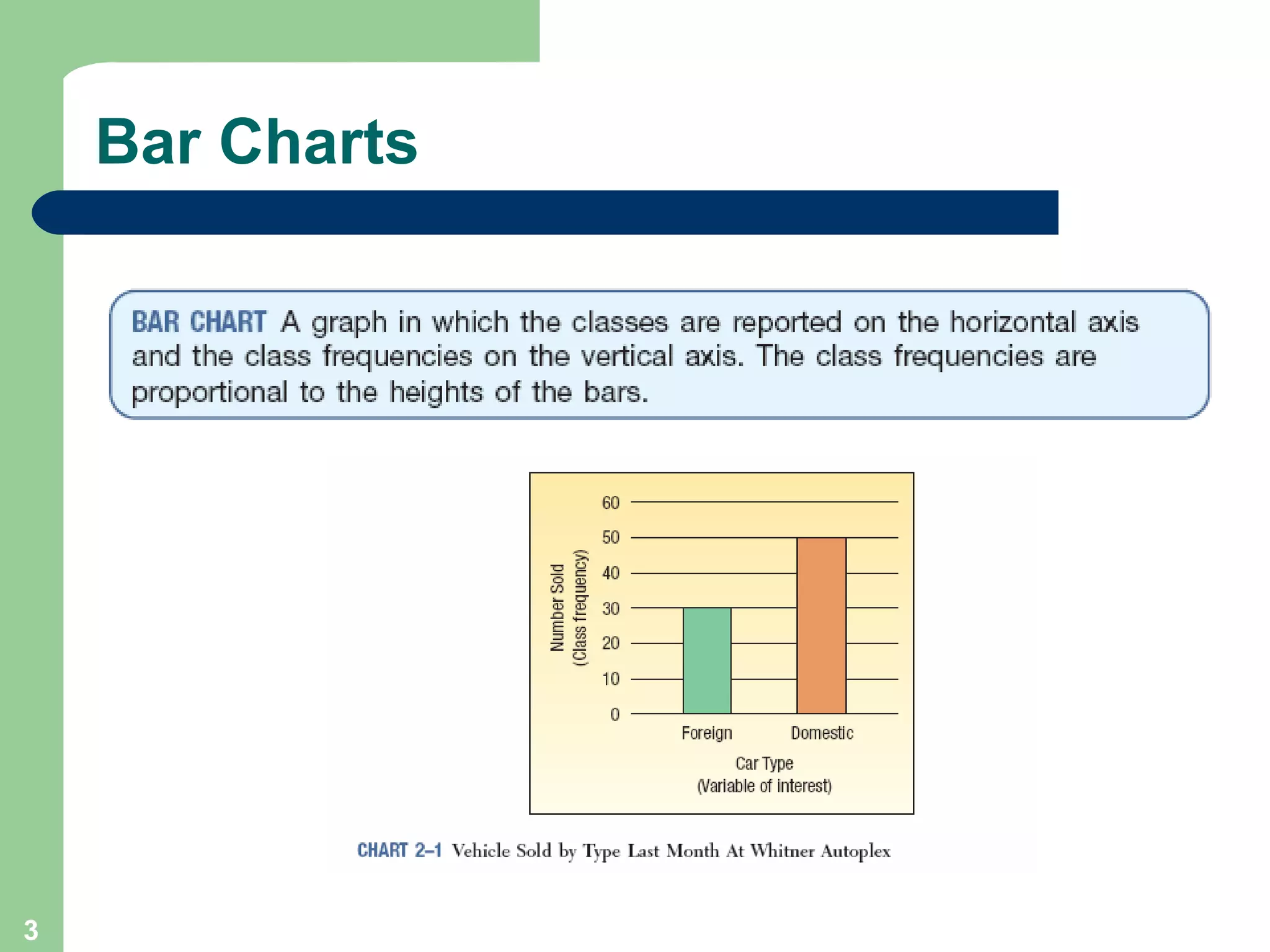
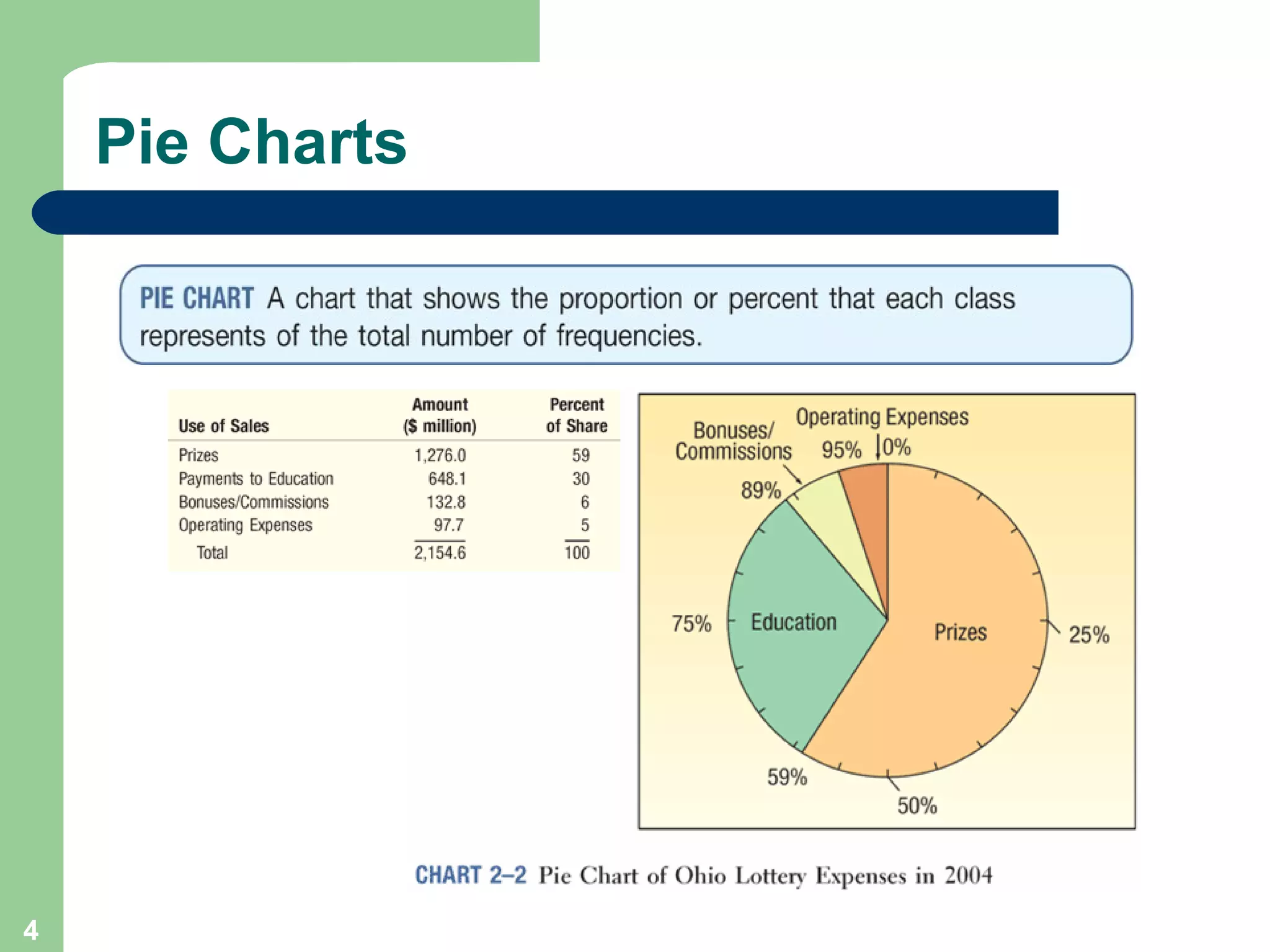
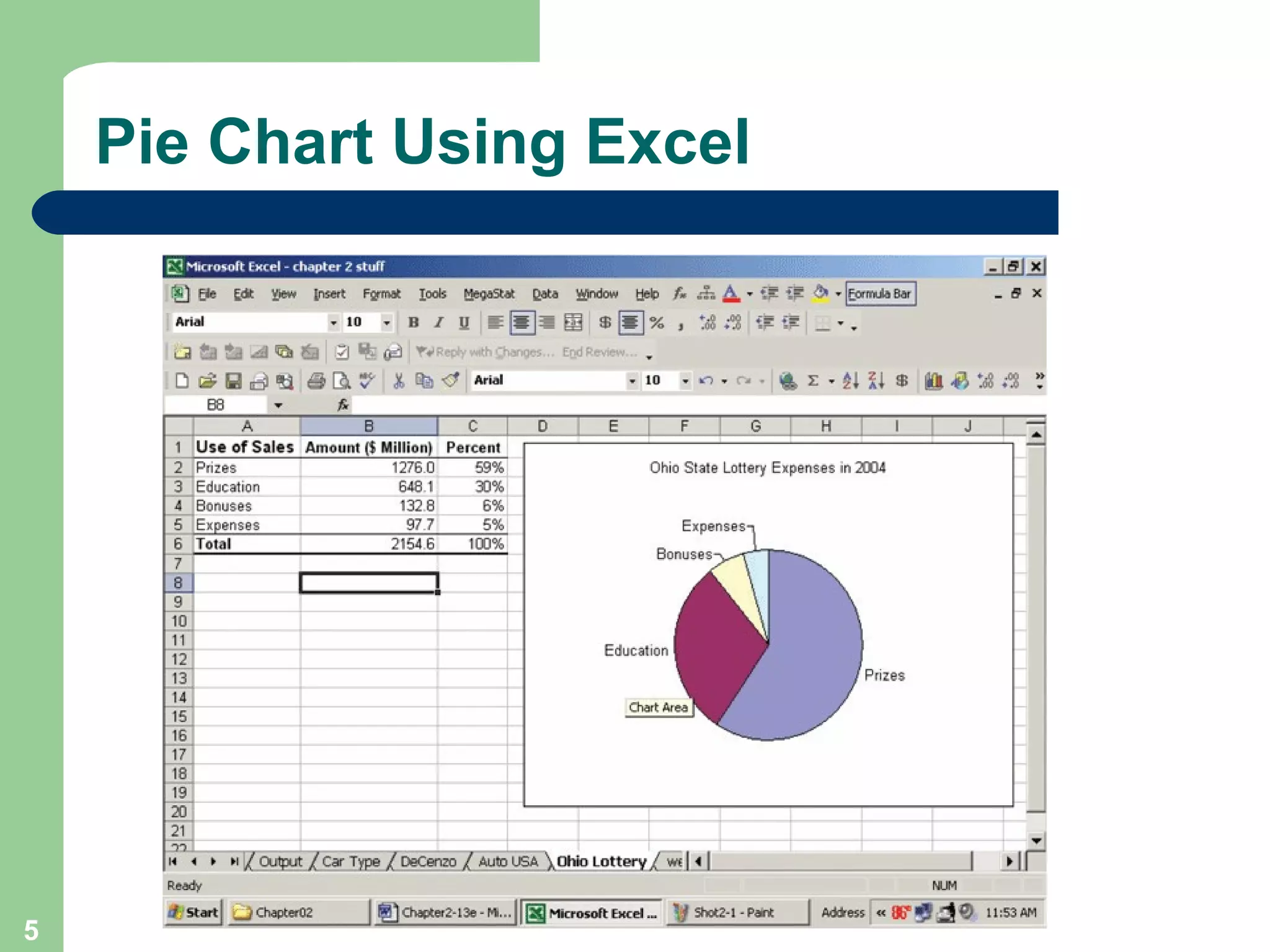
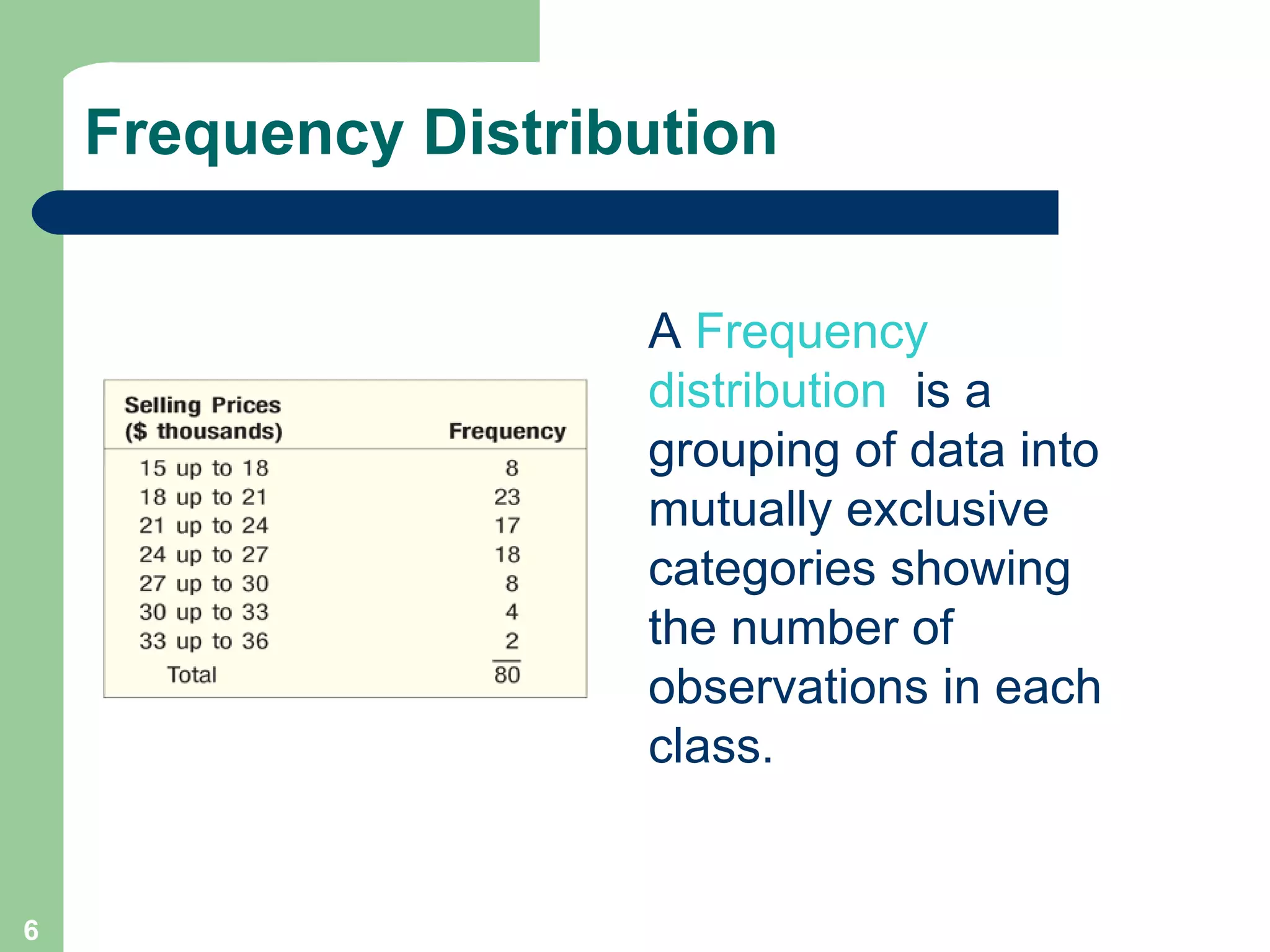
