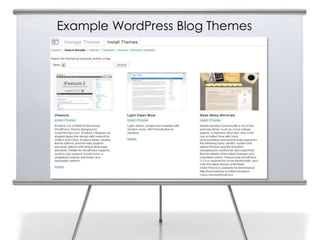
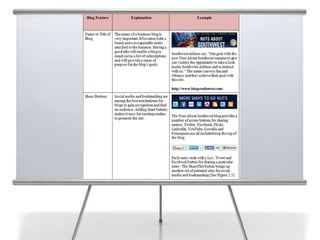
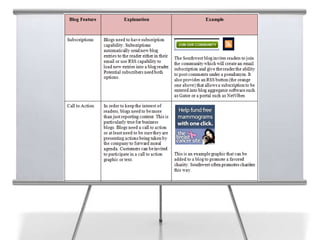
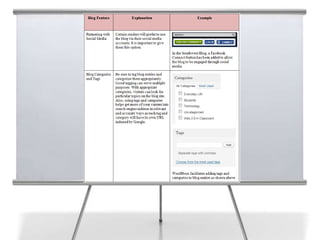
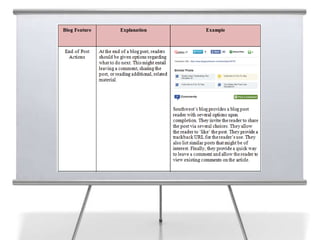
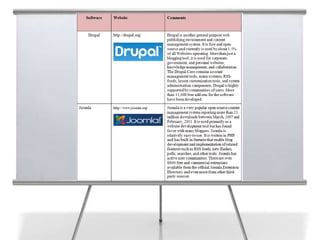
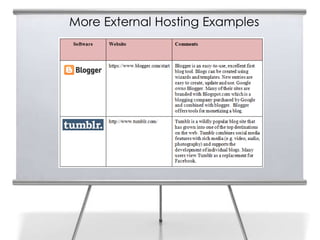
This document provides an overview of blogging for business. It defines what a blog is, noting that it is a website containing an online personal journal with reflections, comments, media, and hyperlinks. Blogs broadcast content using RSS technology and were among the first applications associated with the transition from static web pages to social media. The document discusses how businesses should blog, noting blogs are perfect for connecting with customers and promoting products. It also covers key aspects of an effective business blog such as voice, frequency, style, features, and passion. Businesses must decide whether to host blogs internally or externally using hosting services.