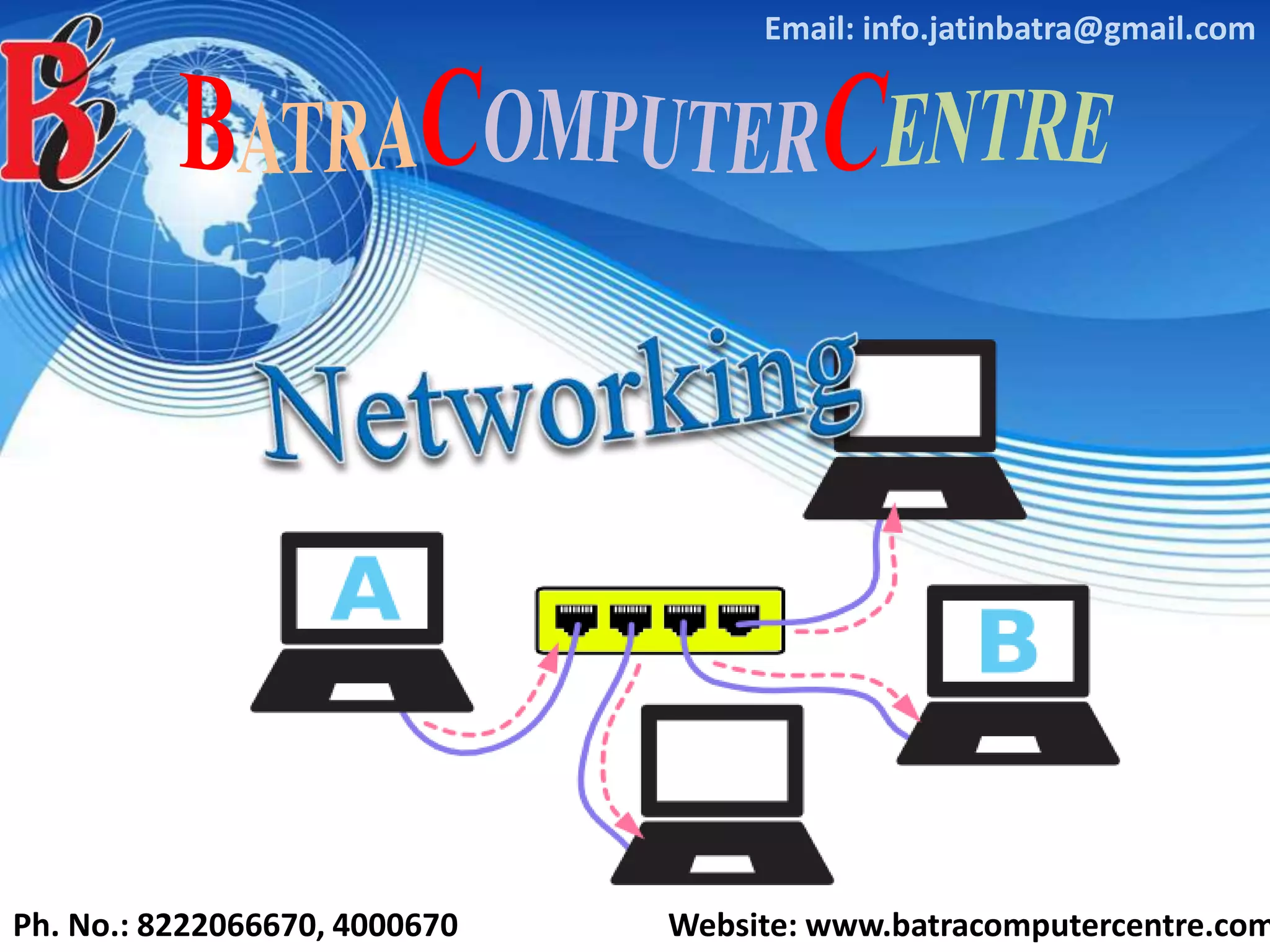
