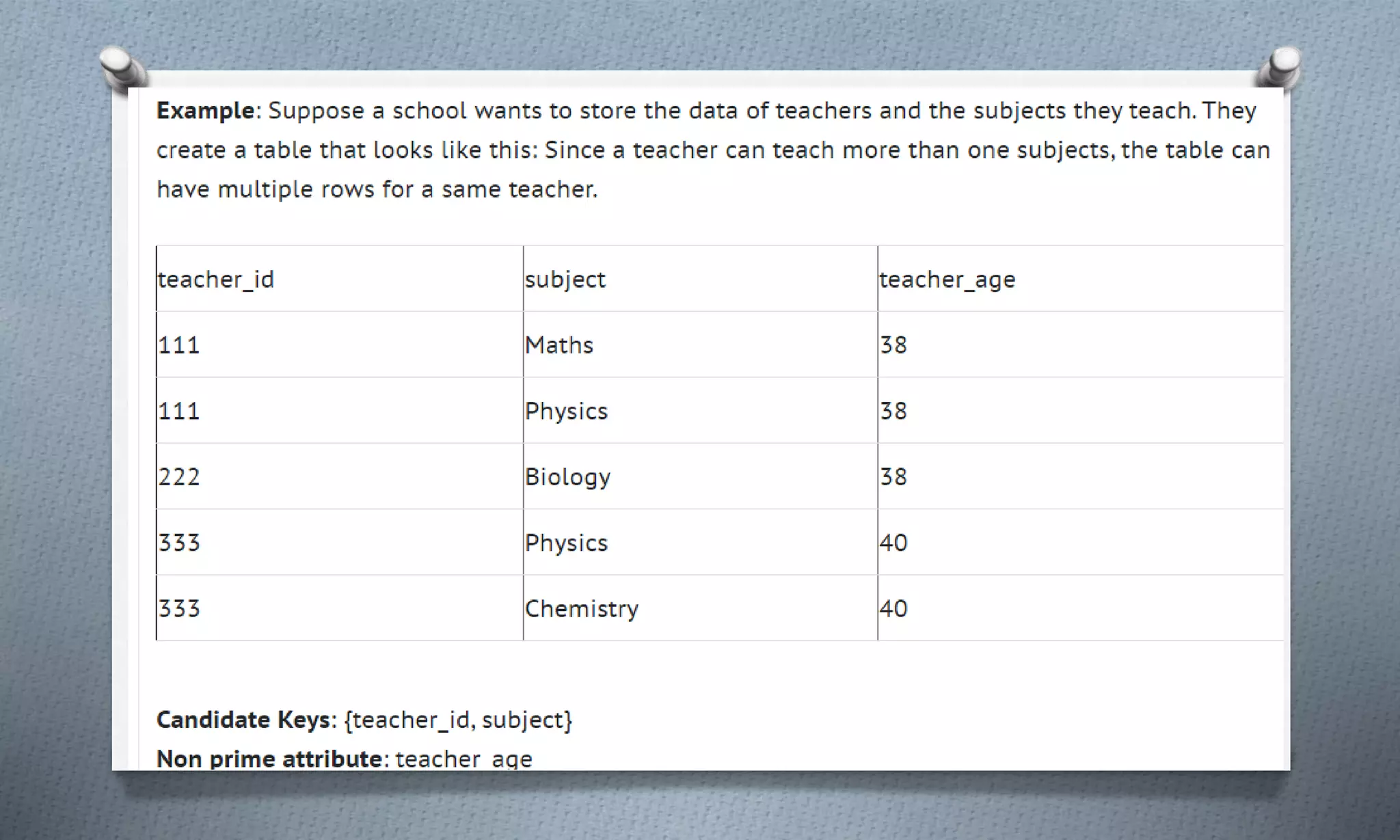
The document outlines various fact-finding techniques used in software analysis and design, including observation, interviews, questionnaires, and prototyping, which aid system analysts in collecting data for system development. It discusses the importance of these techniques in eliminating redundancy and improving system effectiveness and introduces decision tables and trees as tools for organizing complex business logic. Additionally, it covers normalization methods that ensure data integrity by reducing redundancy in databases.