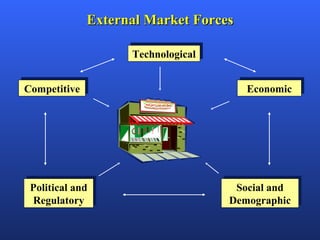
Strategic management involves developing a plan to guide a company in accomplishing its goals. It is crucial for building a successful business and creating a competitive advantage. The strategic management process includes steps such as developing a vision and mission statement, assessing strengths and weaknesses, analyzing competitors, and establishing controls to monitor performance. Strategic management provides direction, motivates employees, and allows a company to differentiate itself in the market.