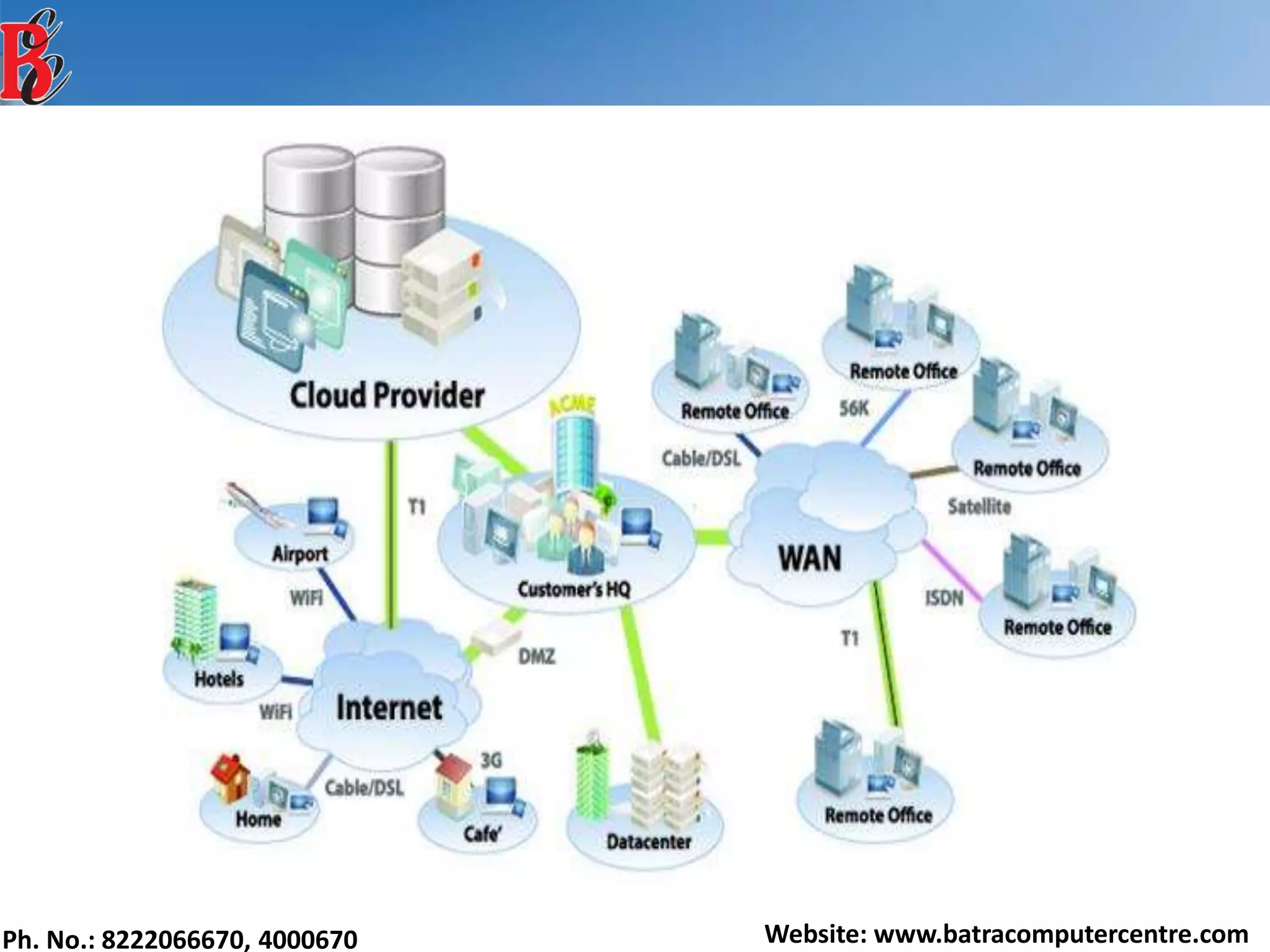
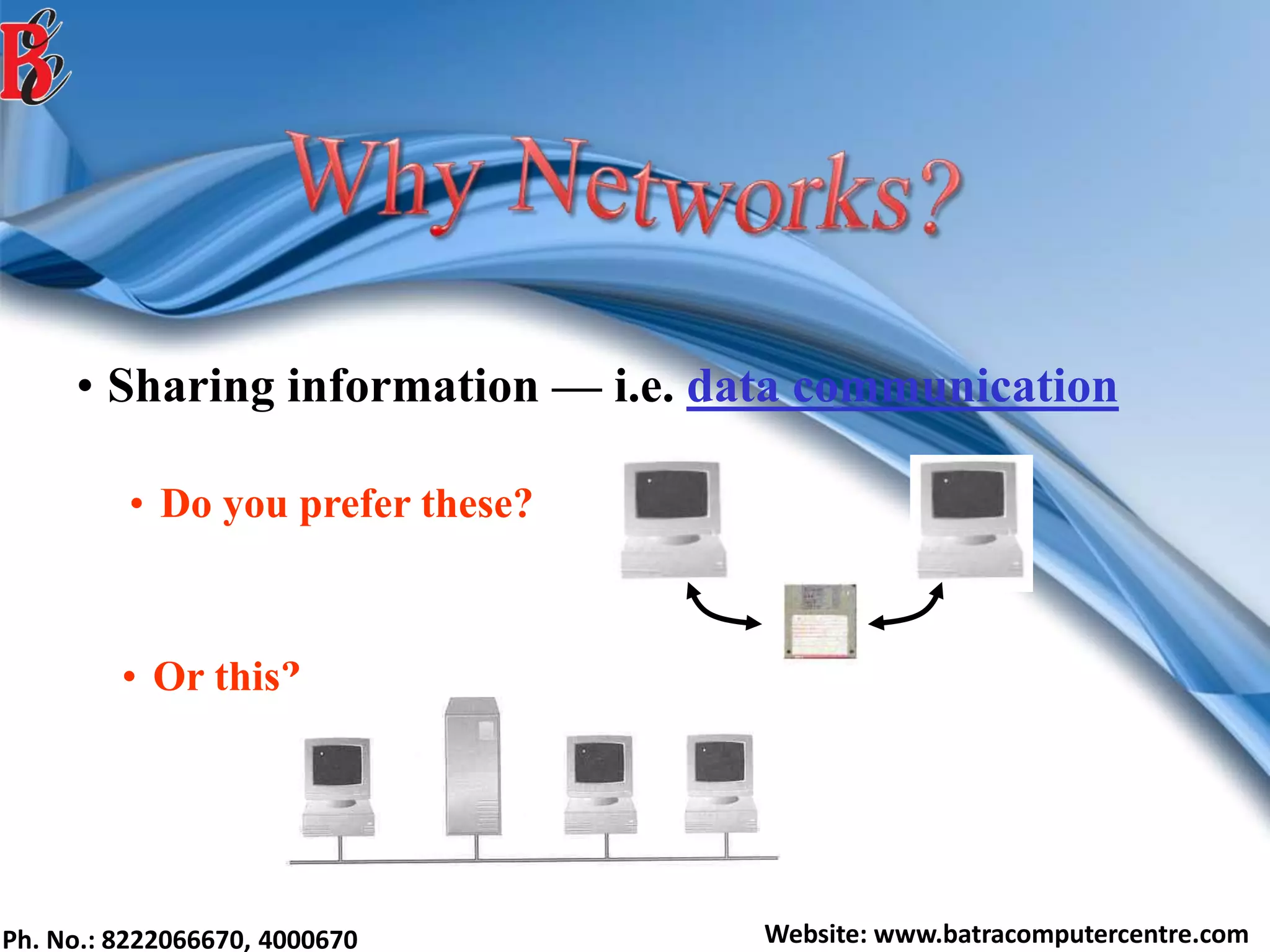
