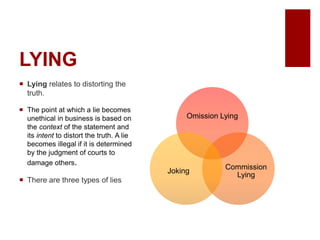
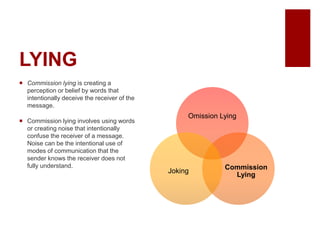
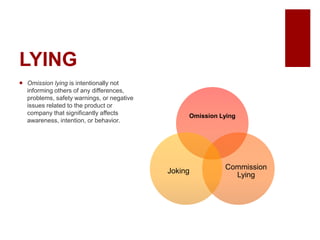
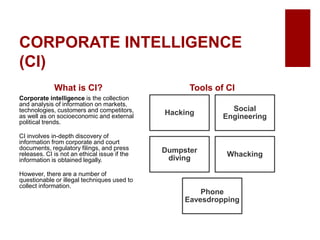
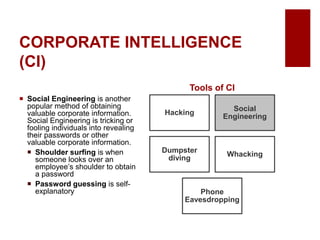
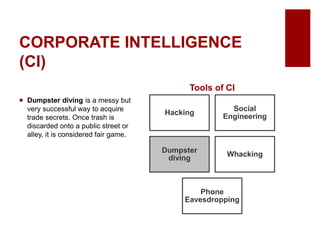
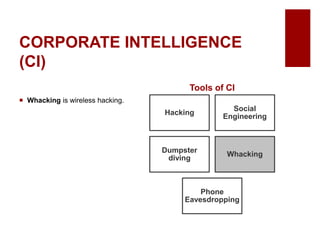
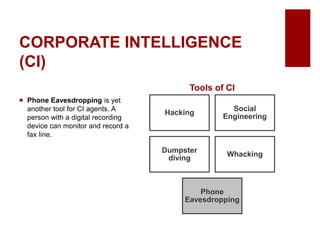
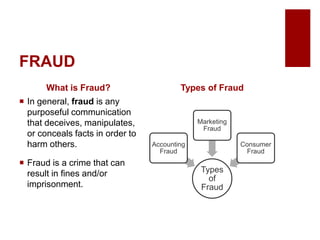
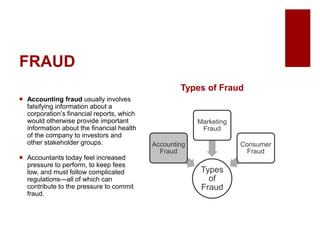
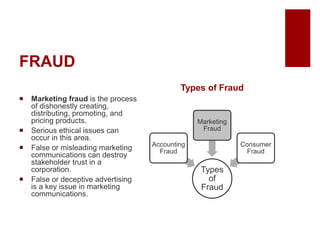
This document discusses emerging ethical issues in business. It begins by explaining the importance of recognizing ethical issues and identifying foundational values like honesty, integrity, and fairness. The document then explores specific ethical issues and dilemmas businesses may face, such as misuse of company time/resources, abusive behavior, lying, conflicts of interest, bribery, corporate intelligence, discrimination, and more. It also addresses the challenge of determining what constitutes an ethical issue in business decisions.