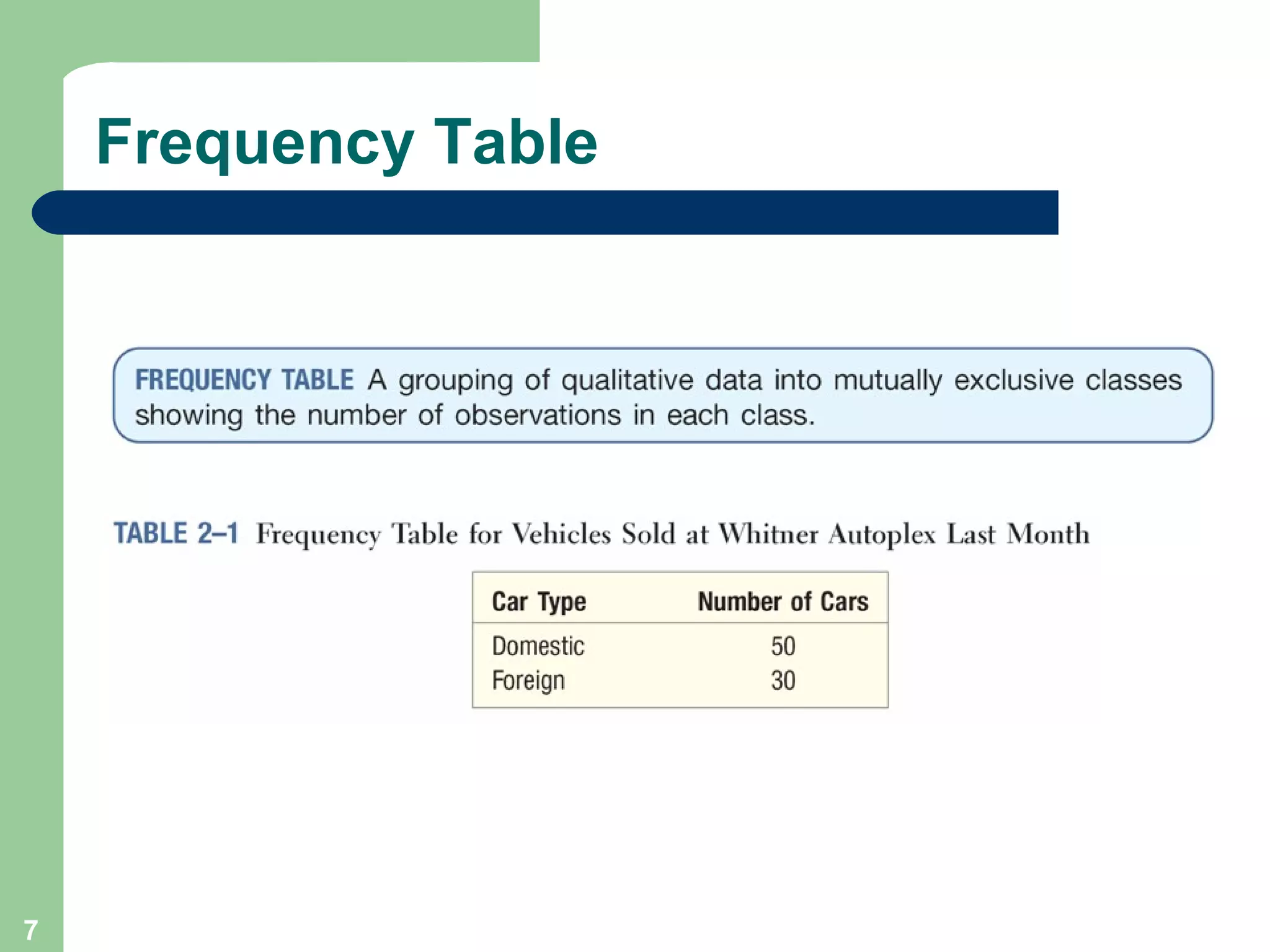
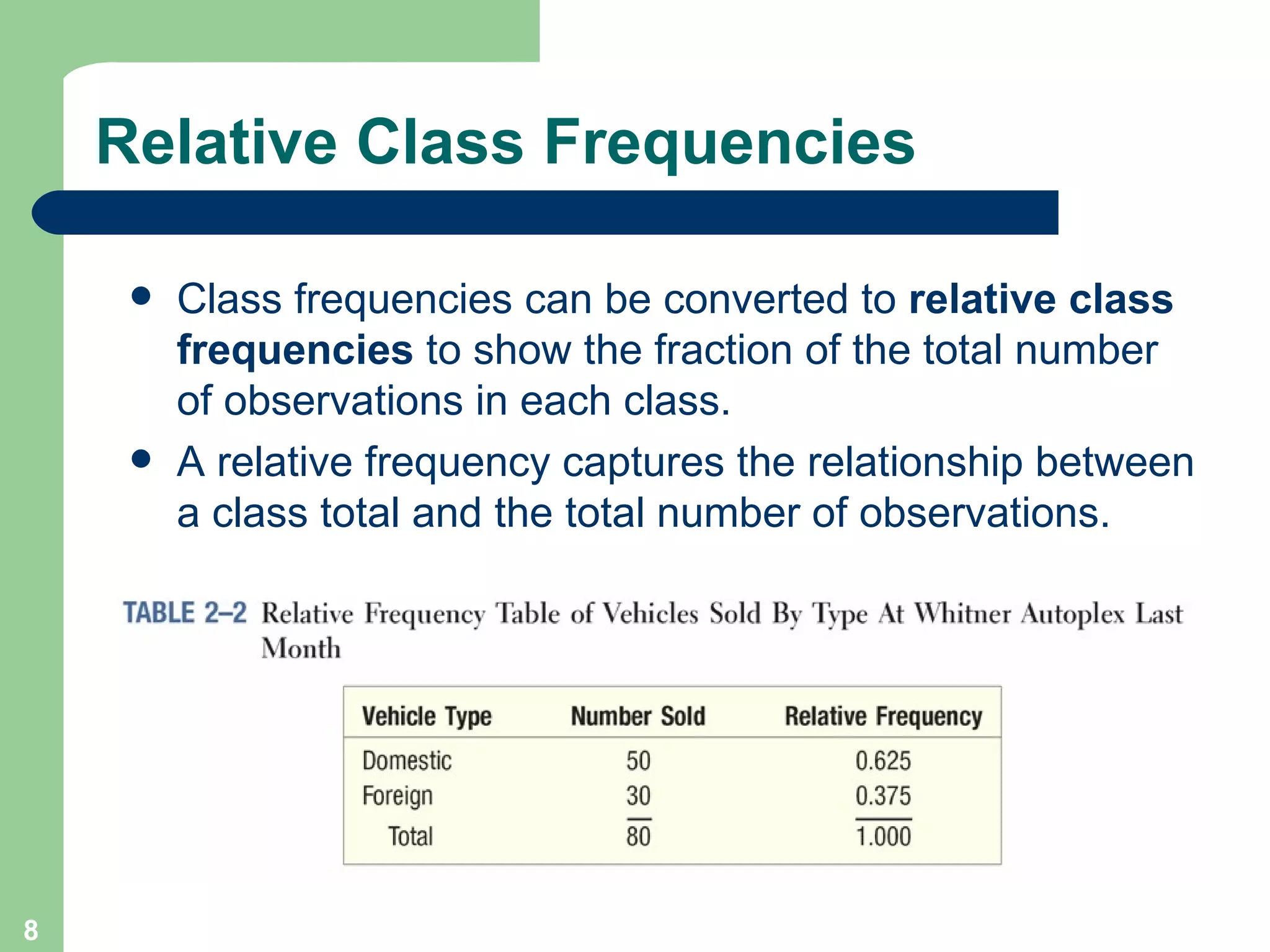
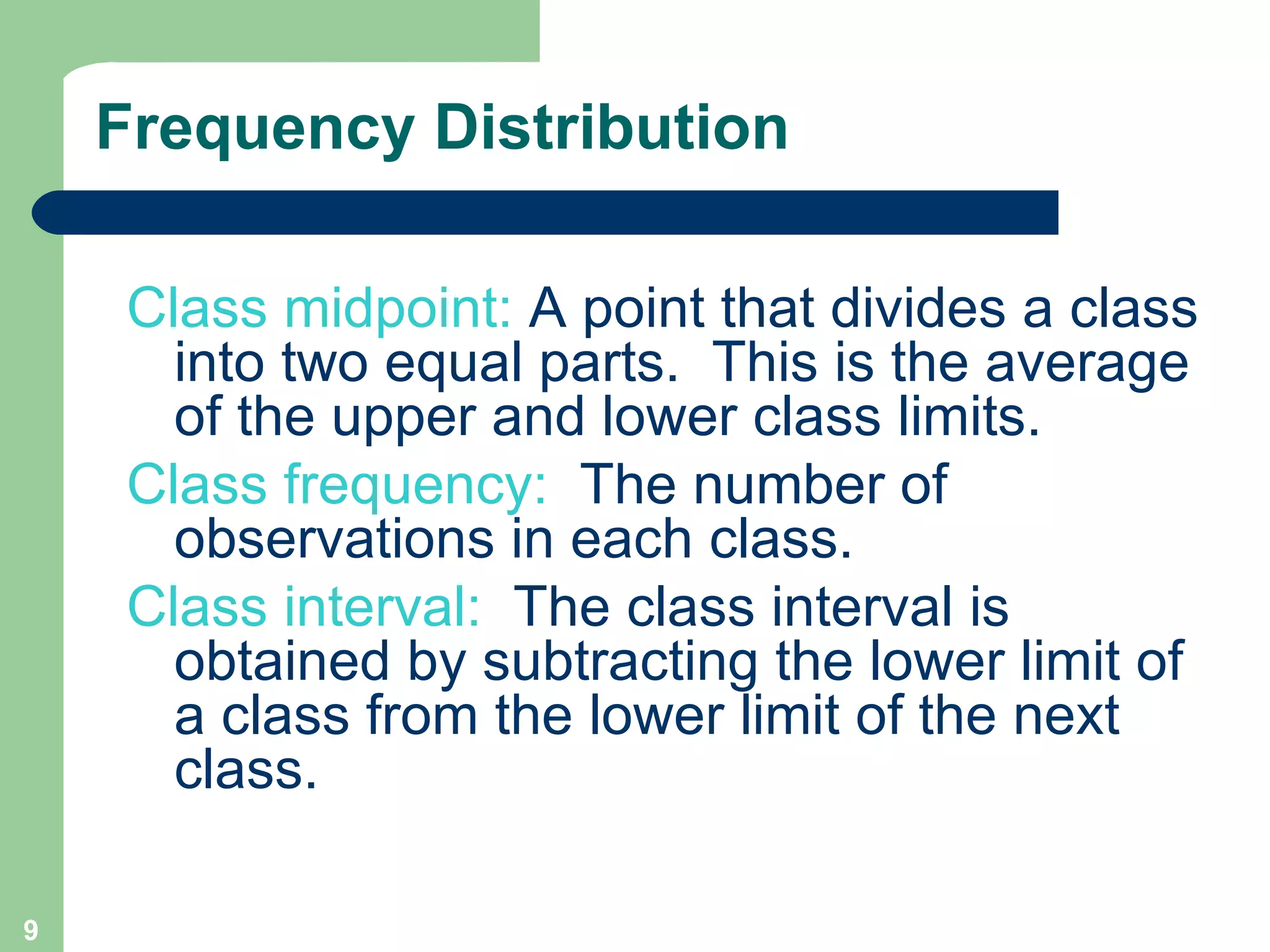
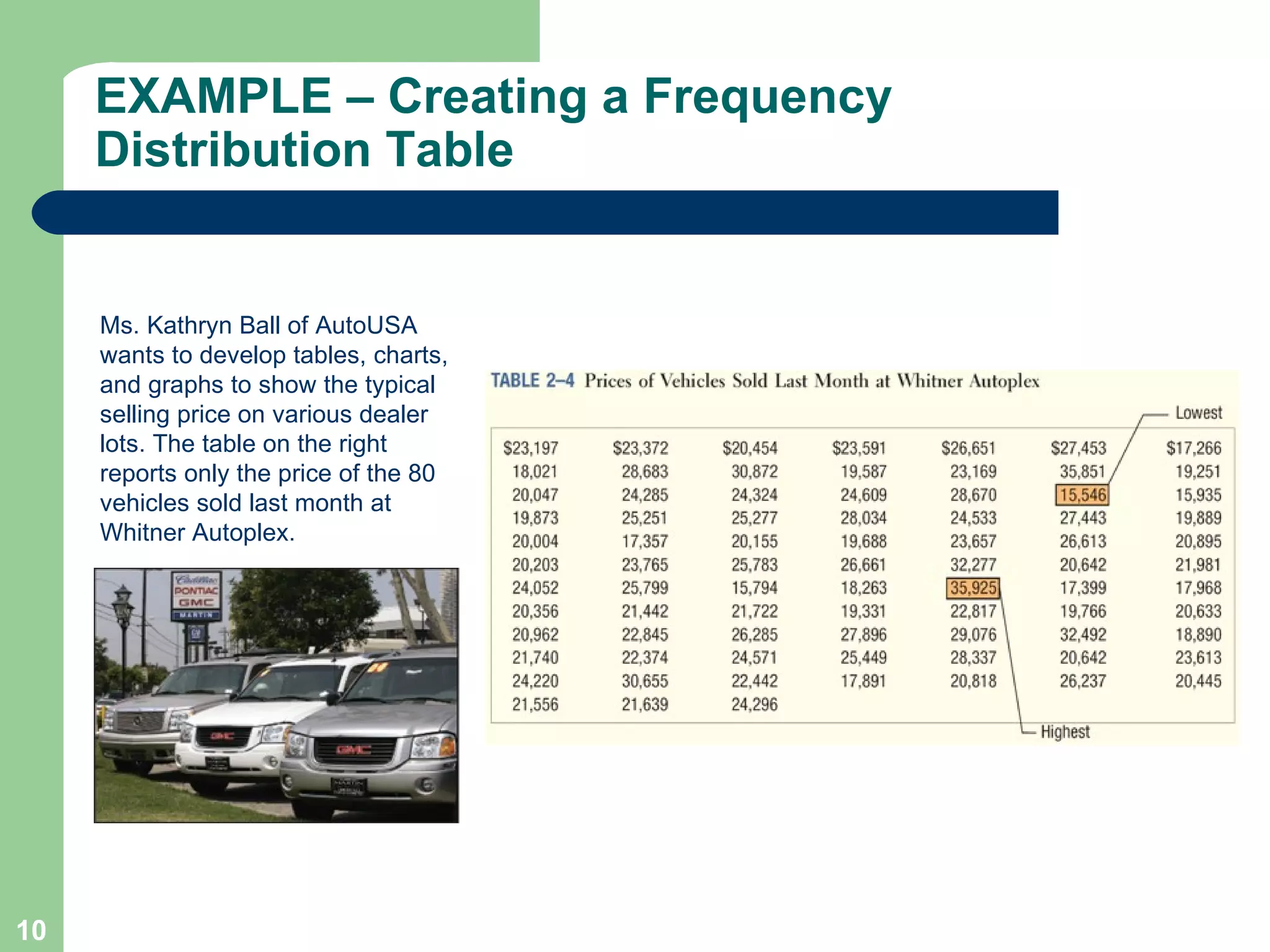
