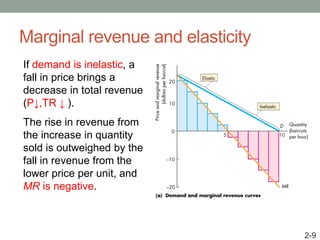
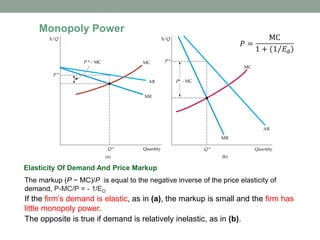
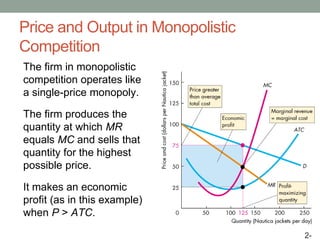
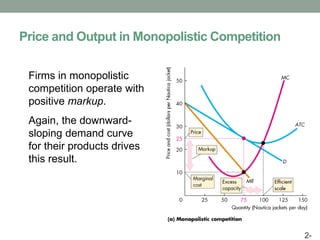
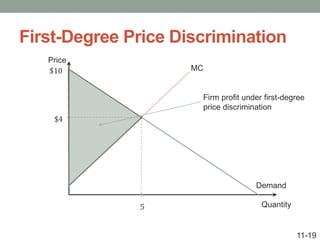
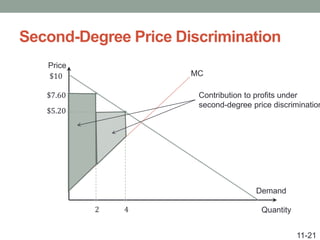
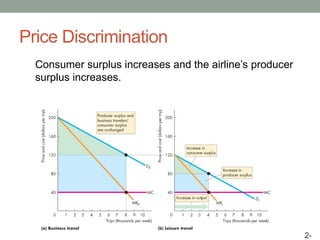
This document discusses pricing strategies for firms with market power. It explains how firms can maximize profits by setting price where marginal revenue equals marginal cost. The document also discusses various pricing strategies including price discrimination, cross subsidies, transfer pricing, and strategies to mitigate intense price competition. Firms can extract consumer surplus through these various pricing strategies.