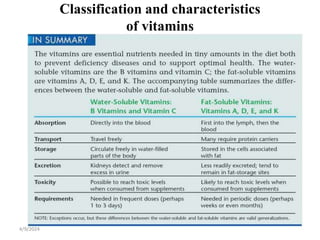
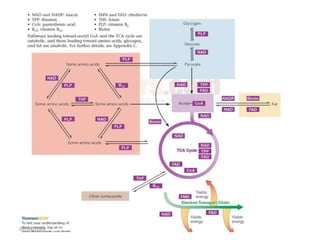
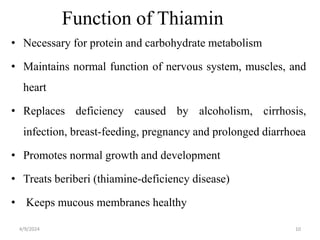
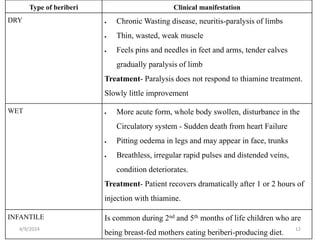
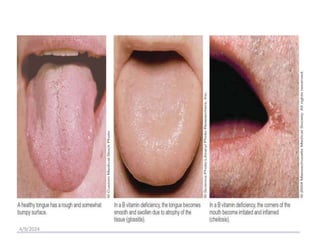
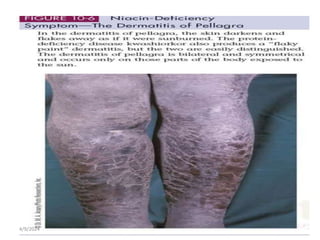
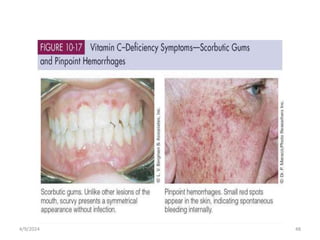
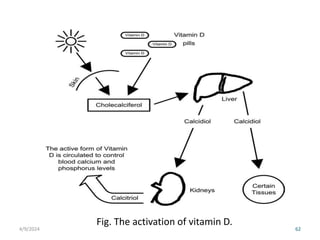
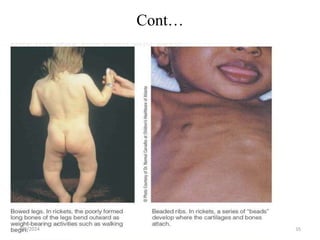
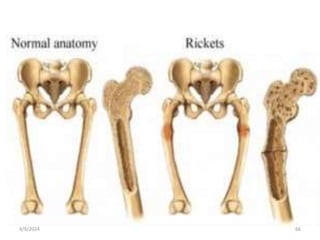
This document discusses vitamins, including their classification, functions, food sources, and deficiency symptoms. It provides details on several water soluble vitamins: thiamine (B1), riboflavin (B2), niacin (B3), vitamin B6, and folic acid (B9). For each vitamin, the summary describes its role as a coenzyme, food sources, recommended daily intake, and clinical manifestations of deficiency. The document aims to describe vitamins and their importance for human nutrition and health.