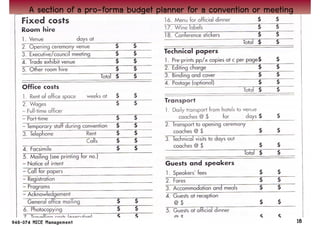
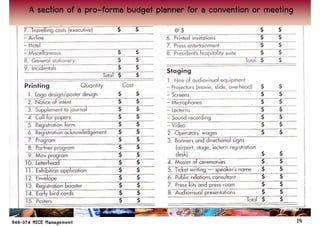
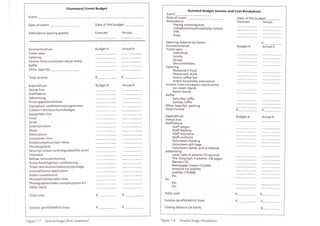
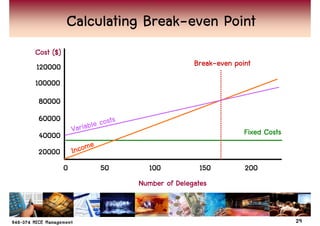
This chapter discusses key financial considerations for managing conventions and meetings (MICE). It outlines how to design, monitor, and control an event budget, covering both expenses and potential income. Budgeting involves identifying sources of revenue and areas of expenditure. Negotiating with venues focuses on items like room rates, space rental, and food & beverage. The billing process establishes a master account and payment terms. Monitoring the budget through regular reporting allows for cost containment. Break-even analysis helps set prices to cover variable and fixed costs.