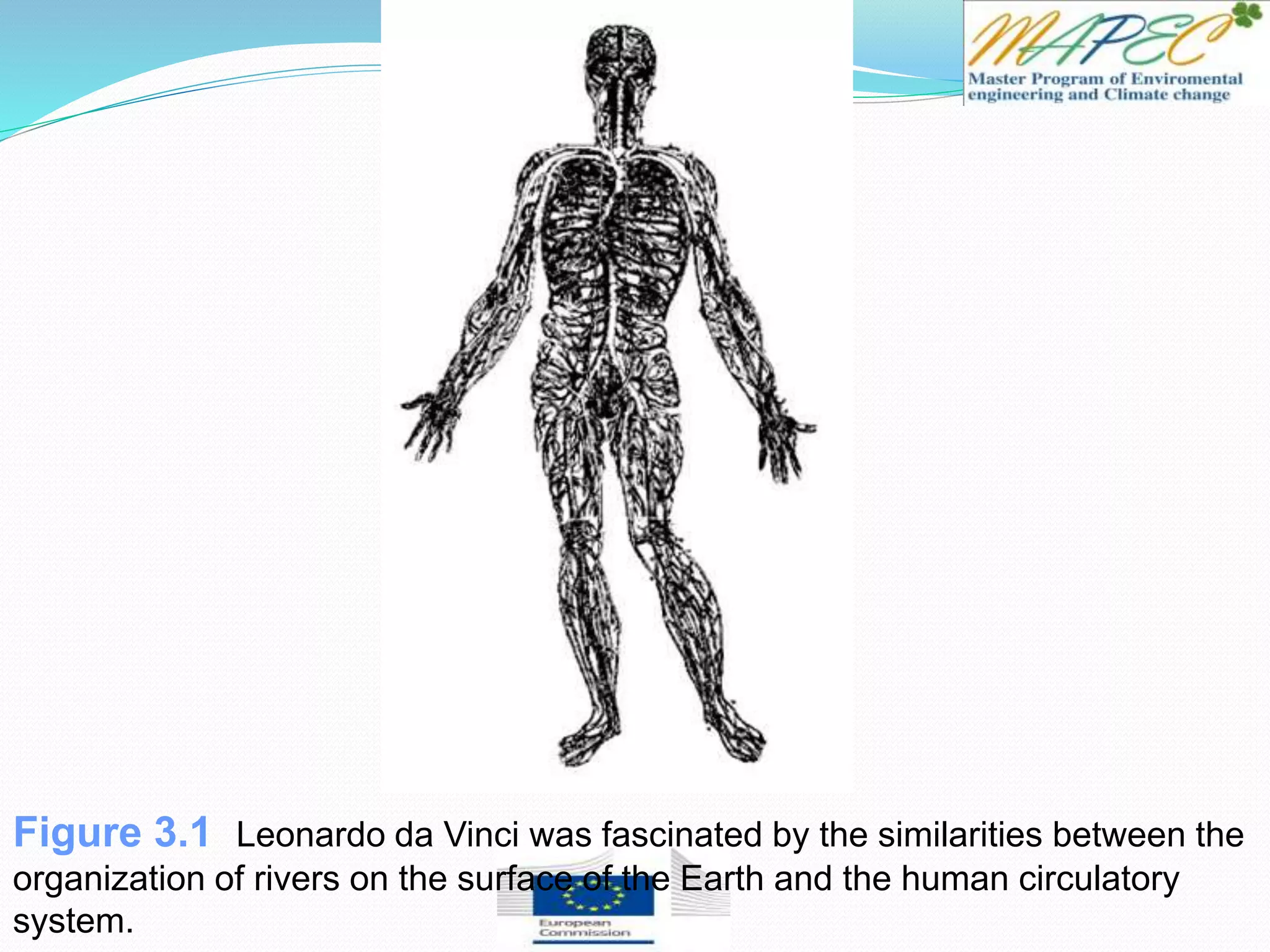
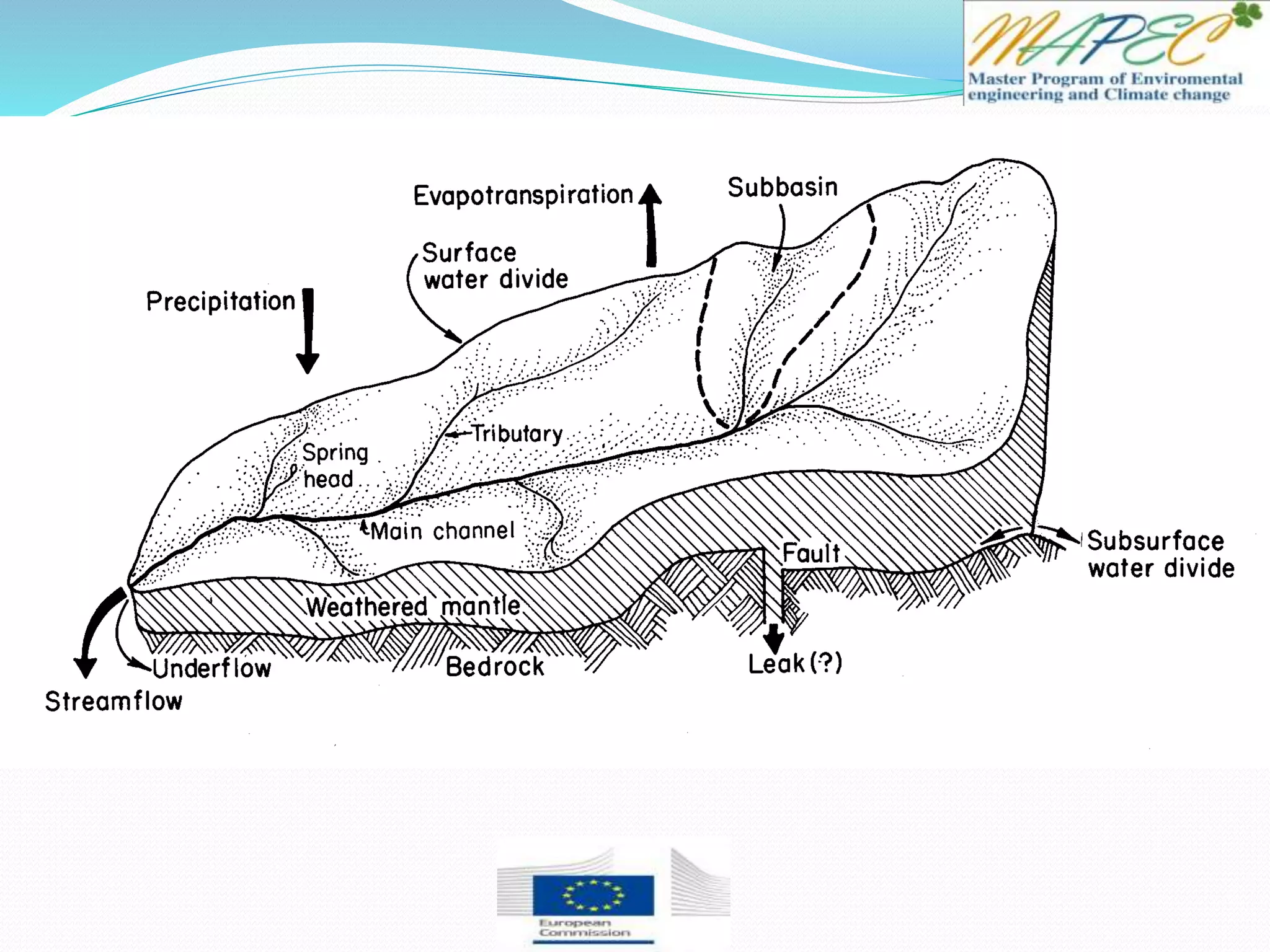
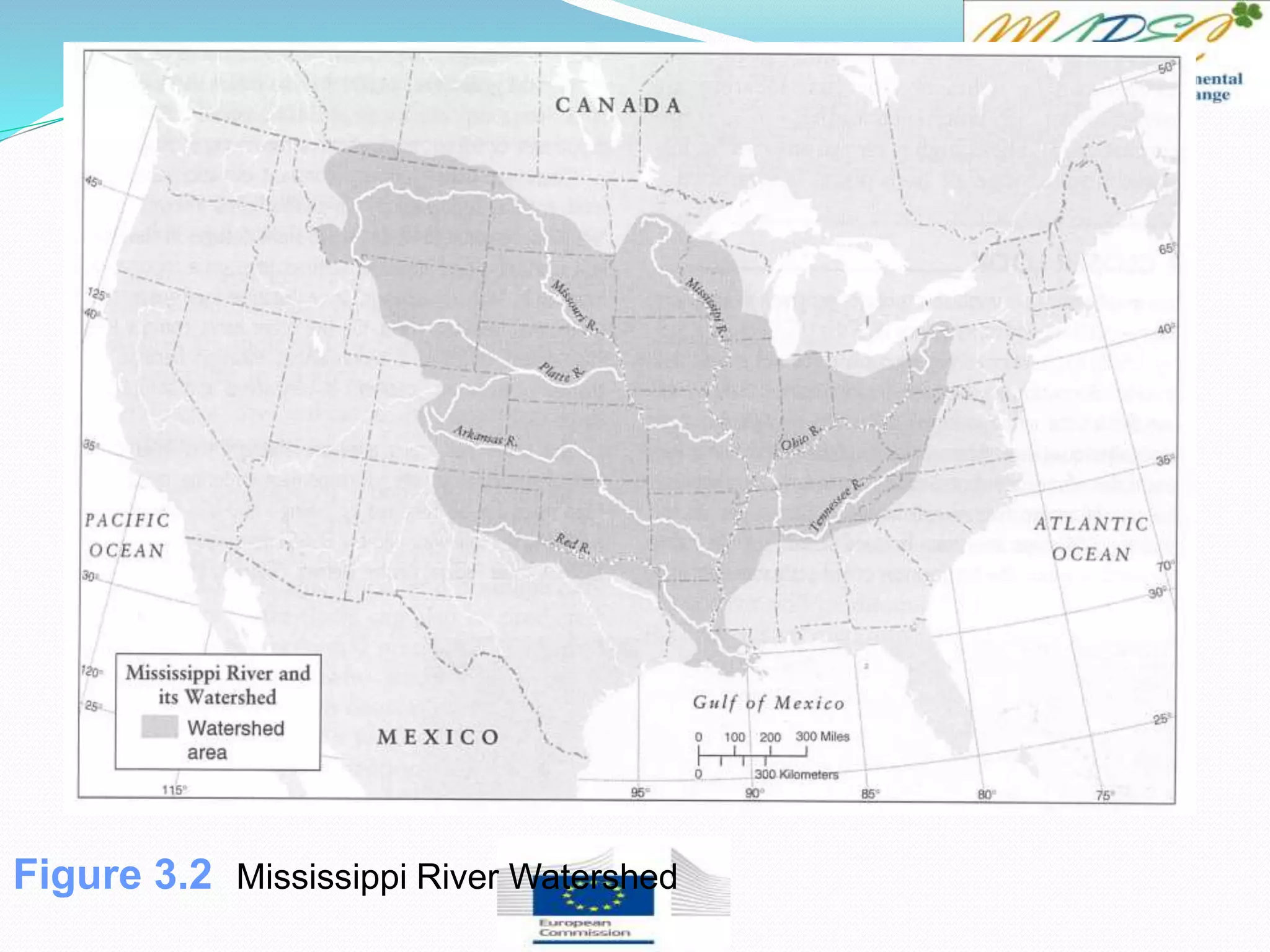
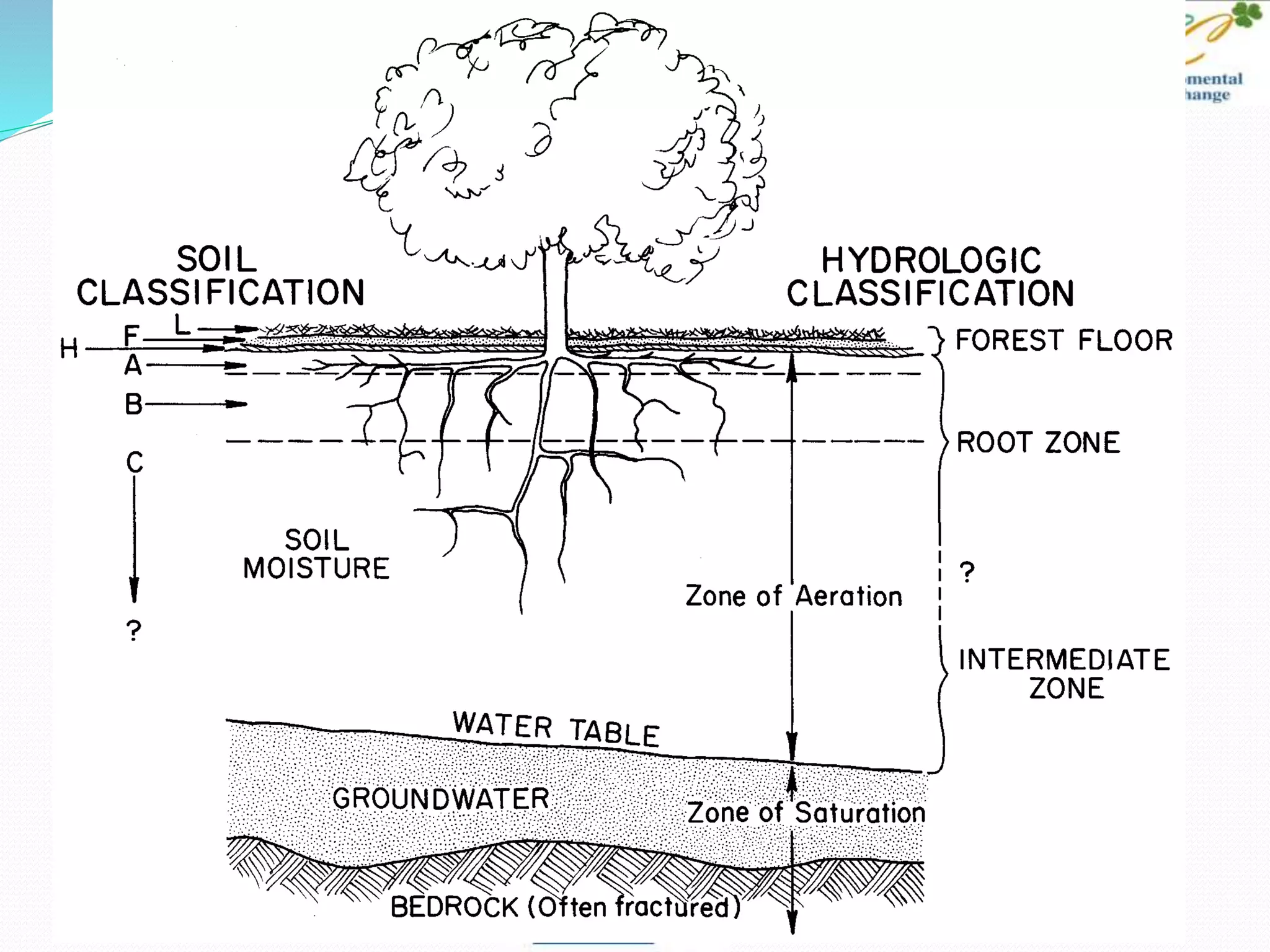
