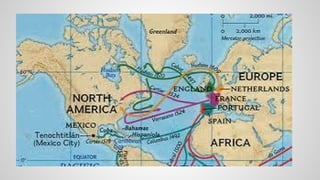
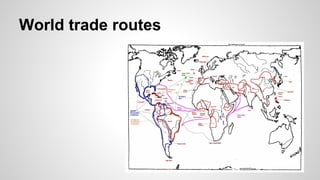
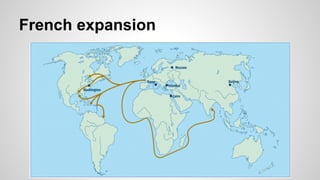
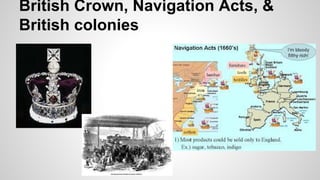
The document discusses the diversity of colonial societies in North and South America between 1530-1770. It describes how European colonization introduced diseases that devastated indigenous populations. Europeans also brought food crops, livestock, and institutions from the Old World. In Spanish and Portuguese colonies, the Catholic Church worked to convert indigenous groups while exploiting their labor. Economies were based on mining and plantations using encomienda, mita, and slave labor systems. British colonies developed economies around tobacco, rice, fur trading, fishing and mixed farming. Colonies were diverse with influences from different European groups and interactions with indigenous populations.