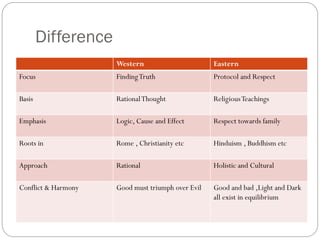
This document discusses ethics in international business. It defines ethics as dealing with what is good/bad or right/wrong, and social responsibility as moral, legal or mental accountability. It questions whether countries with lower ethics attract more business, noting some say yes but the overall answer is no. It discusses banana republics and how FDI is greater in countries with stronger worker rights and higher standards. It notes applying ethics globally is difficult as standards change over time and situation. Examples discuss Toyota improving working conditions at a California plant. Ethical issues discussed include child labor, discrimination, and workers' rights. It outlines Western philosophy focuses on duty and virtue ethics while Eastern focuses on respecting protocols and seeing people as part of the universe.