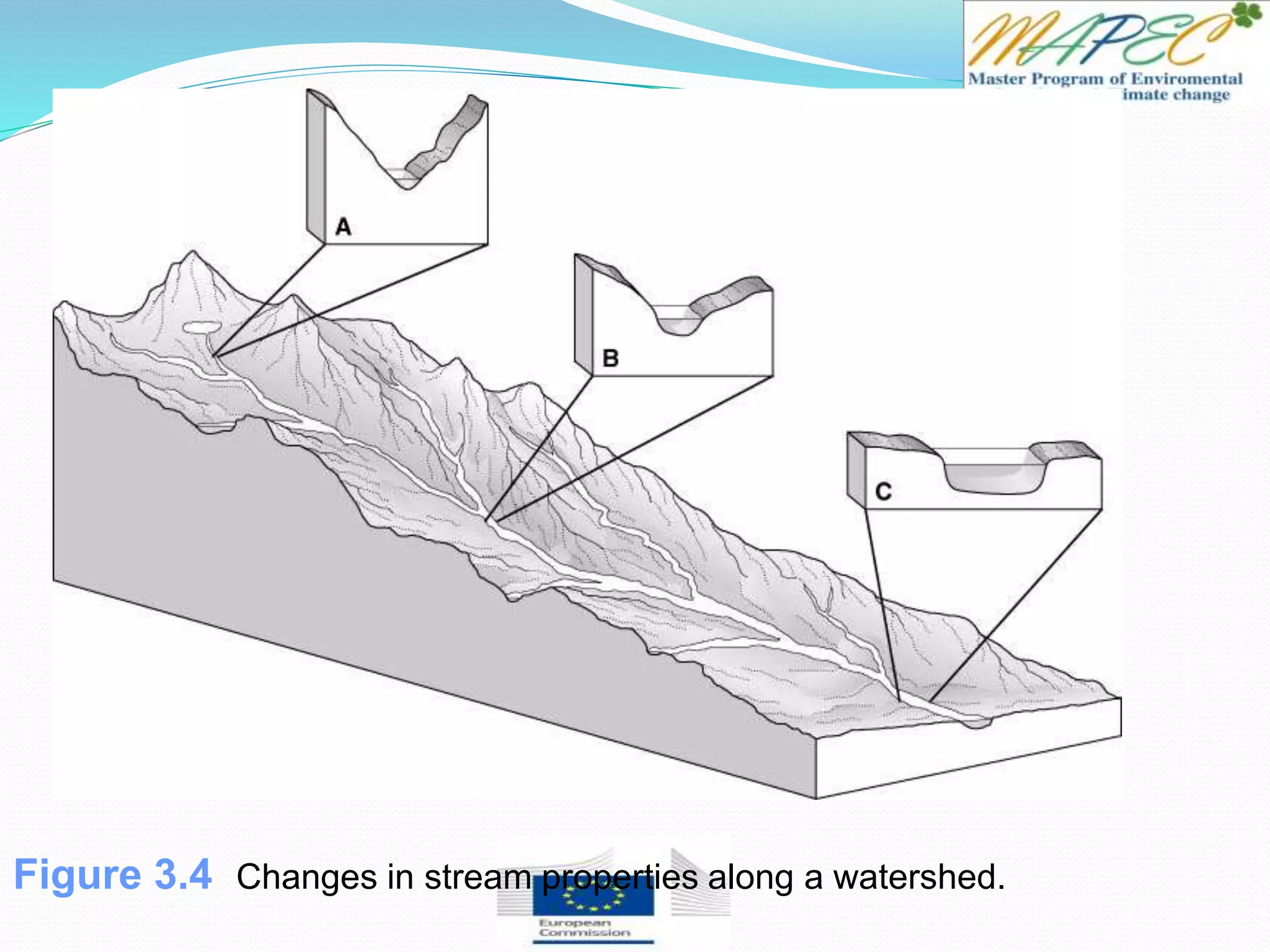
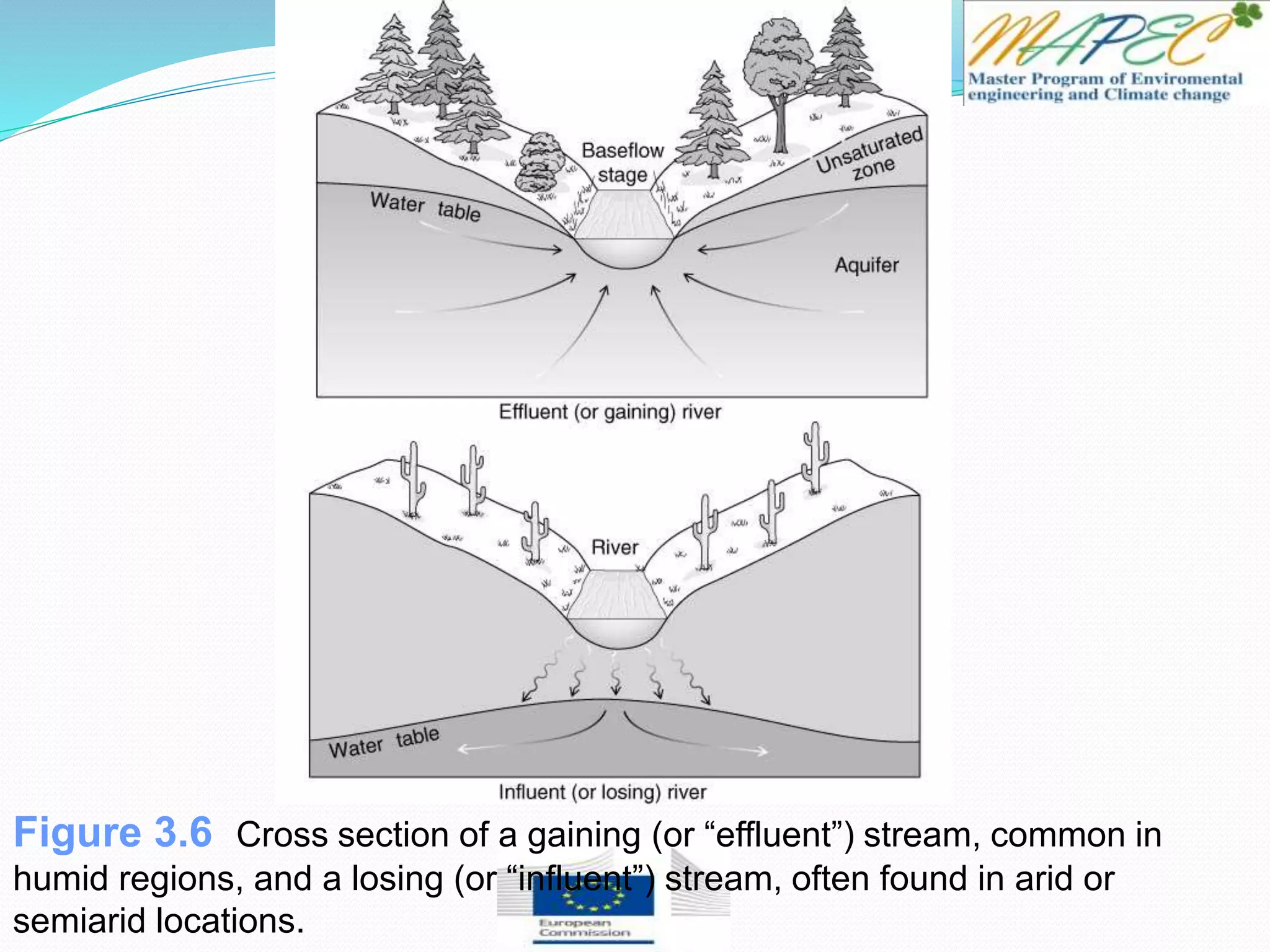
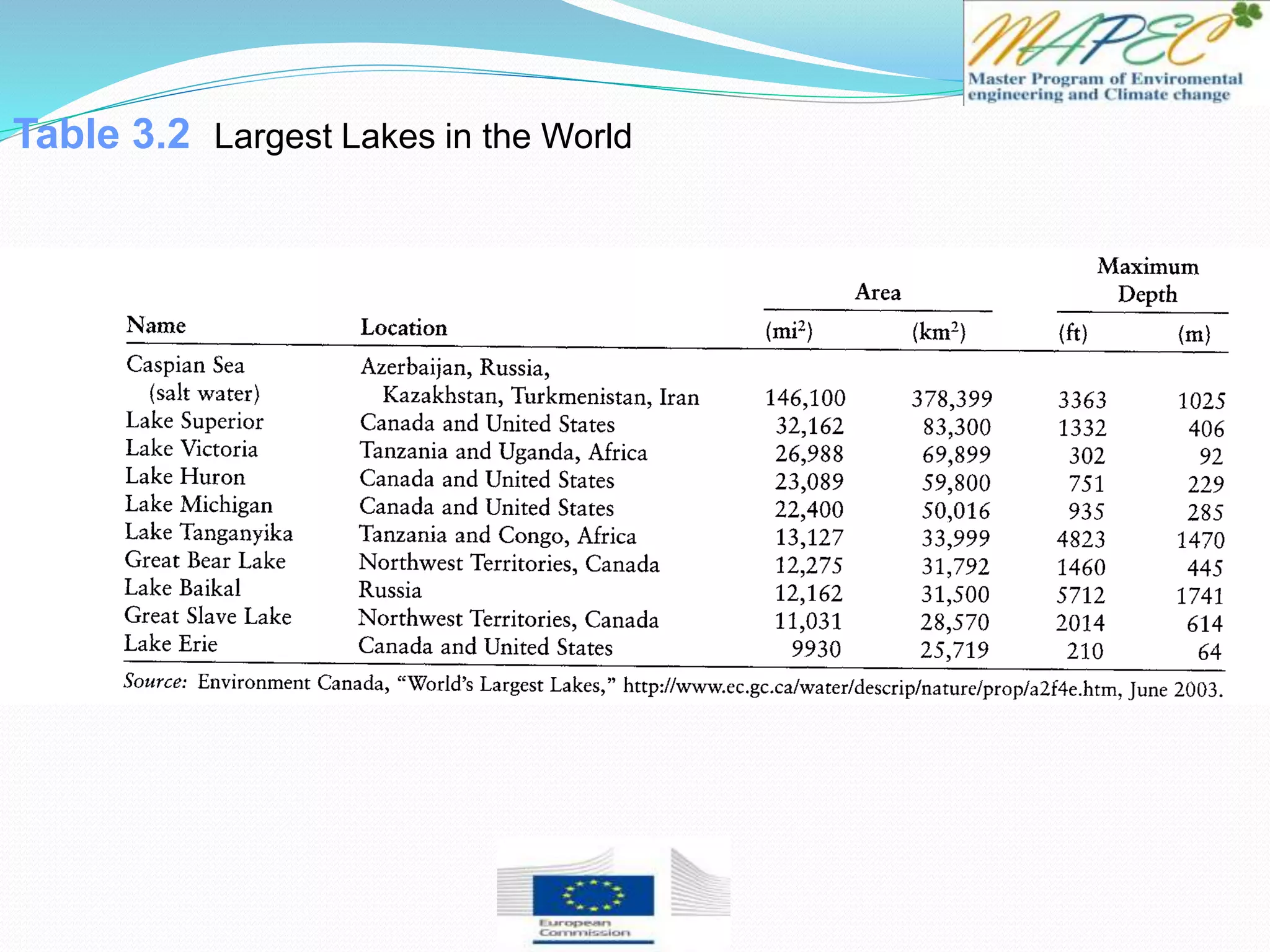
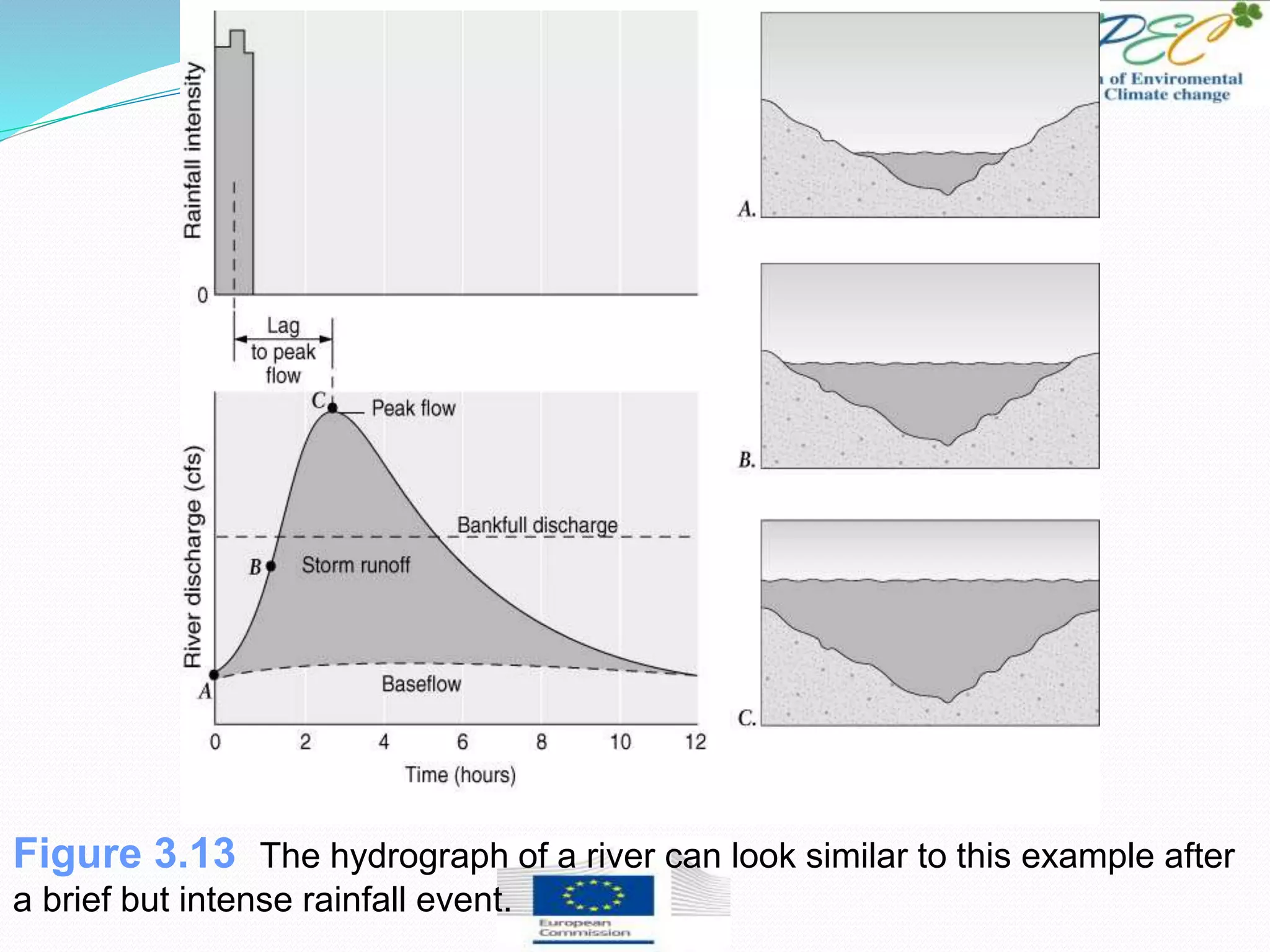