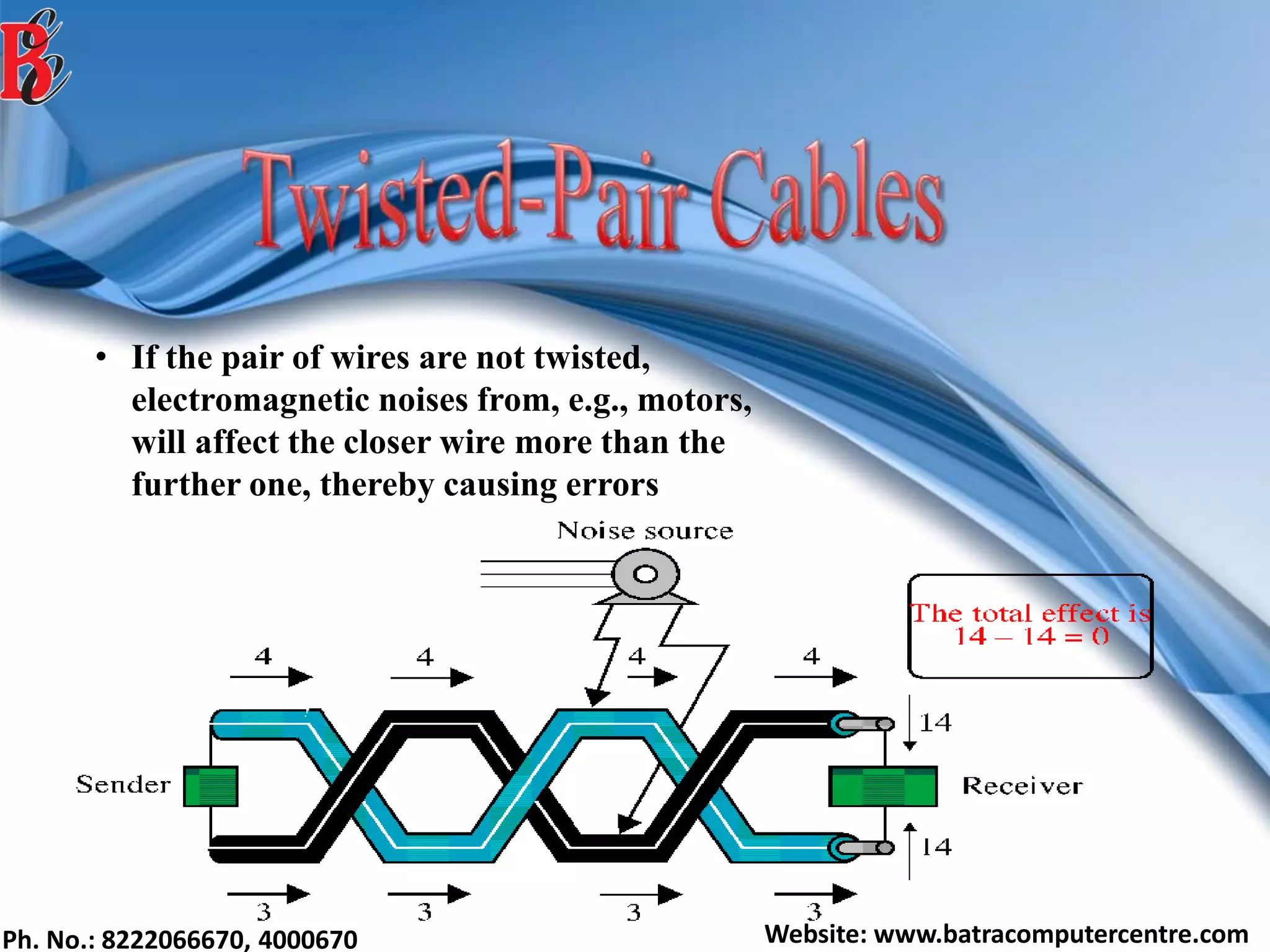
