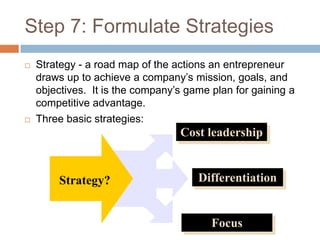
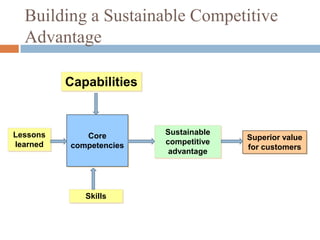
This document outlines the strategic management process for designing a competitive business model and strategic plan. It discusses developing a vision and mission, assessing strengths and weaknesses, analyzing opportunities and threats, identifying success factors, analyzing competitors, setting goals and objectives, formulating strategies, implementing action plans, and establishing controls like balanced scorecards. The overall strategic management process involves 9 steps to guide a company's mission and keep it on course to gain a competitive advantage.



















![Step 6: Create Company Goals
and Objectives
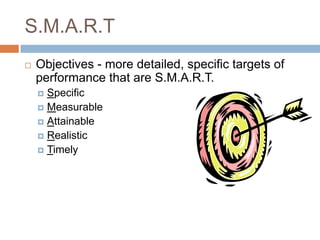
Goals - broad, long-range attributes to be
accomplished.
“BHAGs” Big Hairy Audacious Goals
The term Big Hairy Audacious Goal ("BHAG") was
proposed by James Collinsand Jerry Porras in their 1994
book entitled Built to Last: Successful Habits of Visionary
Companies.[1] A BHAG encourages companies to define
visionary goals that are more strategic and emotionally
compelling. Many businesses set goals that describe what
they hope to accomplish over the coming days, months or
years. These goals help align employees of the business
to work together more effectively. Often these goals are
very tactical, such as "achieve 25% revenue growth in the
next 6 months."](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presntaton-120103143712-phpapp02/85/chapter-3-Designing-a-Competitive-Business-Model-and-Building-a-Solid-Strategic-Plan-23-320.jpg)