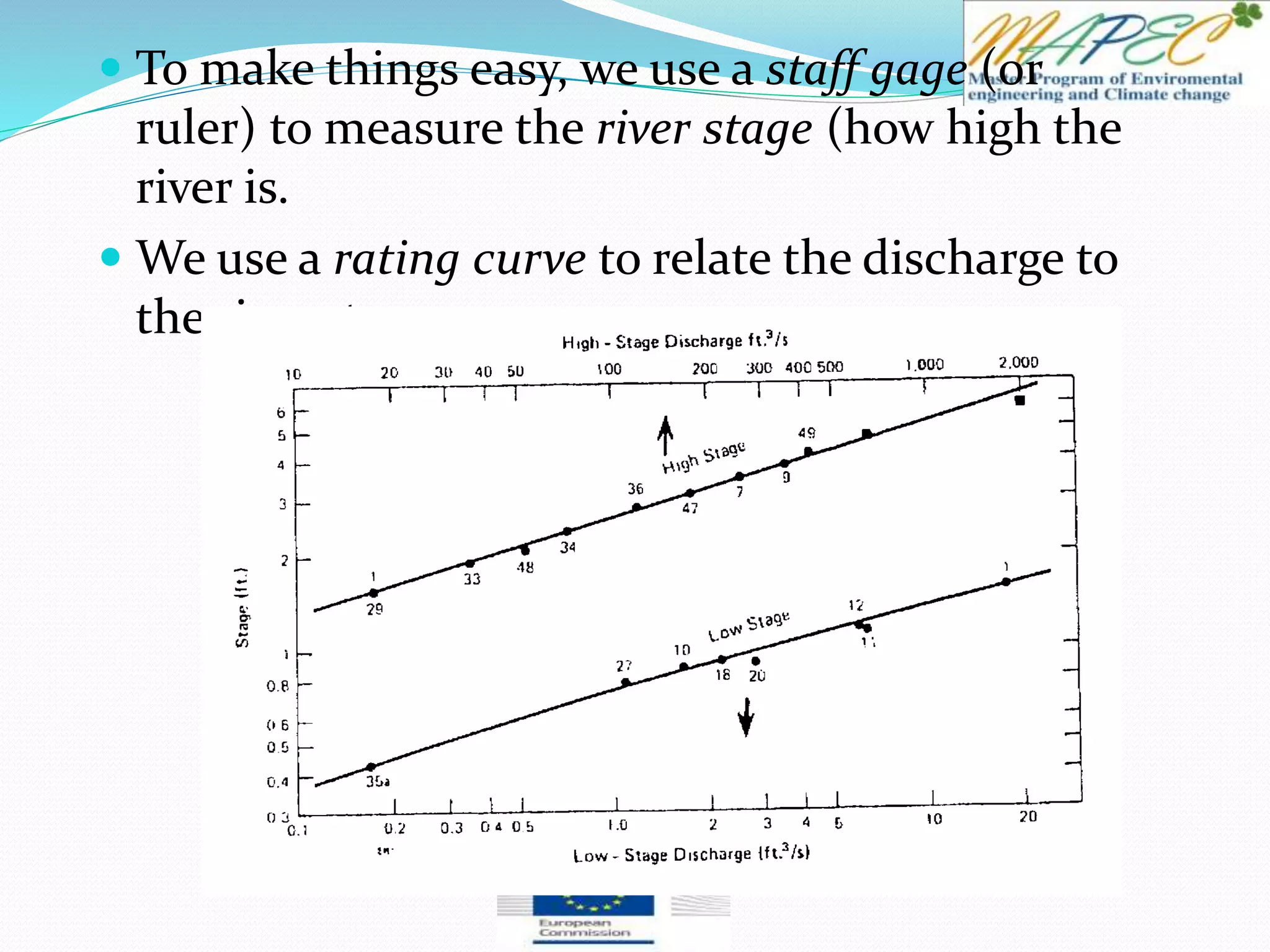
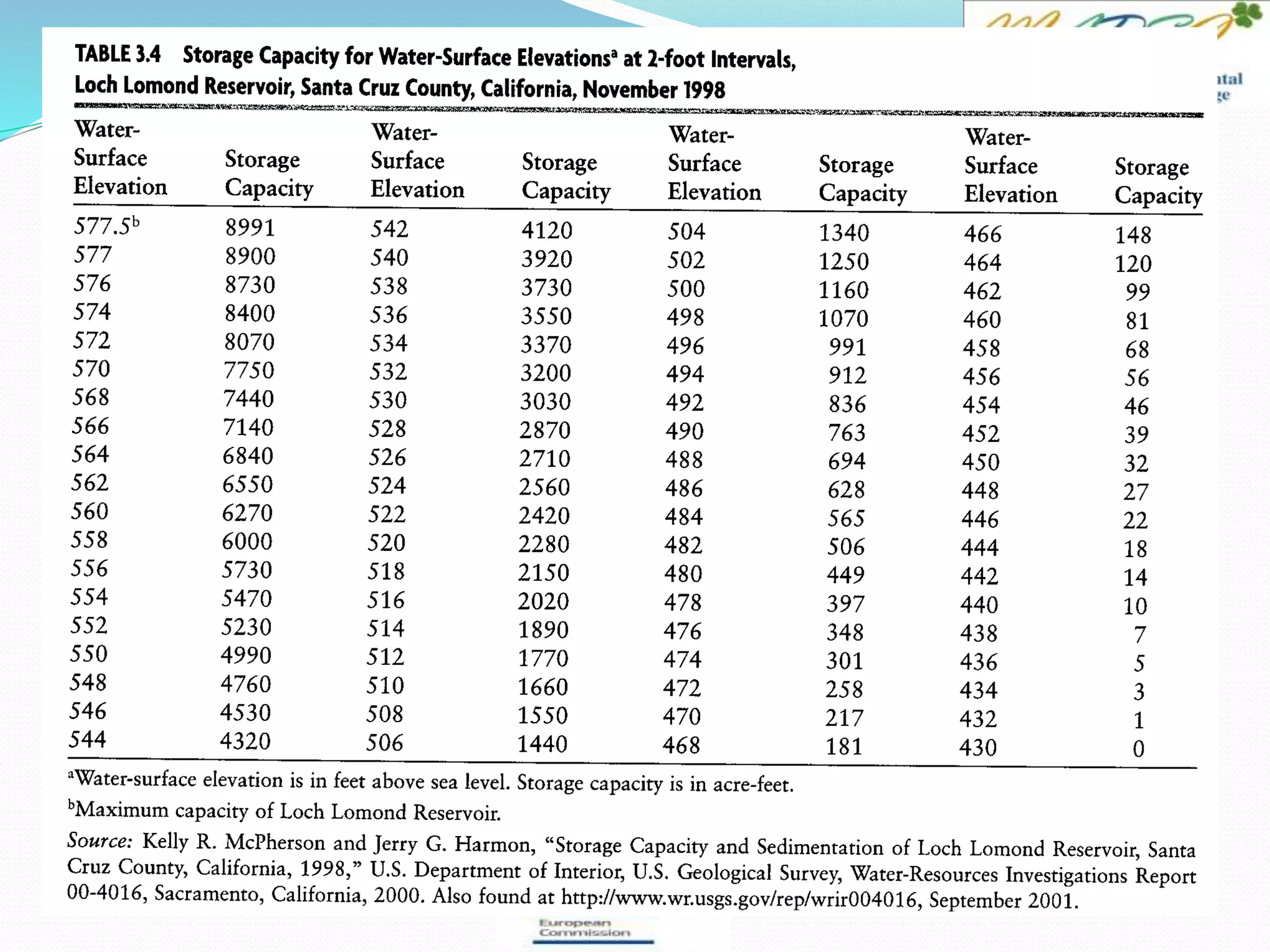
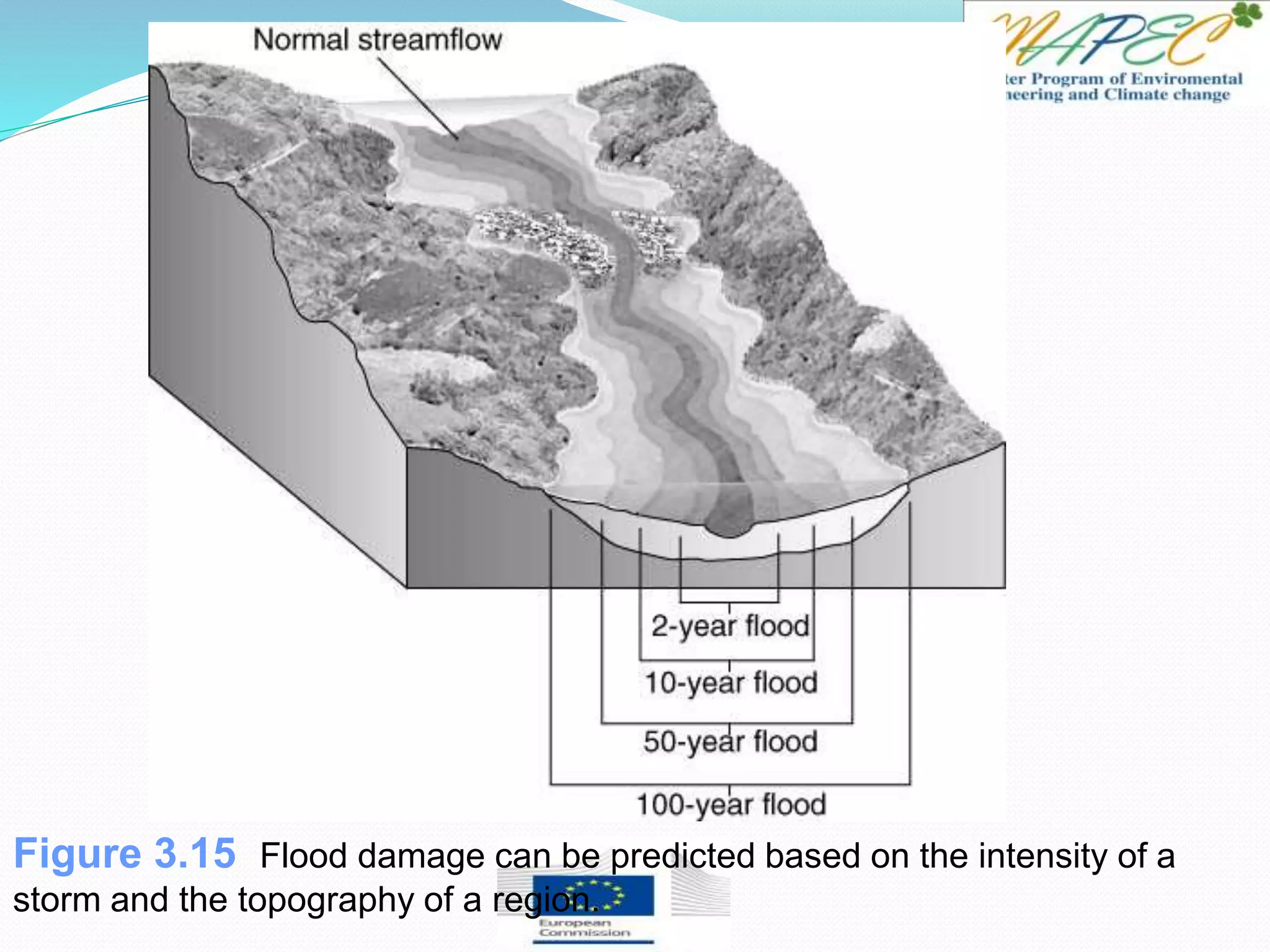
This document provides an overview of key concepts in surface water hydrology. It defines surface water hydrology and discusses watersheds, overland flow, rivers, lakes, sediment transport, water measurement, flood events, and the use of GIS mapping. Key terms are defined such as runoff, infiltration, discharge, flood frequency. Methods for measuring river flow rate and discharge are presented. The largest lakes in the world are listed and components of the hydrologic cycle are depicted in figures.





