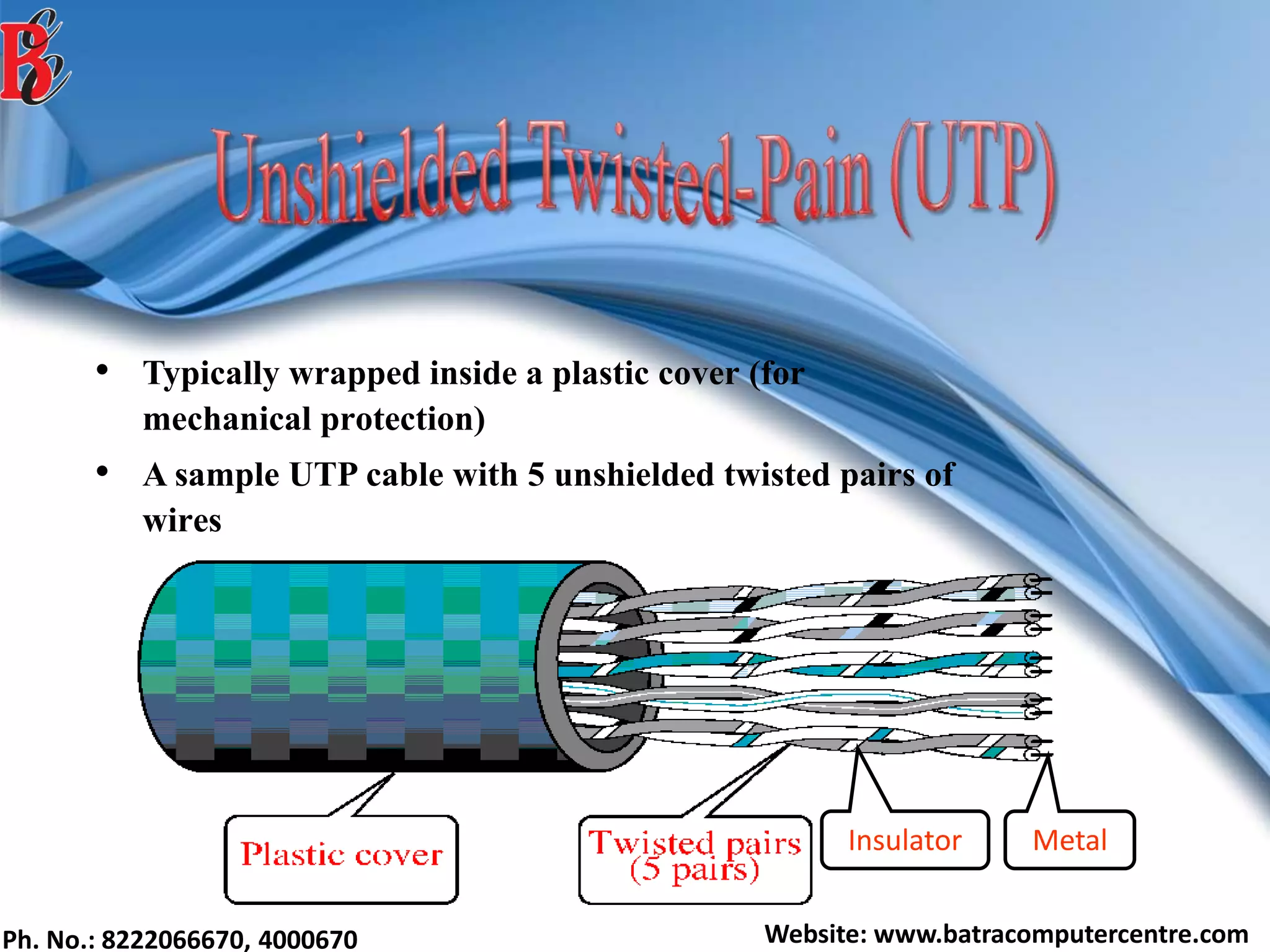
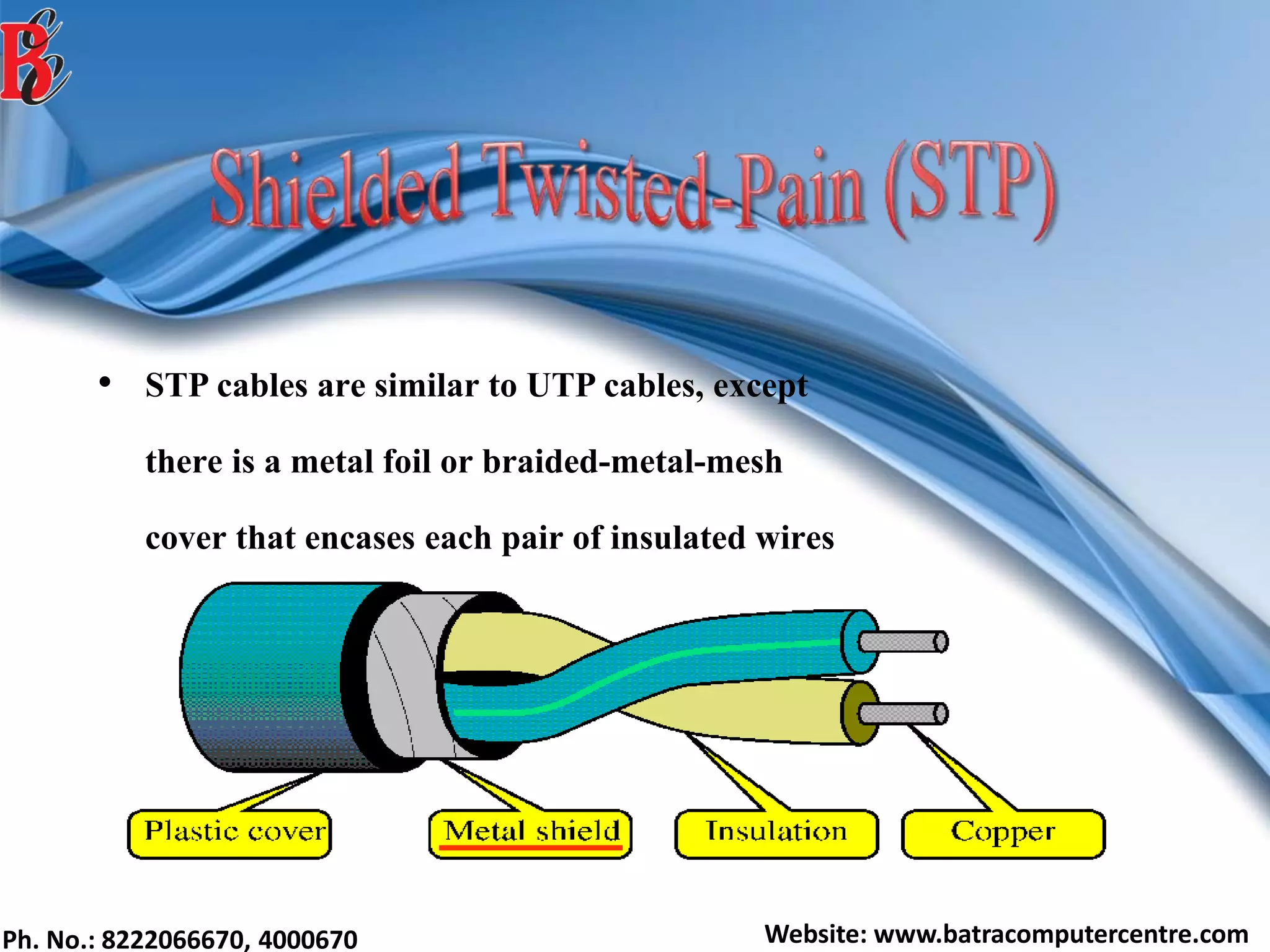
