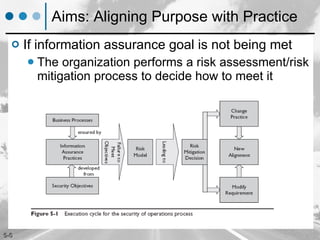
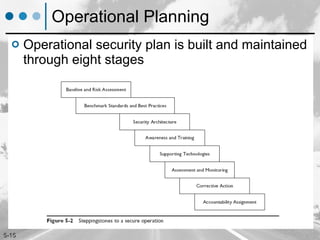
The document discusses maintaining security of operations through establishing routine security processes, ensuring operational response to incidents, and aligning security purposes with practices. It outlines key elements of an operational security process including sensing threats, analyzing risks, responding to issues, and managing the overall process. The document provides guidance on implementing security of operations through configuration management, operational planning, response to incidents, and day-to-day operational housekeeping activities.