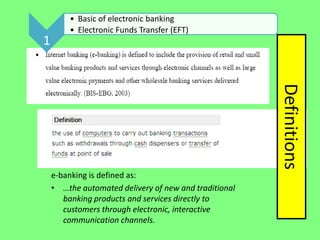
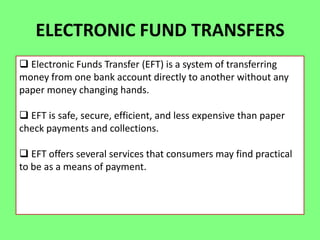
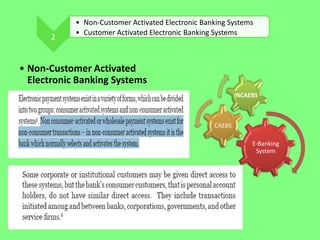
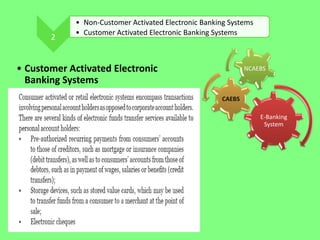
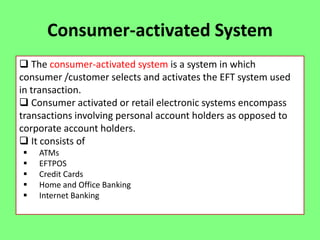
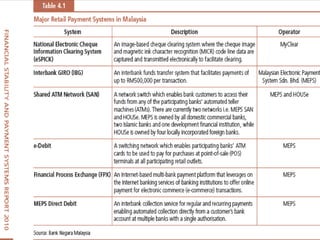
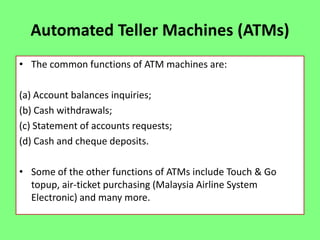
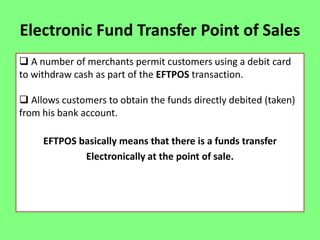
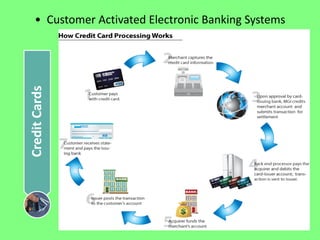
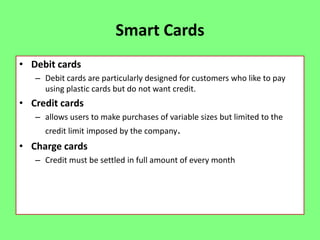
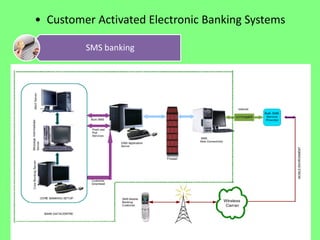
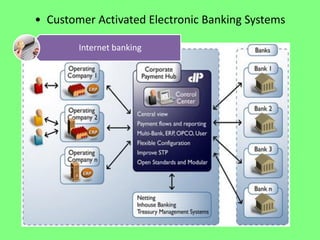
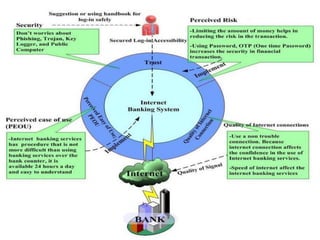
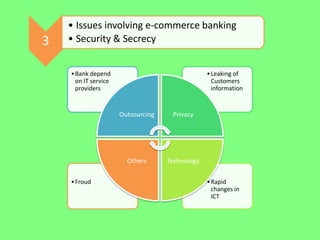
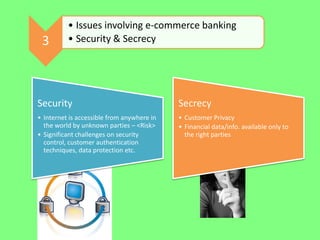
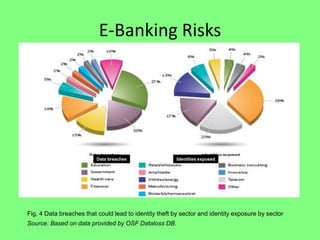
Electronic banking systems allow customers to access banking services electronically rather than through traditional paper-based methods. The document defines electronic banking and electronic funds transfer, and identifies the key types of electronic banking systems including non-customer activated systems like SWIFT used between financial institutions, and customer activated systems like ATMs, EFTPOS, credit/debit cards, home banking, mobile banking, and internet banking. It discusses functions of these systems like cash withdrawals, deposits, transfers, and bill payments. The document emphasizes issues like security, secrecy and banks' reliance on IT services for electronic banking.