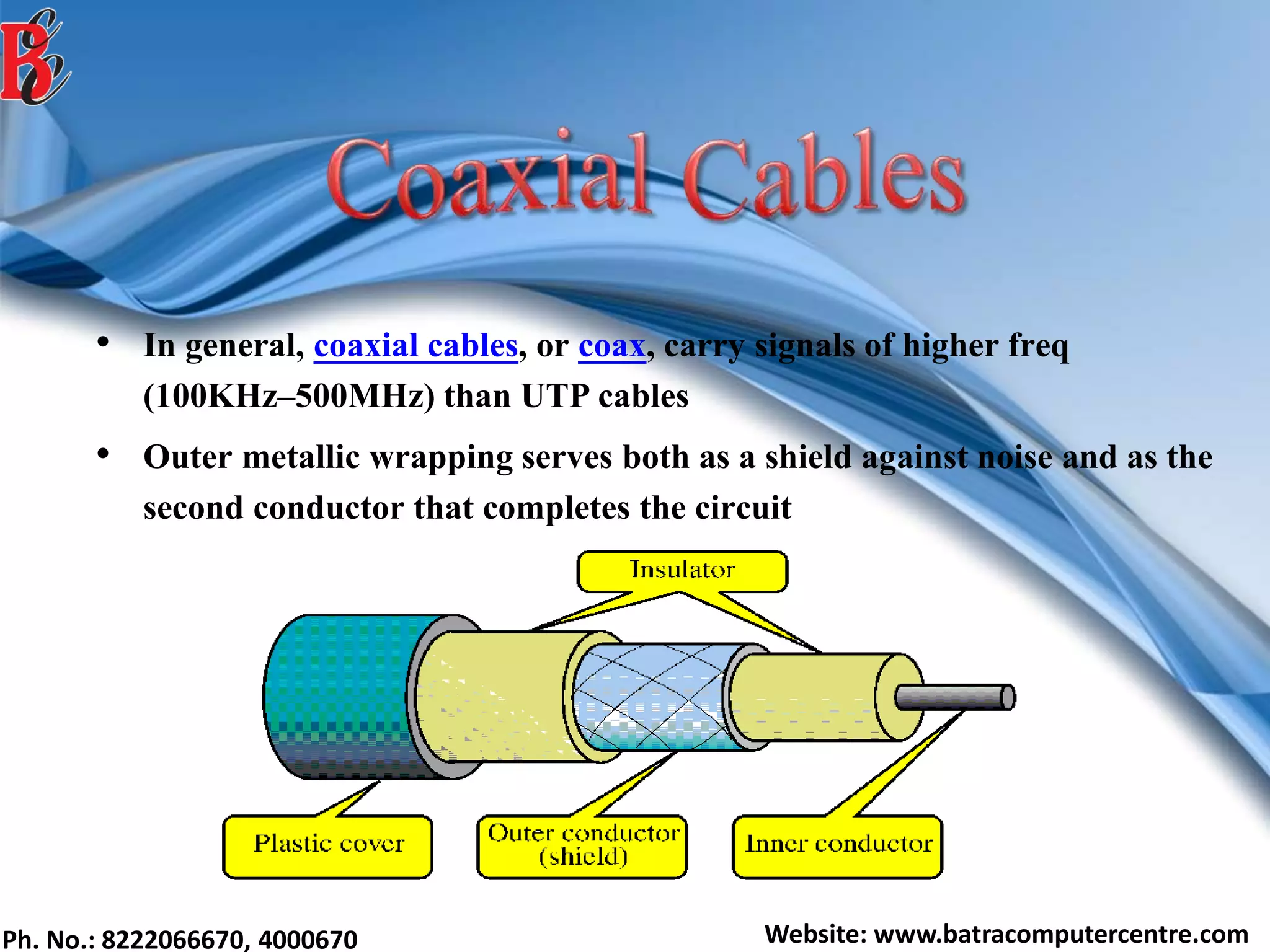
