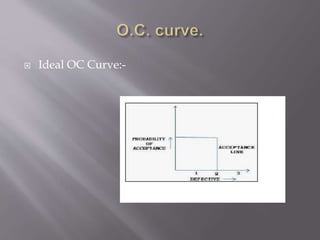
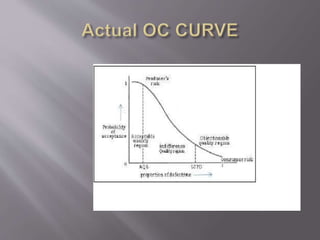
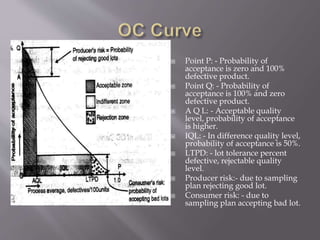
The document discusses statistical quality control (SQC) and process capability. It defines key terms like the normal distribution curve, process capability, and acceptance quality limits. The benefits of SQC are outlined as ensuring efficient inspection, reducing scrap, detecting faults early, and improving productivity through adhering to specifications and eliminating bottlenecks. Process capability is defined as the minimum variation needed to include 99.7% of measurements from a given process. Key aspects of process capability curves like the ideal OC curve and points representing different probability levels and risks are also summarized.