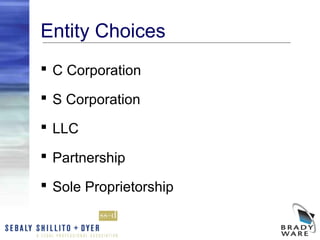
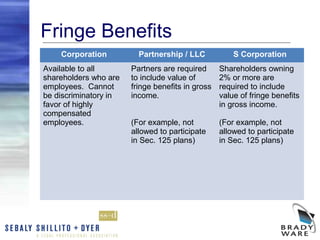
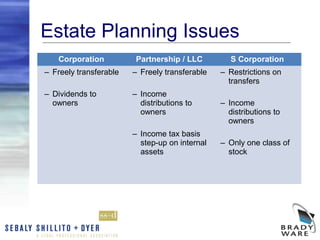
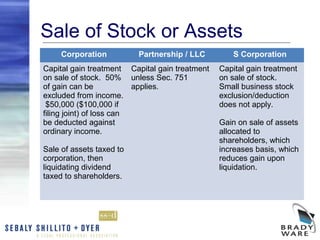
The webinar discusses the key factors to consider when choosing a business entity, including various types of entities like C corporations, S corporations, LLCs, partnerships, and sole proprietorships. It covers differences in liability, ownership restrictions, taxation of income, employment taxes, deductibility of fringe benefits, and implications of distributions and sales. The webinar analyzes these considerations and pros and cons for each entity type to help business owners determine the most suitable structure. It also reviews procedures for changing entity forms.