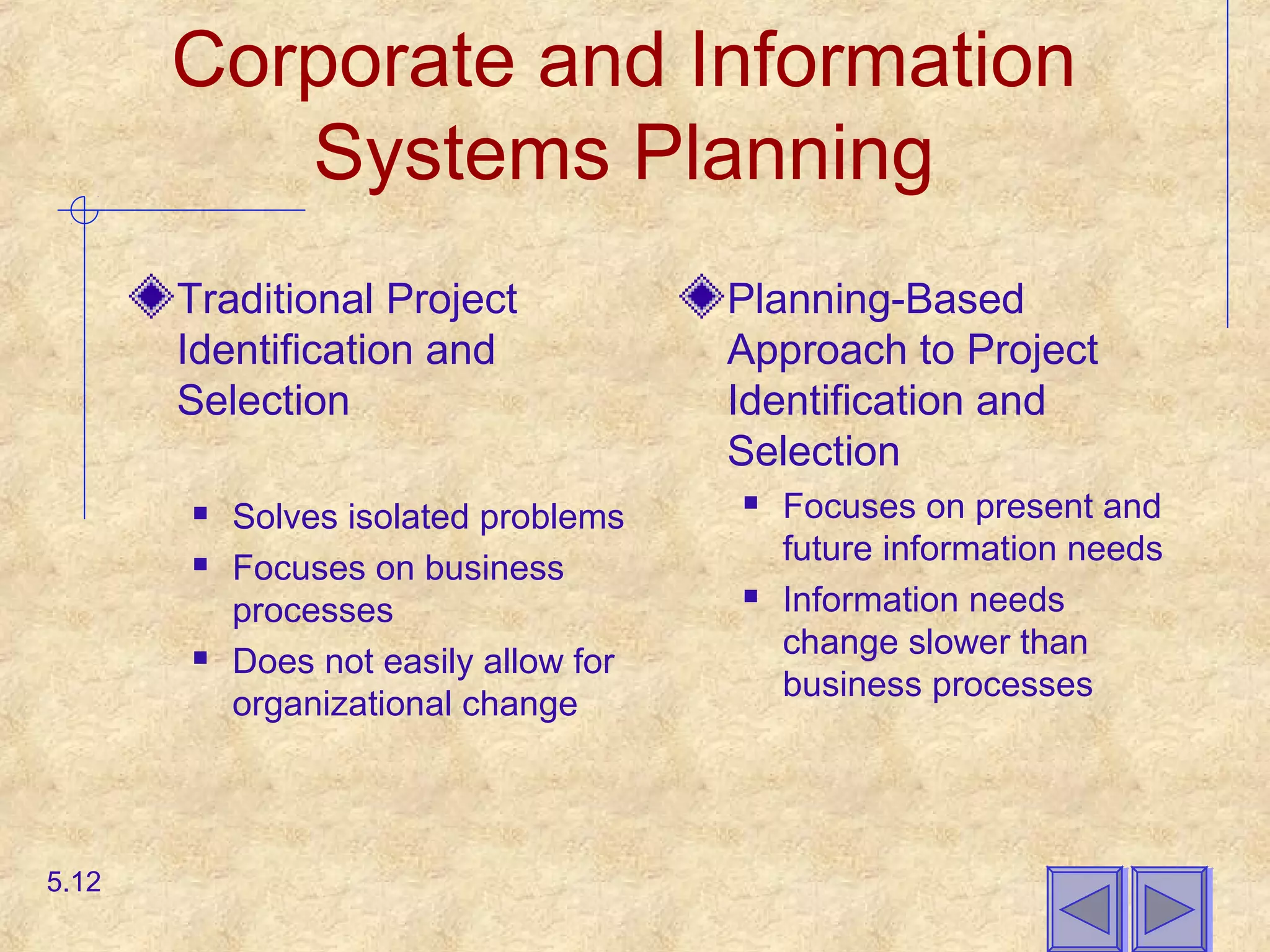
This document discusses project identification and selection processes. It describes corporate strategic planning and information systems planning, noting that IS planning can help identify projects that align with business objectives. Projects may be identified through top-down or bottom-up processes. IS planning involves describing the current and target situations and developing a transition plan. The document also discusses electronic commerce applications like the internet, intranets, and extranets.