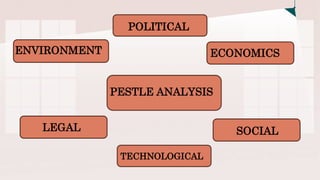
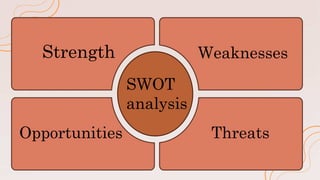
This document discusses various business analysis tools and techniques including PESTLE, SWOT, and Porter's Five Forces analyses. PESTLE is used to analyze political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors impacting a business. SWOT evaluates a company's internal strengths and weaknesses as well as external opportunities and threats. Porter's Five Forces examines competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, threat of substitutes, and threat of new entry to understand a company's competitive position. The document provides examples and explanations of each analysis technique to help understand their importance for business strategy and decision making.