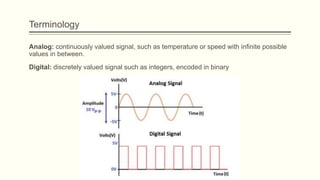
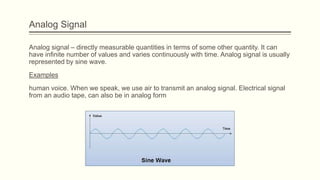
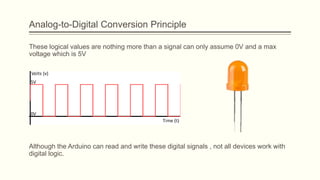
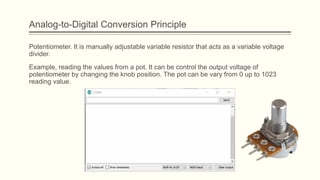
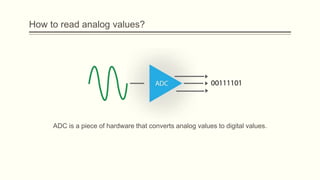
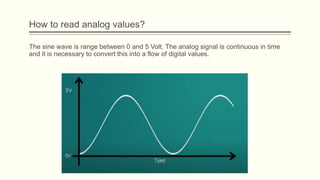
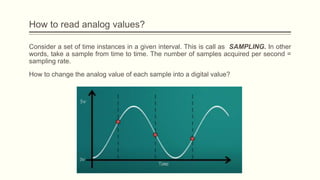
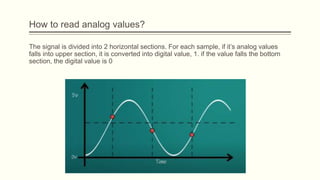
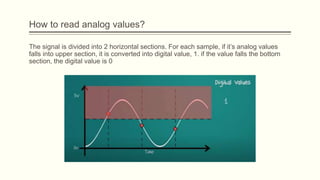
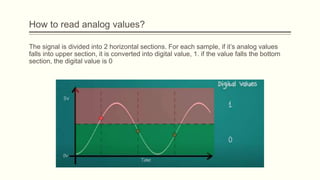
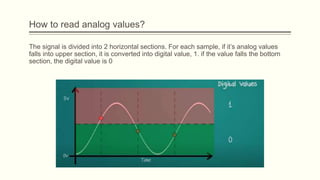
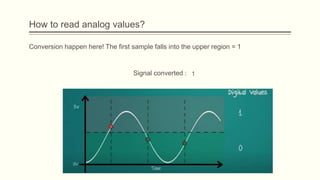
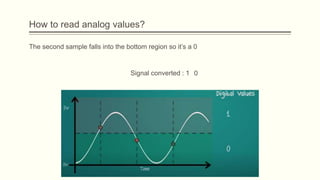
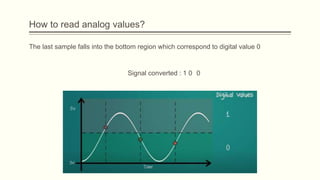
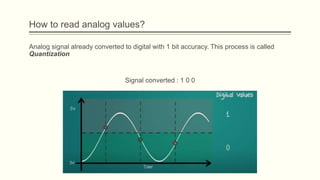
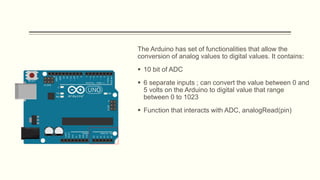
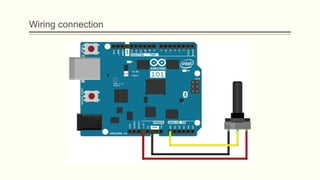
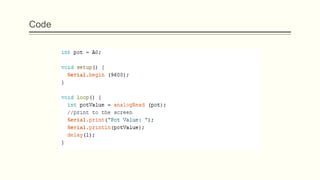
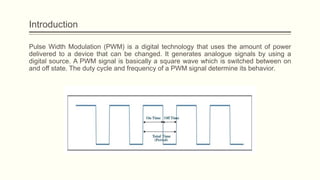
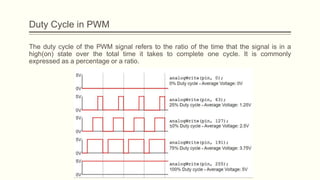
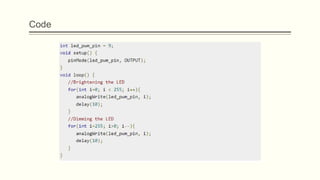
The document discusses analog vs digital signals in Arduino. It defines analog signals as continuously variable signals like temperature, while digital signals can only have discrete values like 1s and 0s. It explains that Arduino uses an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) to convert analog sensor output to digital values readable by the microcontroller. The ADC divides the analog range into discrete steps, returning a number between 0-1023. Functions like analogRead() are used to read analog pin values as digital numbers.