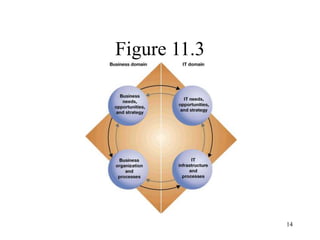
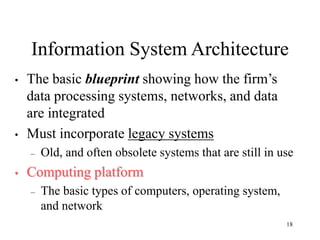
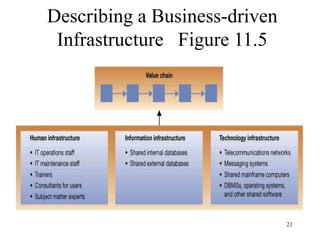
The document discusses the significance of information systems planning in aligning IT initiatives with business strategies, emphasizing the need for collaboration between IS departments and user roles like sponsors and champions. It addresses challenges and principles in business planning, including resource allocation between new and existing information systems, while also covering the implications of outsourcing, project management, and risk assessment. Key topics include critical success factors, project roles, and the integration of information systems within organizational frameworks.