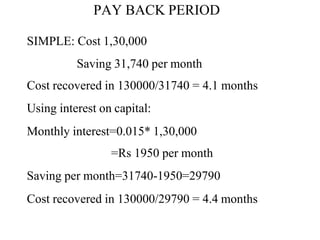
This document discusses feasibility analysis for a proposed hostel information system. It identifies deficiencies in the current manual system, formulates goals and sub-goals to address the deficiencies, and evaluates three alternative solutions: 1) improving the manual system, 2) using a periodic update PC system, and 3) an online system with server and clients. It determines that solution B of using a PC system is technically and operationally feasible. A cost-benefit analysis shows that the estimated costs of 130,000 rupees would be recovered within 4-5 months due to savings from reduced inventory, early payments, and other benefits. An executive summary and system proposal structure are also outlined.