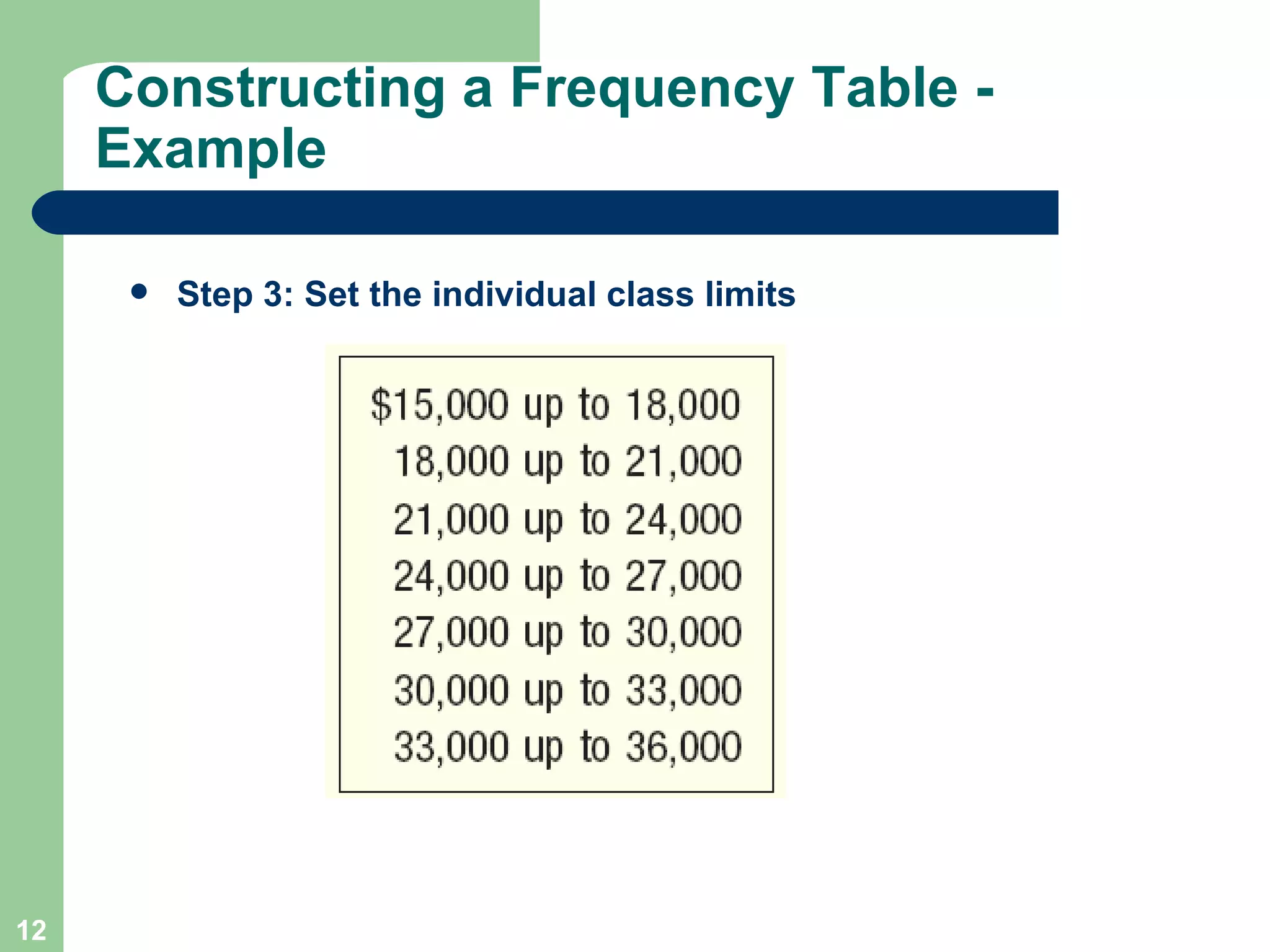
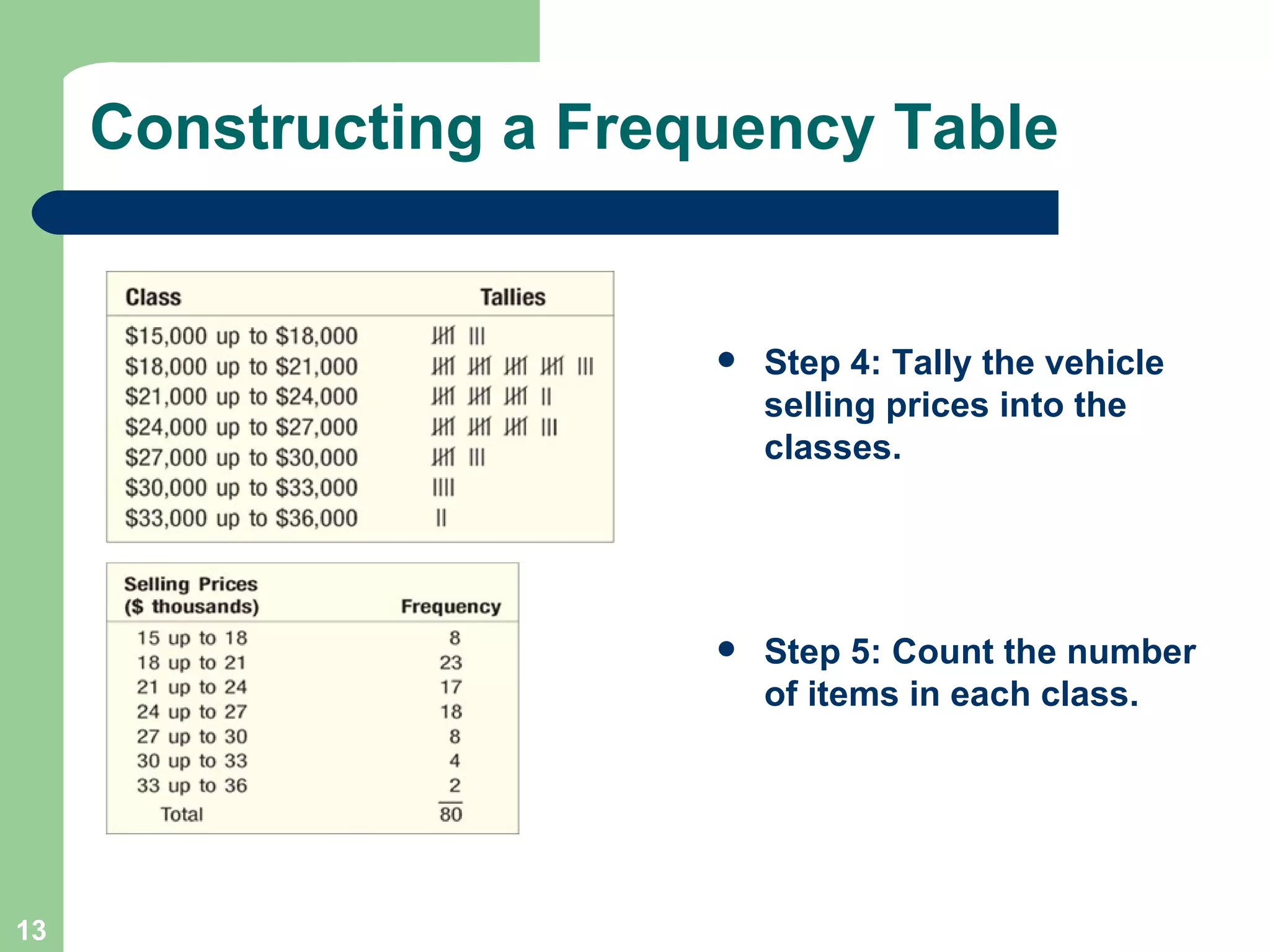
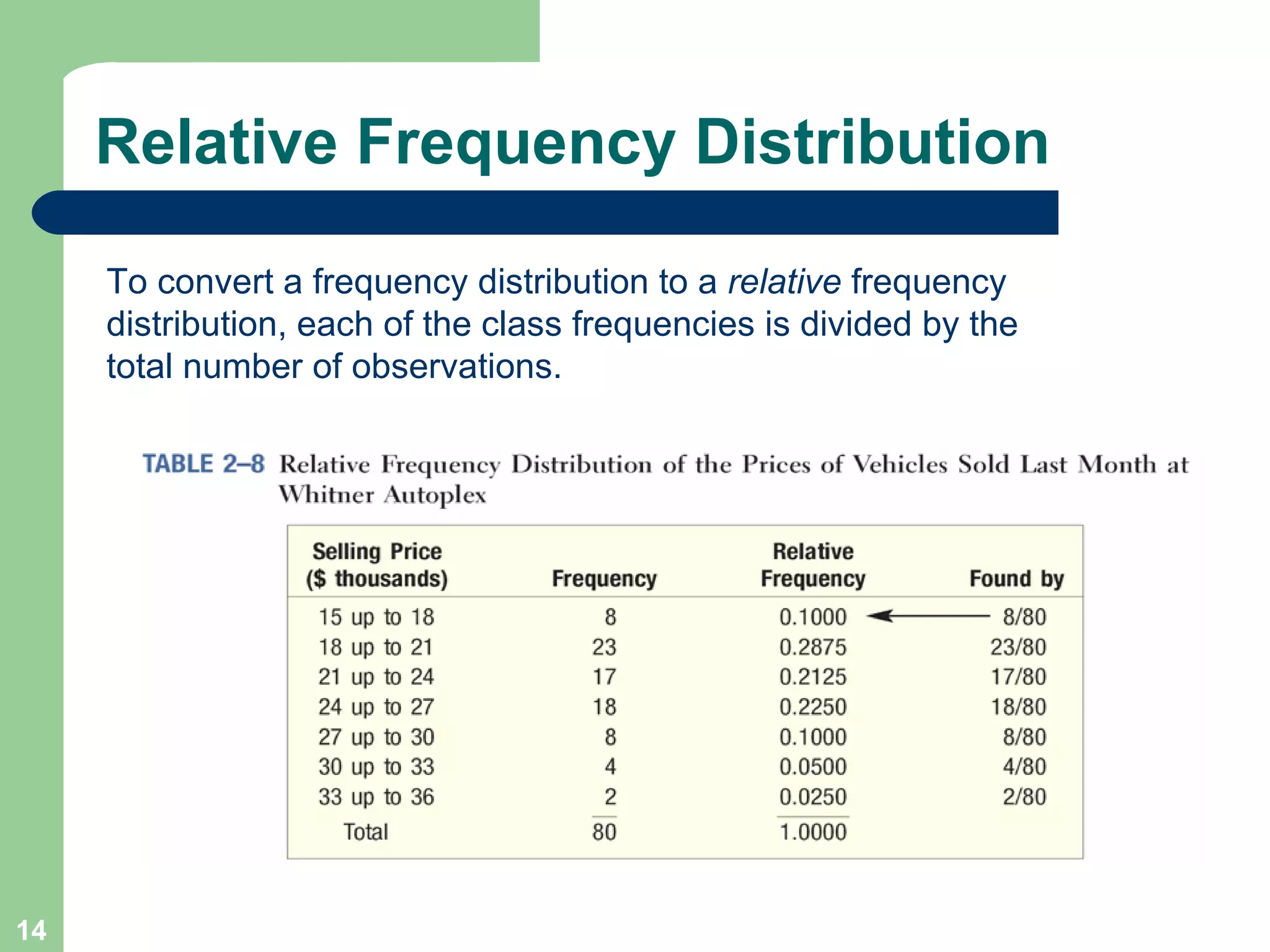