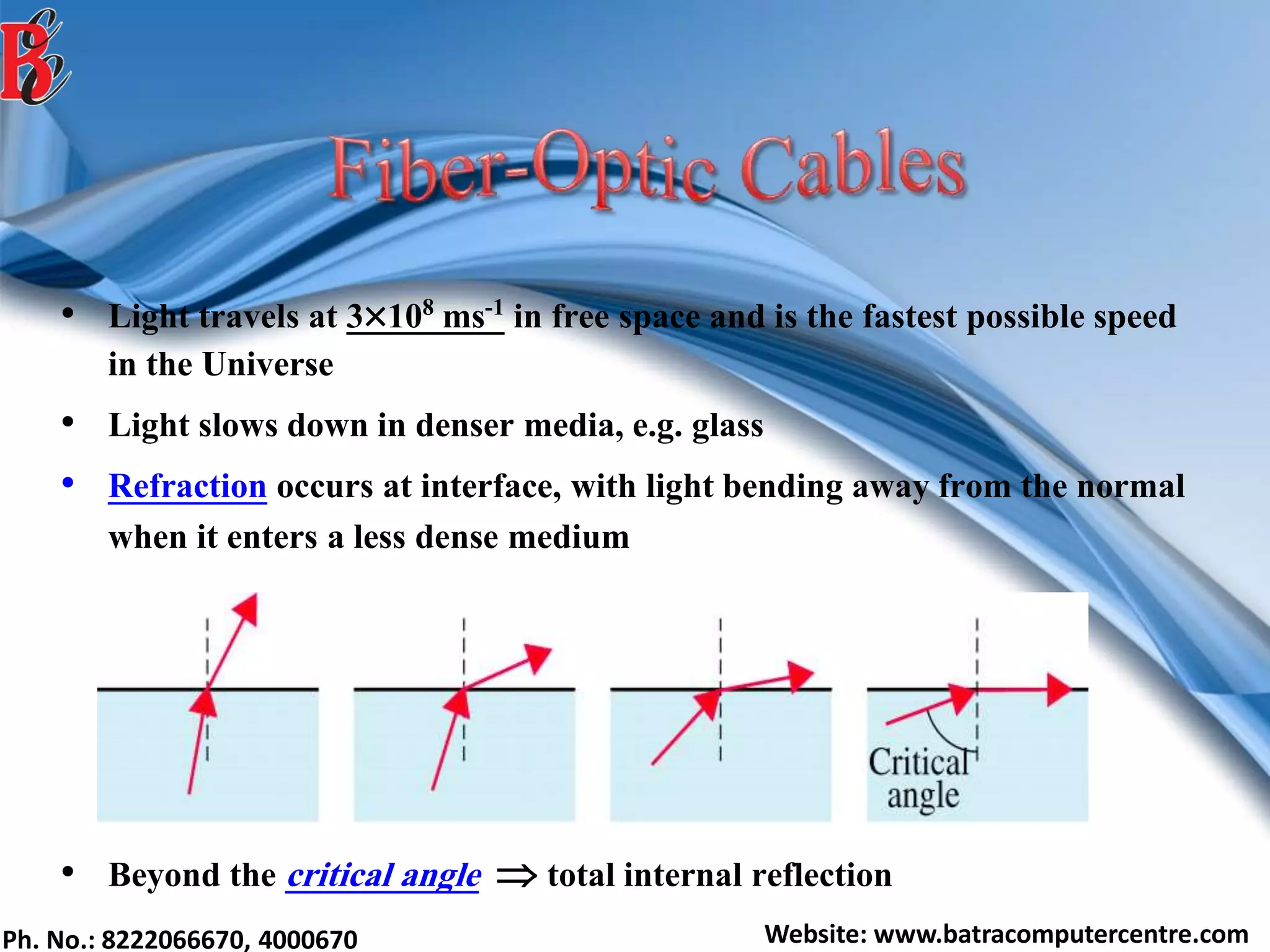
