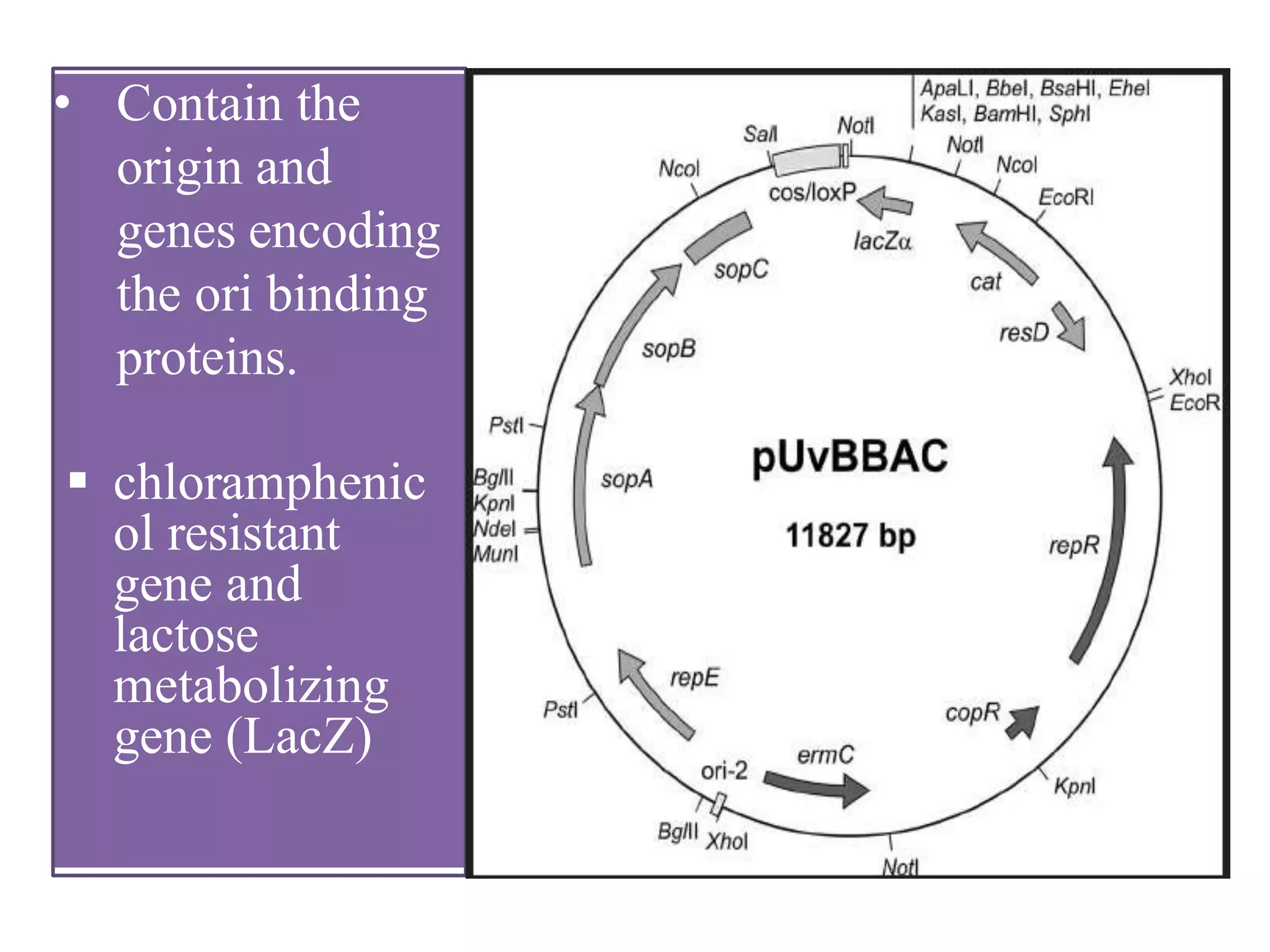
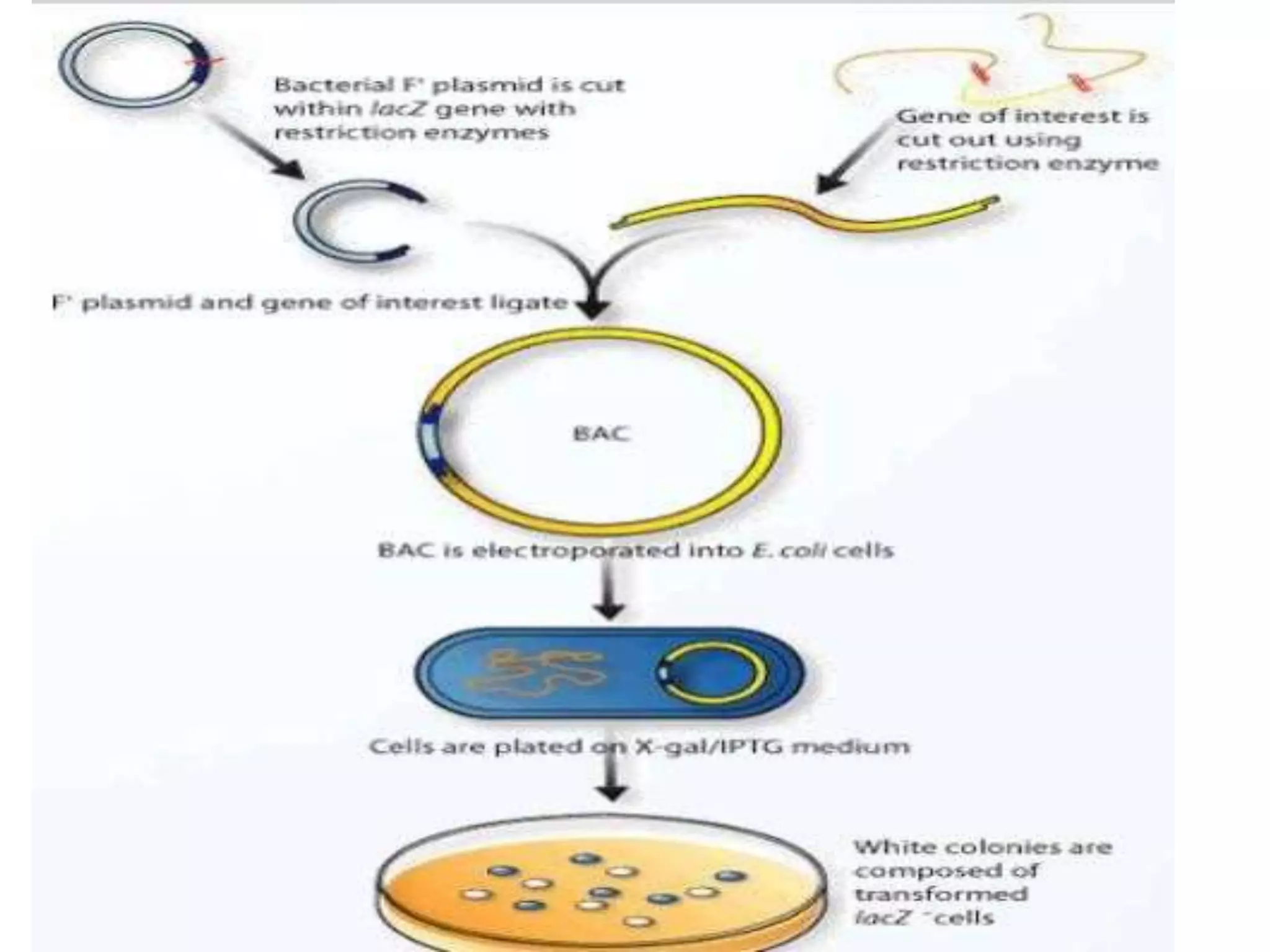
A cloning vector is a small piece of DNA that can accept foreign DNA fragments for cloning. There are several types of cloning vectors including plasmids, bacteriophages, cosmids, bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs), yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs), and human artificial chromosomes (HACs). Cosmids combine features of plasmids and bacteriophages, allowing large foreign DNA fragments of up to 42 kb to be delivered into host cells. BACs are artificially synthesized plasmids that can accommodate even larger DNA sequences of 150-350 kb without risks associated with other vectors. The choice of vector depends on factors like size of the foreign DNA and stability.