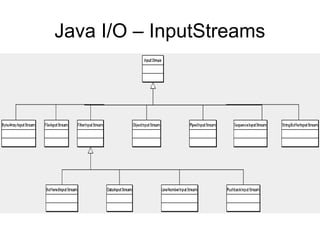
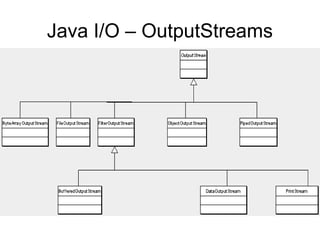
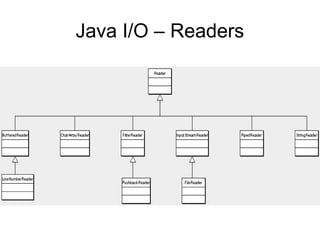
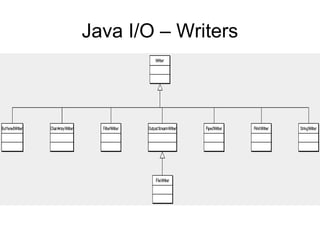
- Java performs I/O through streams which are abstractions that produce or consume data and are linked to physical devices.
- There are two types of streams in Java: byte streams which handle input/output of bytes and character streams which handle input/output of characters more efficiently.
- The main classes for byte streams are InputStream, OutputStream and their subclasses like FileInputStream and FileOutputStream. The main classes for character streams are Reader and Writer.
- The predefined streams System.in, System.out and System.err represent standard input, standard output and standard error streams in Java.















![Methods defined by
InputStream
Method Description
int avaiable() Returns the number of bytes of input currently
available for reading
void close() Close the input source
void mark(int numbytes) Places a mark at the current point in the input stream
that will remain valid until numBytes bytes are read.
boolean
marksupported()
Returns true if mark() / reset() are supported by the
invoking stream.
int read() Returns an integer representation of the next
available byte of input.
-1 is returned when end of the stream is
encountered.
int read(byte buffer[]) Attempts to read up to buffer.length bytes into buffer
and returns the actual number of bytes that were
successfully read](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap3usingio-150629132714-lva1-app6892/85/Using-Input-Output-20-320.jpg)
![int read(byte buffer[],int
offset,int numbytes)
Attempts to read the
numBytes bytes into buffer
starting at buffer[offset],
returning the number of
bytes successfully read.
void reset() Resets the input pointer to
the previously set mark
long skip(long
numbytes)
Ignores numBytes bytes of
input, returning the number
of bytes actually ignored.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap3usingio-150629132714-lva1-app6892/85/Using-Input-Output-21-320.jpg)
![Methods of OutputStream
Method Desccription
void close() Closes the output stream
void flush() Causes an output that has been buffered
to be sent to its destination
void write(int b ) Writes a single byte to an output stream
void write(byte
buffer[])
Writes a complete array of bytes to an
output stream
void write(byte
buffer[],int
offset,int
numBytes)
Writes a subrange of numBytes from
array buffer beginning at buffer[offset]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap3usingio-150629132714-lva1-app6892/85/Using-Input-Output-22-320.jpg)

![• System.in is an instance of InputStream
• InputStream defines only one method called read()
which reads byte
• Three versions of read() exists
• int read() throws IOException
• int read(byte data[])throws IOException
• int read(byte data[], int start,int max) throws IOException
• Reading from System.in,pressing Enter generates end of
stream condition](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap3usingio-150629132714-lva1-app6892/85/Using-Input-Output-24-320.jpg)
![• int read() throws IOException
– Reads a single character from keyboard, returns -1 if it reaches
end of stream
• int read(byte data[])throws IOException
– Reads bytes from input stream and puts them into data until
either array is full , the end of stream is encountered or error
occurs.
• int read(byte data[], int start,int max) throws IOException
– Reads input into data beginning at the location specified by start,
upto max bytes are stored.
– It returns number of byte read or -1 when end of stream is
reached.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap3usingio-150629132714-lva1-app6892/85/Using-Input-Output-25-320.jpg)
![import java.io.*;
class ReadBytes{
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException{
byte data[]=new byte[10];
System.out.println("Enter the charecters:");
System.in.read(data);
System.out.println("You entered:");
for(int i=0;i<=data.length;i++)
System.out.println((char)data[i]);
}//end of main
}//end of class](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap3usingio-150629132714-lva1-app6892/85/Using-Input-Output-26-320.jpg)

![class WriteDemo{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int b;
b='X';
System.out.write(b);
System.out.write('n');
}//end of main
}//end of class](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap3usingio-150629132714-lva1-app6892/85/Using-Input-Output-28-320.jpg)