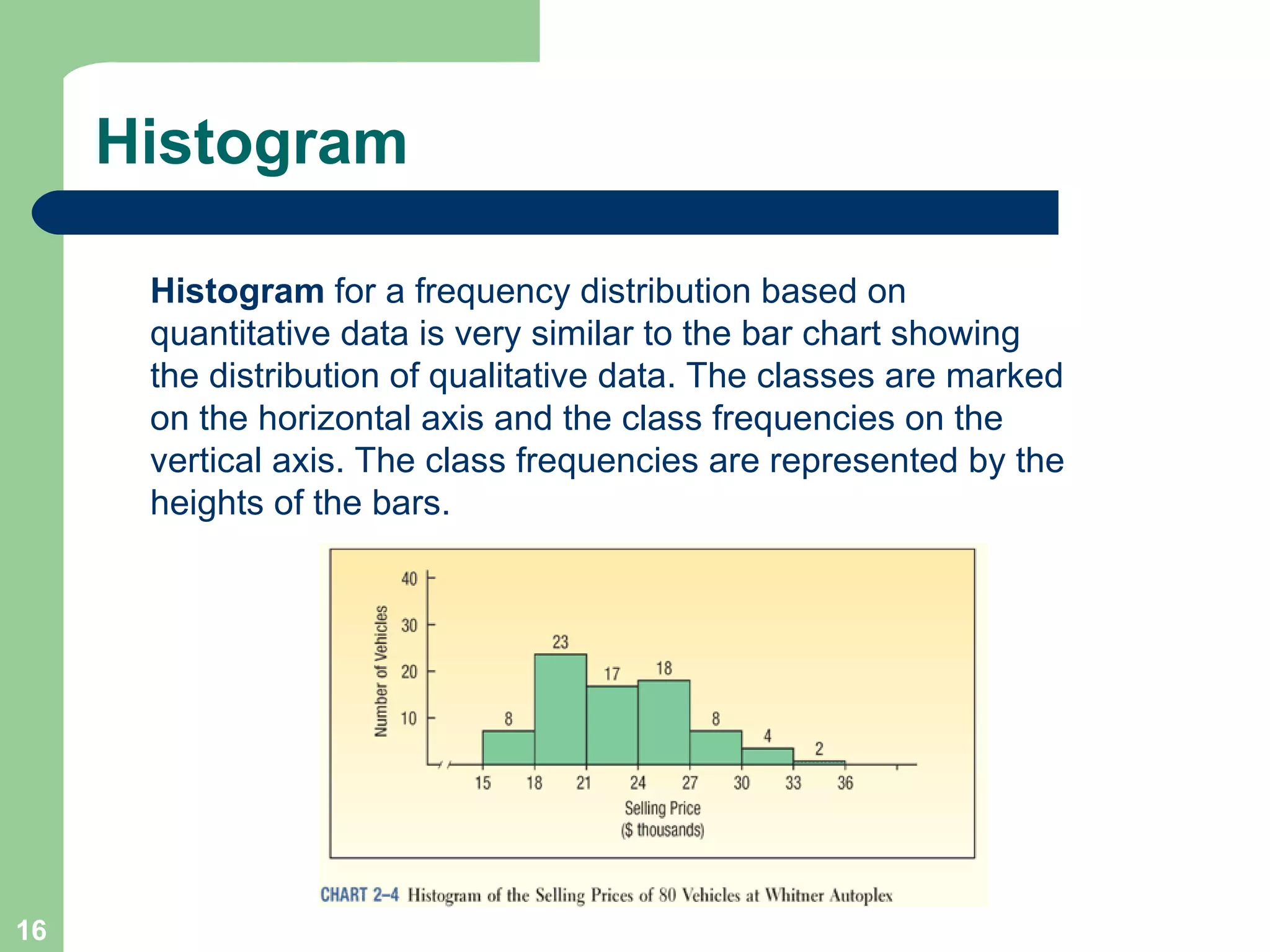
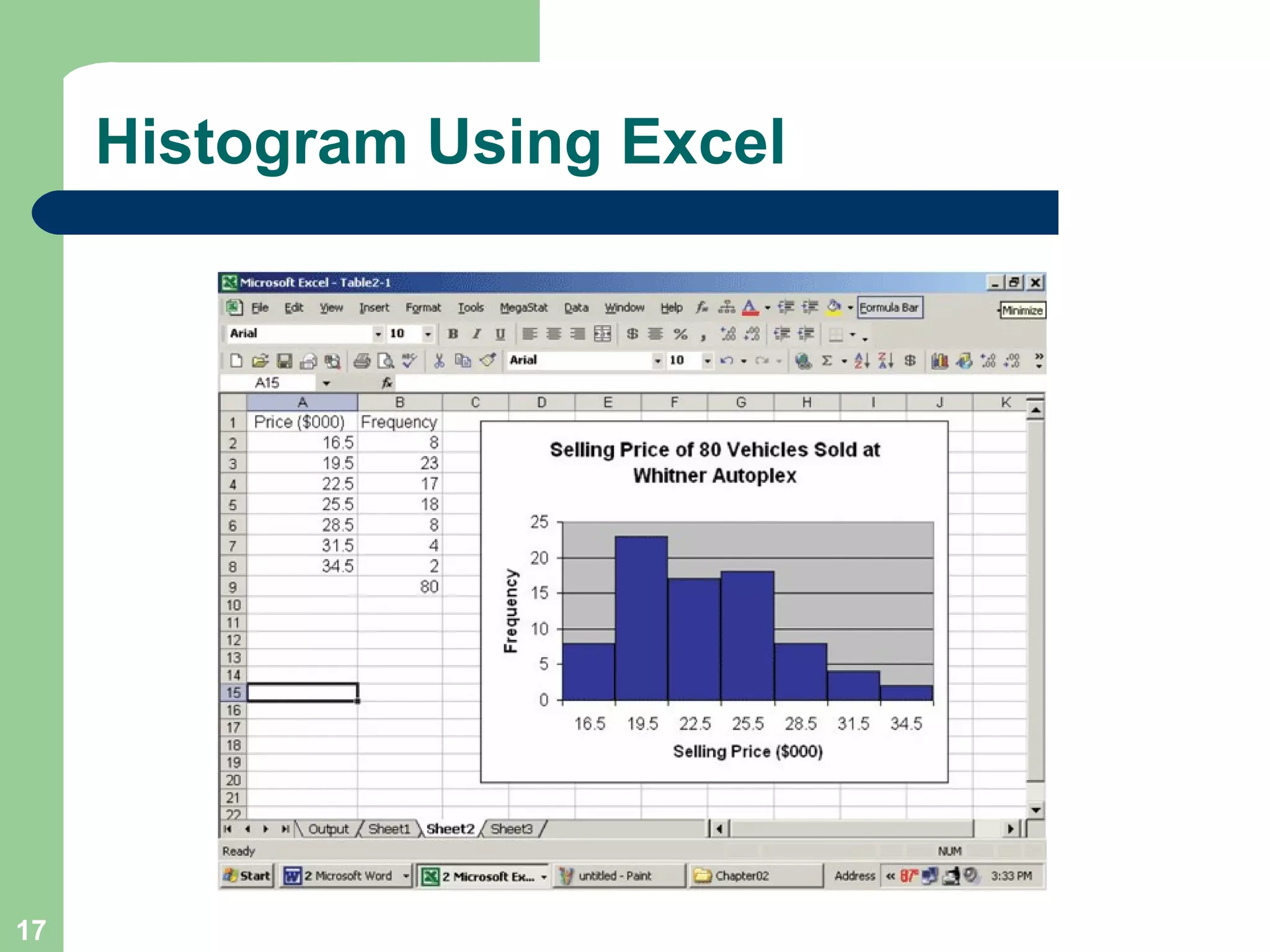
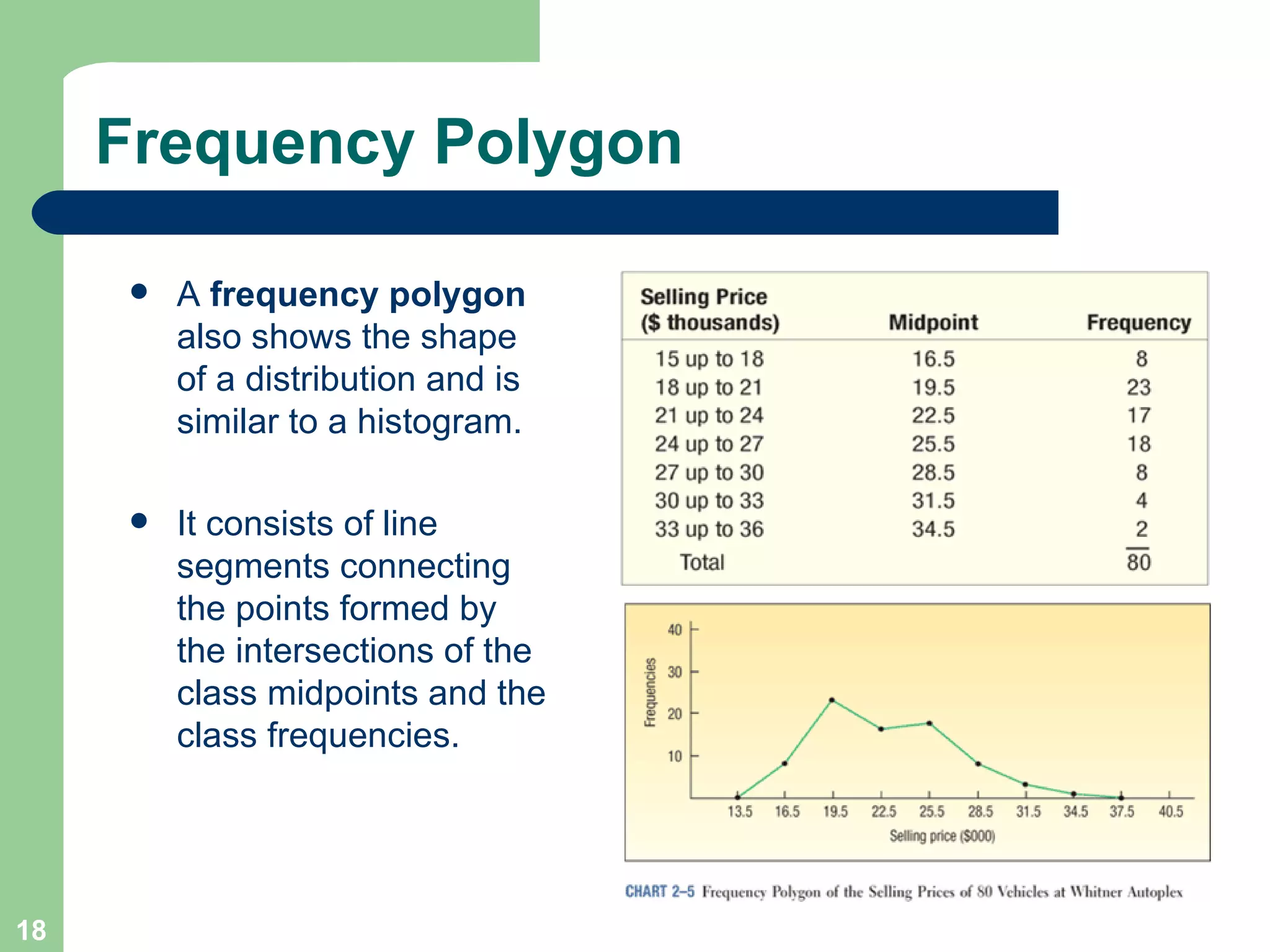
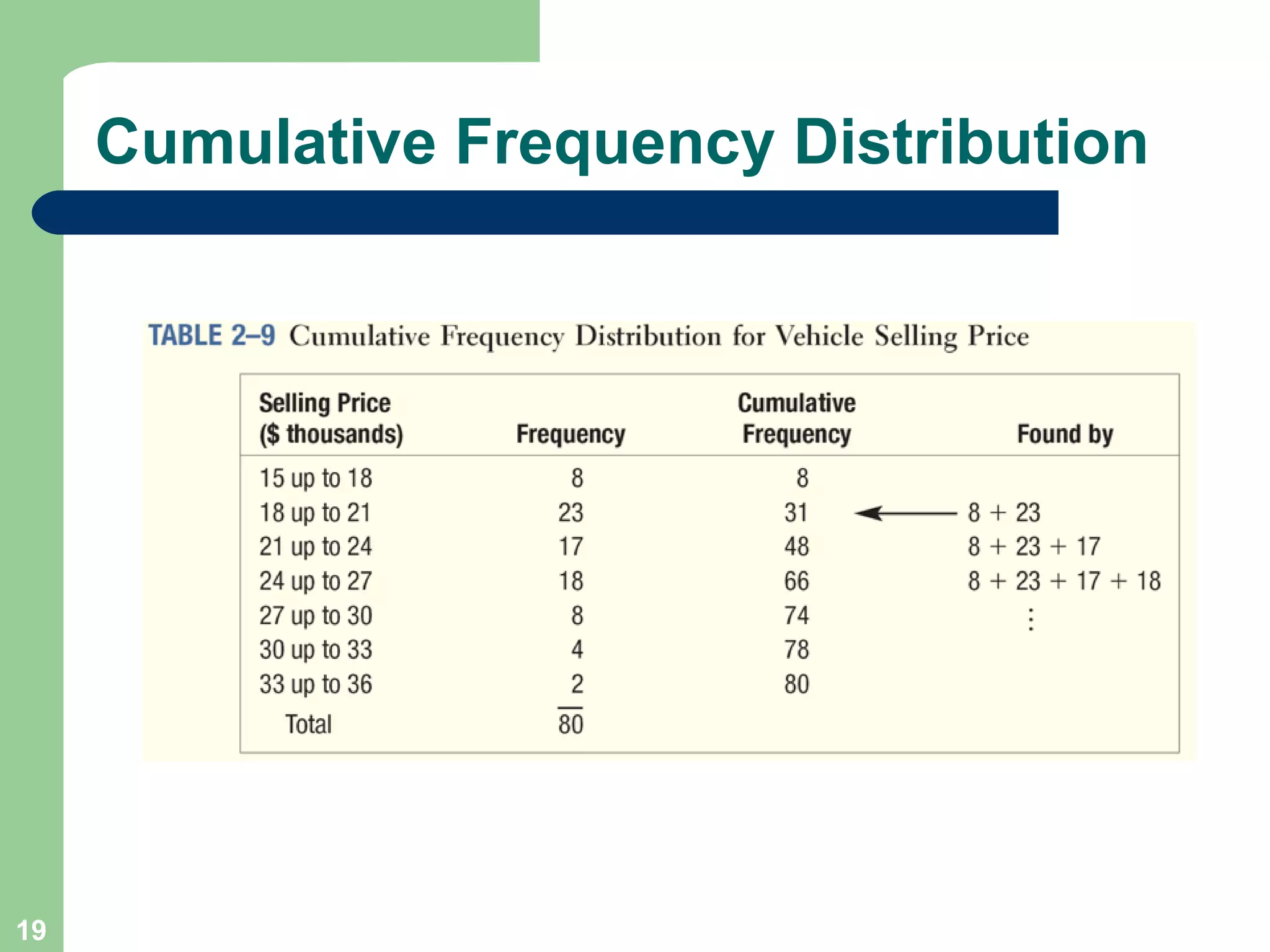