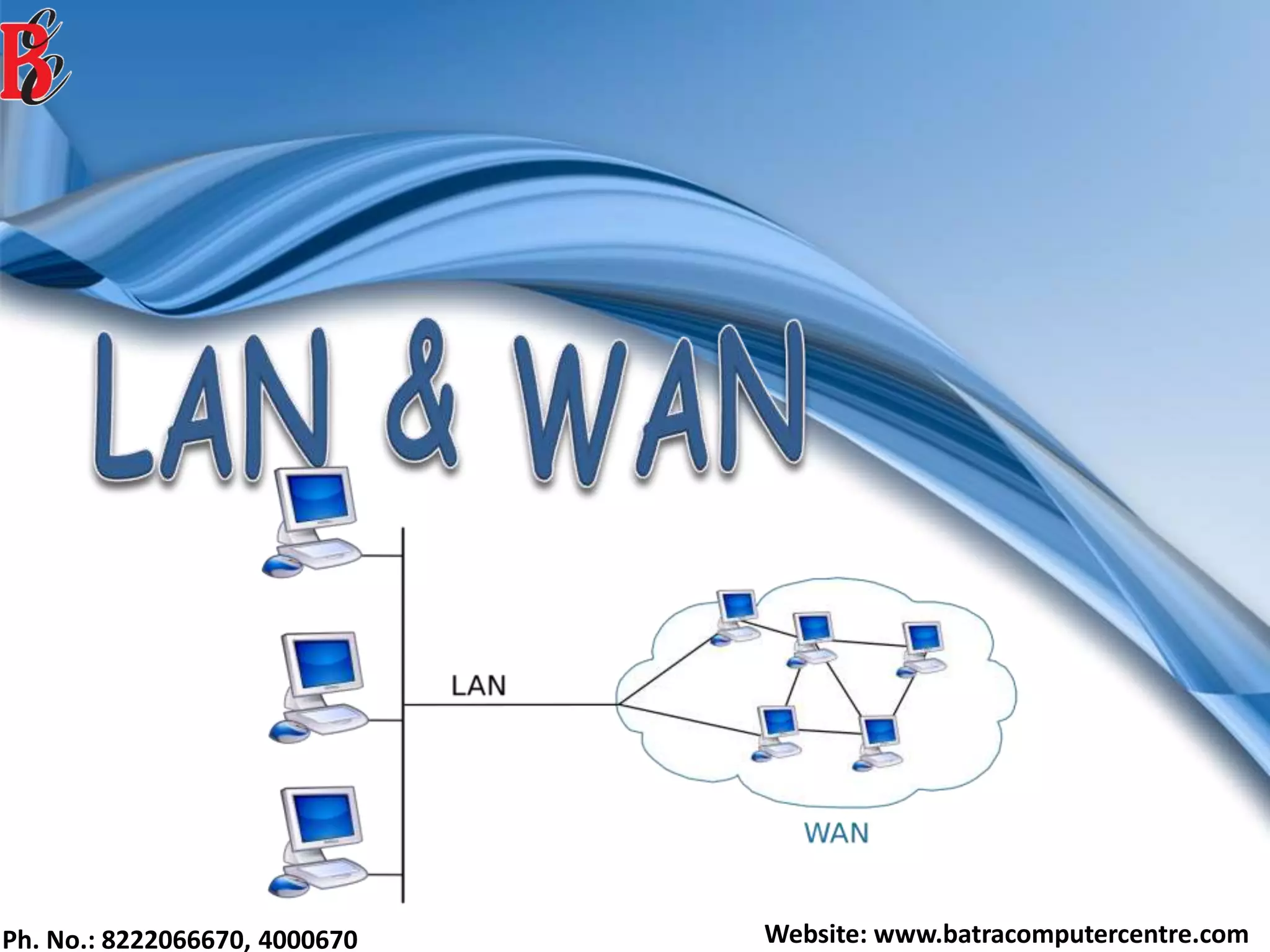
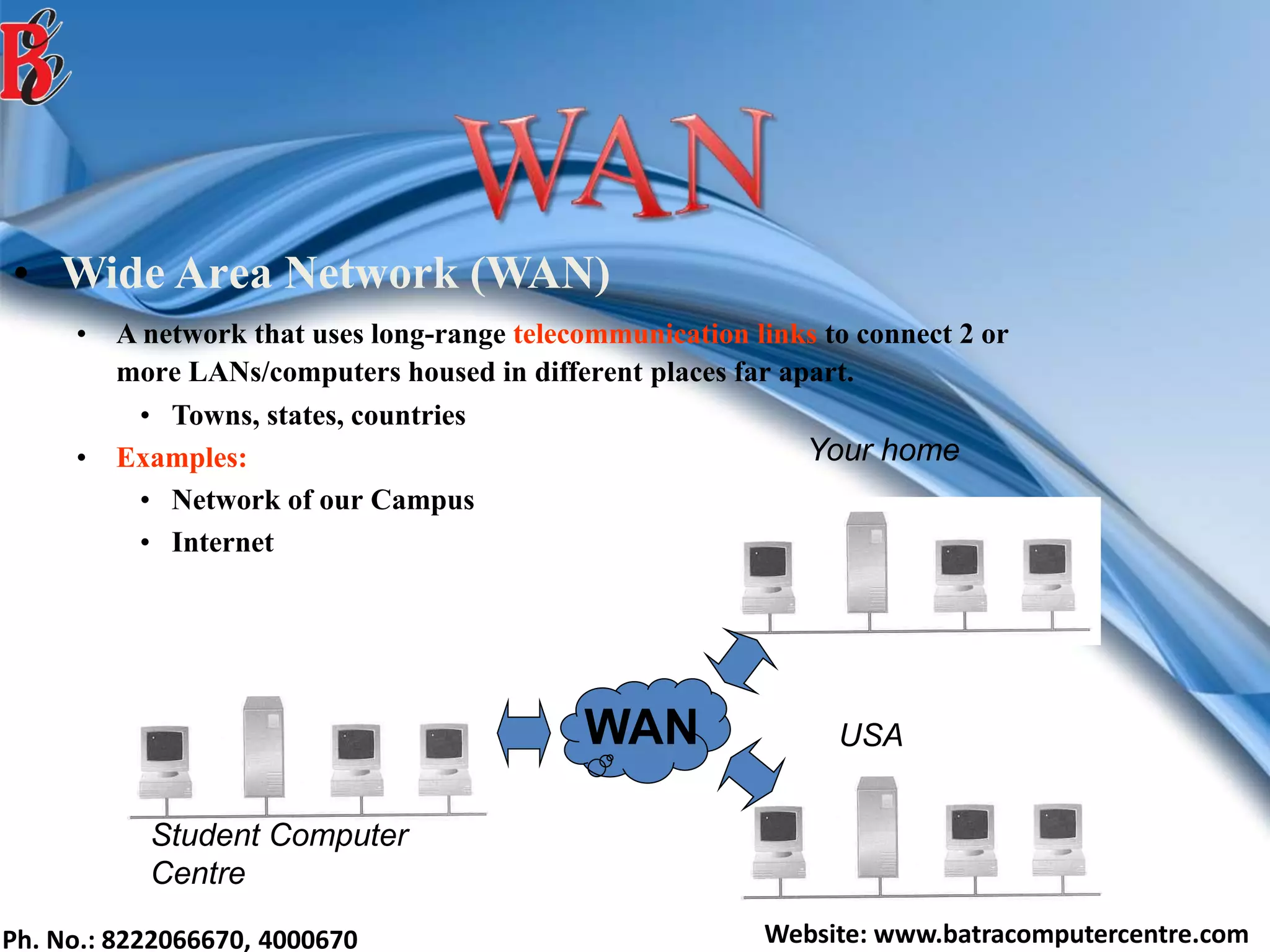
