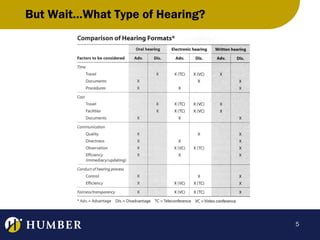
This document discusses different types of administrative law hearings and procedures. It begins by explaining that different agencies allow different types of hearings depending on factors like cost, timeliness and fairness. Hearings can be oral, electronic, or written. Written hearings involve parties submitting documents and evidence in writing without appearing before the tribunal. The document then discusses who has standing to participate in proceedings, the roles of agency counsel and adjudicators, and the typical phases and procedures of a hearing, including preliminary issues, opening statements, fact-finding through examination of witnesses, and closing submissions. It emphasizes that while tribunals are not courts, they have power to control their own processes.