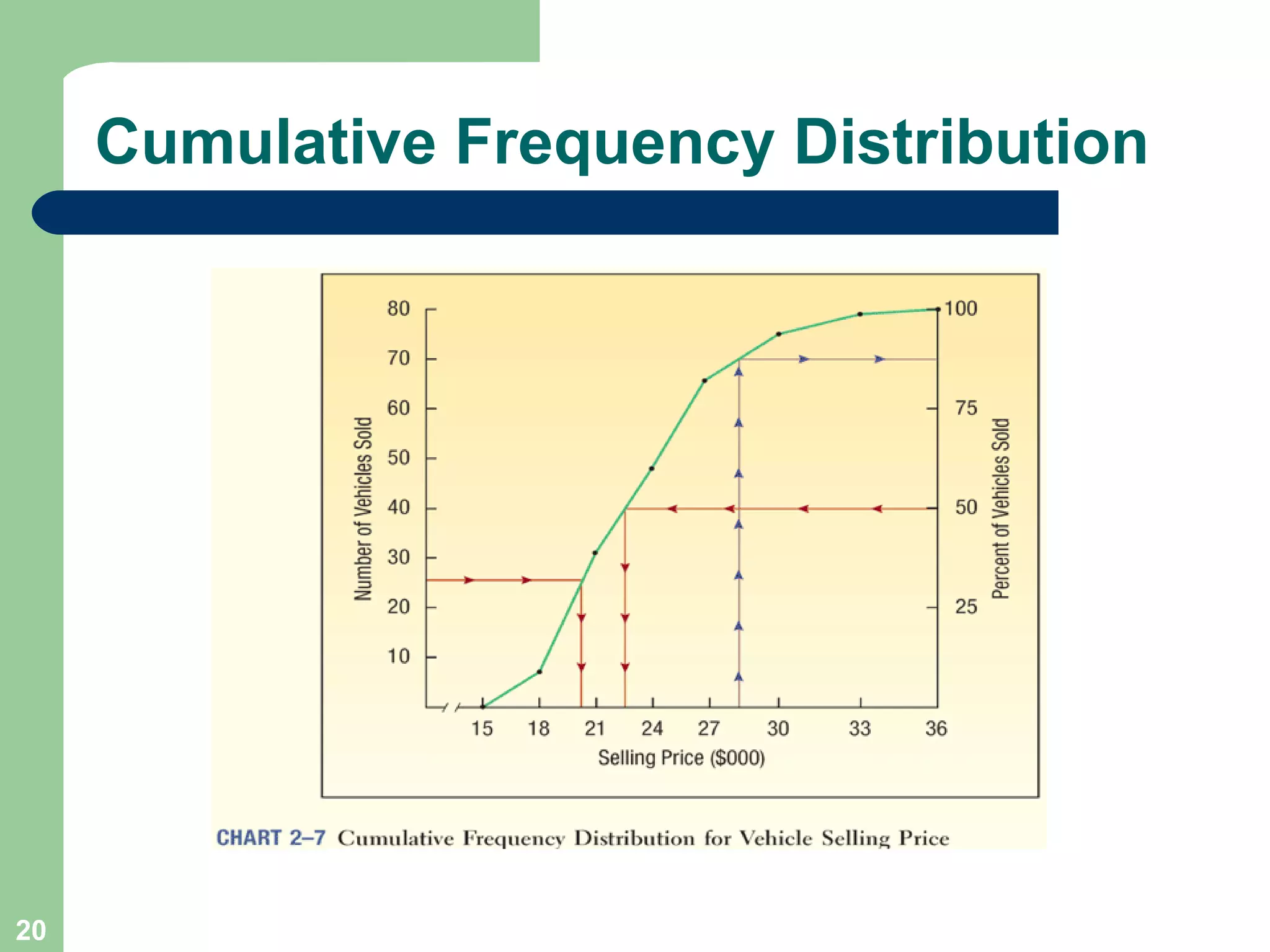
The document discusses methods for organizing and presenting both qualitative and quantitative data, including frequency tables, bar charts, pie charts, and different types of frequency distributions. It provides examples of how to construct a frequency table by determining the number of classes, class intervals, and class limits based on a set of data. It also describes how to create histograms, frequency polygons, and cumulative frequency distributions to graphically display a frequency distribution and highlights key terms such as class frequency, class interval, and relative frequency.