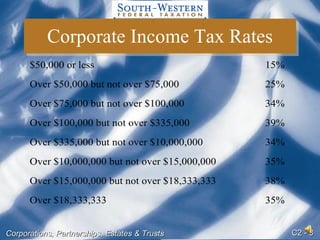
There are various forms of business entities including sole proprietorships, partnerships, S corporations, and regular or C corporations. C corporations are separate taxable entities that report income and expenses on Form 1120 and are subject to double taxation as income is taxed at the corporate level and again when distributed as dividends to shareholders. When selecting an entity form, non-tax issues to consider include liability, capital raising ability, transferability of ownership interests, and continuity of the business.