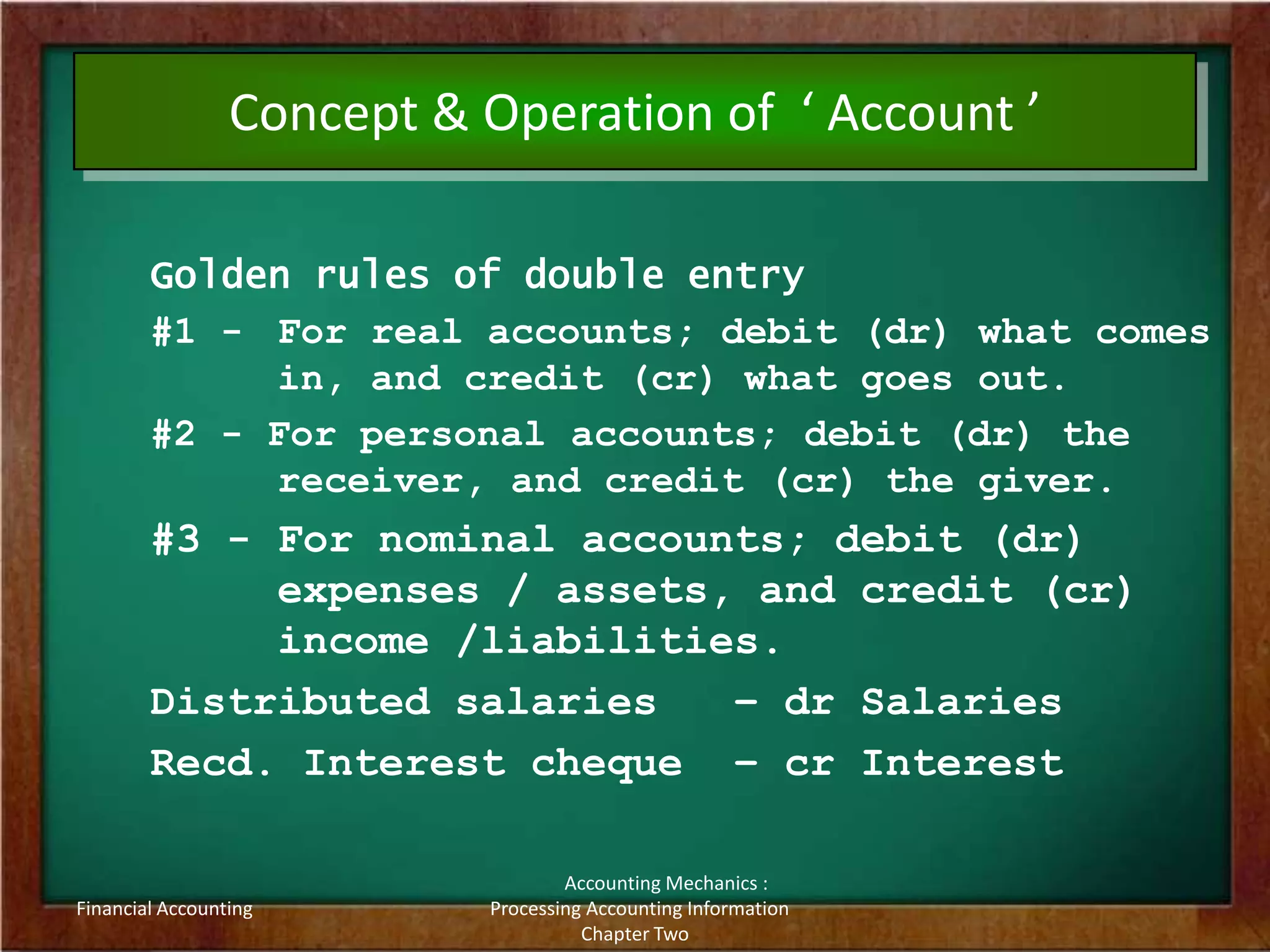
This document discusses accounting mechanics and processing accounting information. It covers key concepts like accounts, the accounting process, journals, ledgers, adjusting entries and financial statements. The accounting process involves identifying transactions, preparing vouchers, analyzing accounts affected, recording entries, posting to ledgers, preparing trial balances and adjusting entries, and finally generating financial statements like the income statement, balance sheet, statement of retained earnings and cash flow statement. Accounts are classified as personal, real or nominal. The accounting mechanics ensure financial data is collected, processed and presented accurately for decision making.