![Quiz 3
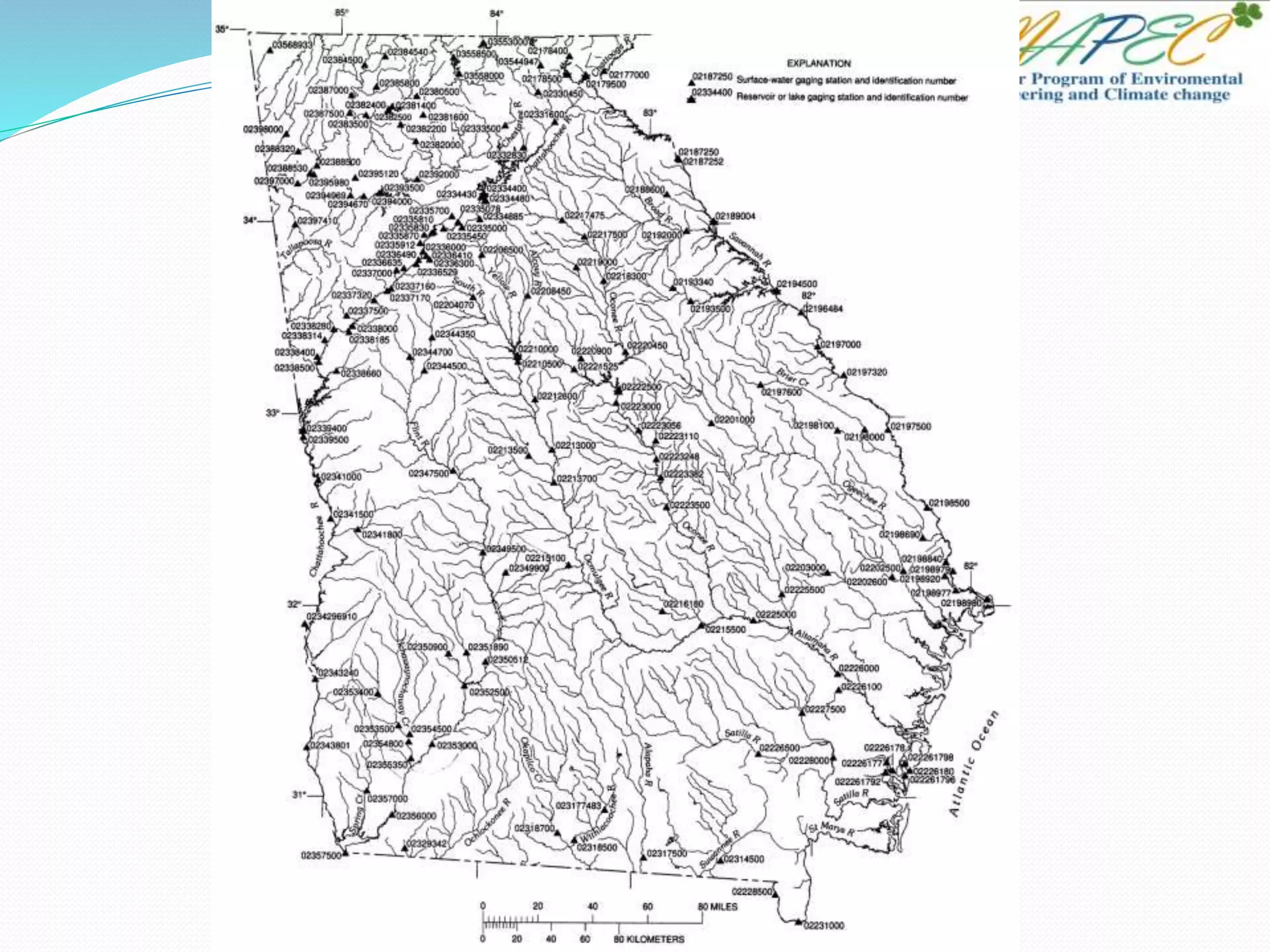
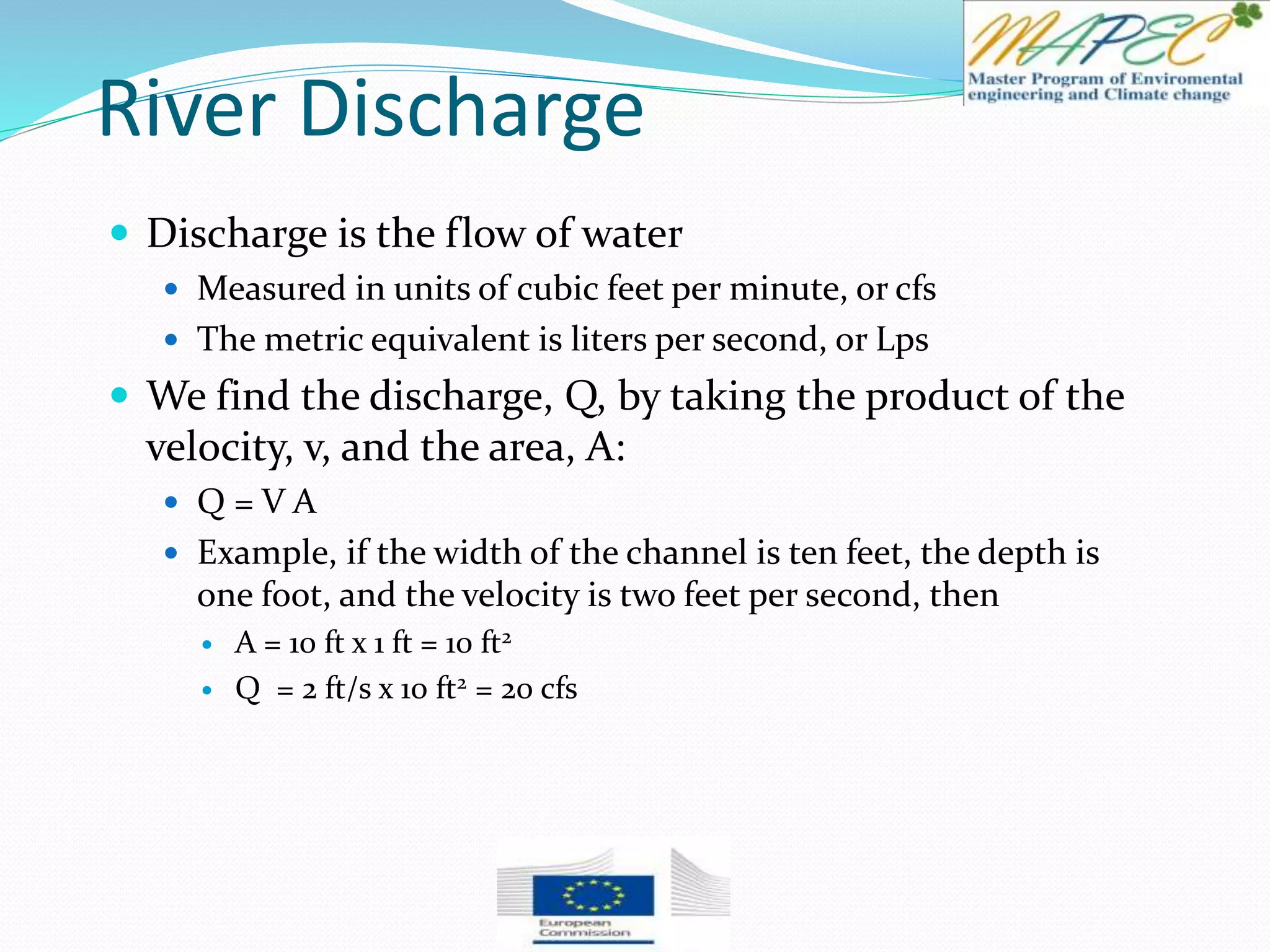
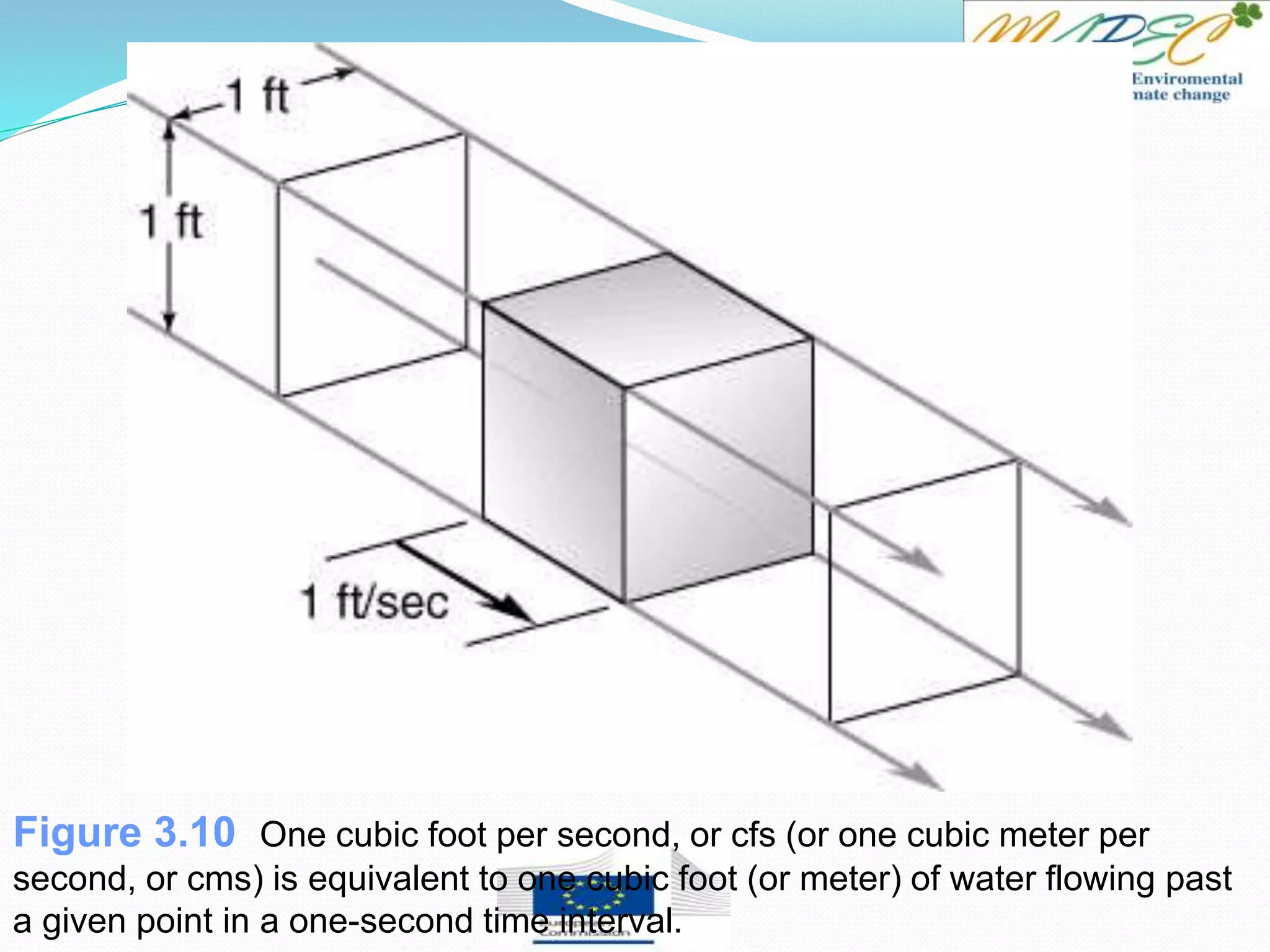
If the Oconee River is flowing at a rate of 1000 ft3/s, how long would it take to fill this
room?
Use the tape measure provided to measure the length, width, and height of the room, and
calculate the volume, in cubic feet. [Use L = 60’, W = 100’, H = 12’]
Calculate the time by dividing the volume (ft3) by the flow rate (ft3/s), giving you the time, in
seconds.
Delineate (draw the boundary around) the Oconee River Watershed using the map
found at: www.hydrology.uga.edu/Georgia.pdf
True - False Questions:
[T / F] Overland flow is more likely in forested watersheds because it rains harder there
[T / F] Urban areas have higher runoff peaks than agricultural areas
[T / F] Sand is easier for rivers to carry than clays
[T / F] A 100-year flood has a 1 percent chance of happening in any one year
[T / F] The Probable Maximum Precipitation is the largest observed rain in a year.
If Athens is located 300 river miles from the coast, and the river flows at a rate of 3 miles
per hour, how long will it take the water to reach the ocean?
For the previous problem, what would happen if there is a lake between Athens and the
coast?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3surfacewaterhydrology-130630055657-phpapp02-180129065914/75/Chapter3surfacewaterhydrology-130630055657-phpapp02-45-2048.jpg)

