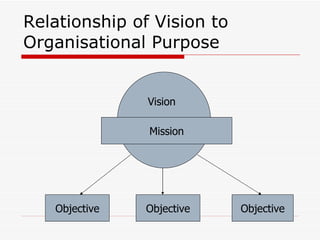
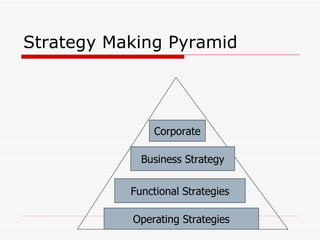
The document discusses strategic objectives and strategy concepts. It defines strategic objectives as more definitive statements that accomplish an organization's mission. Strategic objectives typically have multi-year timeframes and require efforts from multiple departments. Effective strategic objectives are measurable, achievable, flexible, and stretch employees without being unrealistic. The document also defines strategy and discusses the relationship between vision, mission, and objectives. It emphasizes that strategy involves making explicit choices about customers, offerings, and activities.