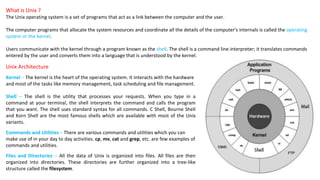
The Unix operating system acts as an interface between the user and computer. The kernel allocates system resources, coordinates internals, and interacts with hardware. Users communicate with the kernel via a shell program that translates commands for the kernel to understand. In Unix, everything is organized into files that are grouped into directories in a tree structure called the filesystem. Common commands allow users to view files and directories, check system information, manage files and directories, and get manual pages.

![3. Who is Logged in?
Sometime you might be interested to know who is logged in to the computer at the same time.
There are three commands available to get you this information, based on how much you wish to
know about the other users: users, who, and w.
4. Display Content of a File
You can use the cat command to see the content of a file.
$ cat filename
• You can display the line numbers by using the -b option along with the cat command
• The syntax to combine 2 files is -
cat file1 file2 > newfilename
• Append data into a file
cat file1 file2 > >file3 [Here content of file1 and file2 is appended in file3]
5. Deleting Files
The 'rm' command removes files from the system without confirmation.
6. Moving files
Suppose we want to move the file "sample2" to location /home/Documents mv sample2 /home/Documents](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basiccommands-part1-230313144351-701ba644/85/Basic-Commands-part1-pptx-4-320.jpg)