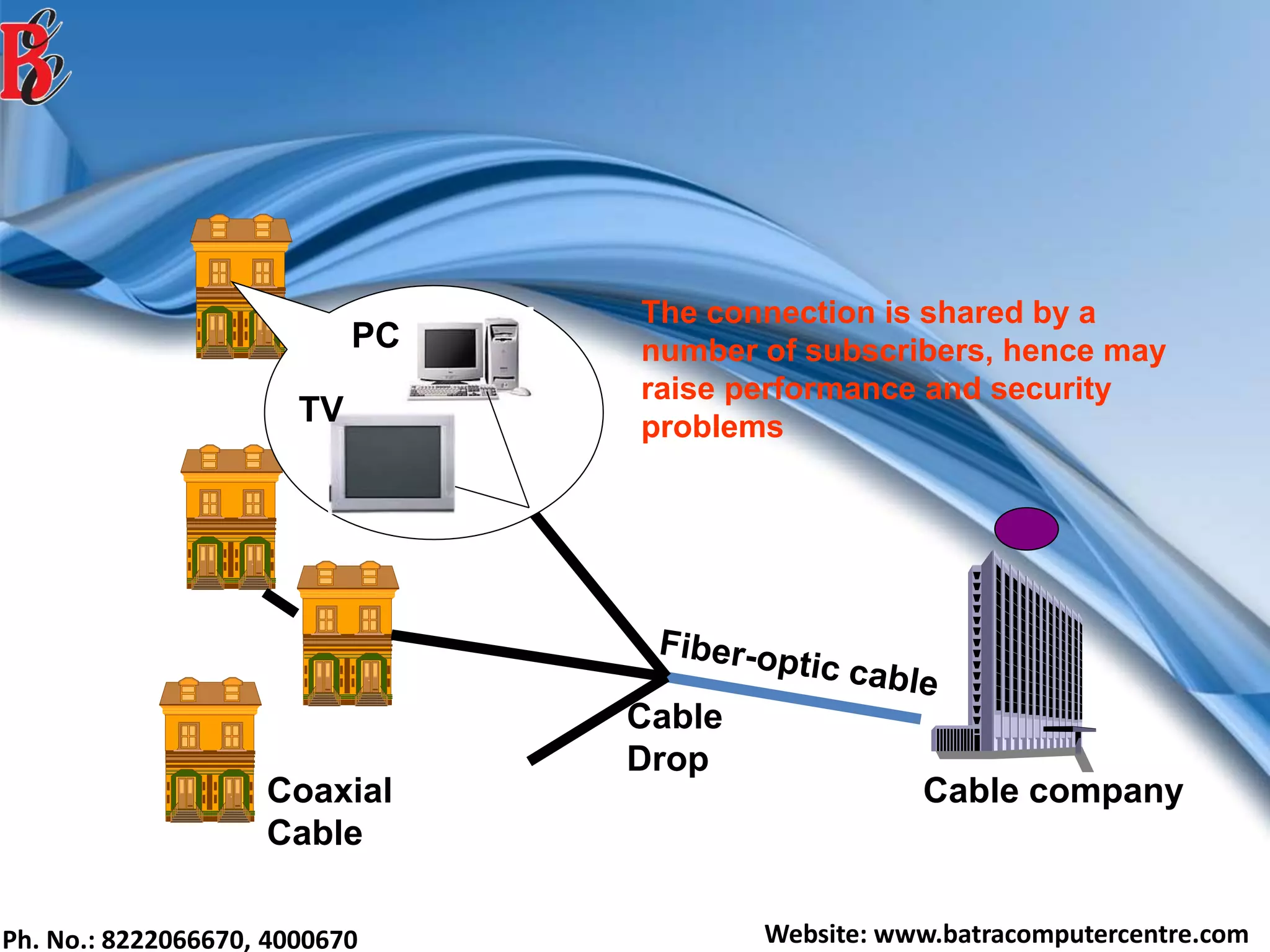
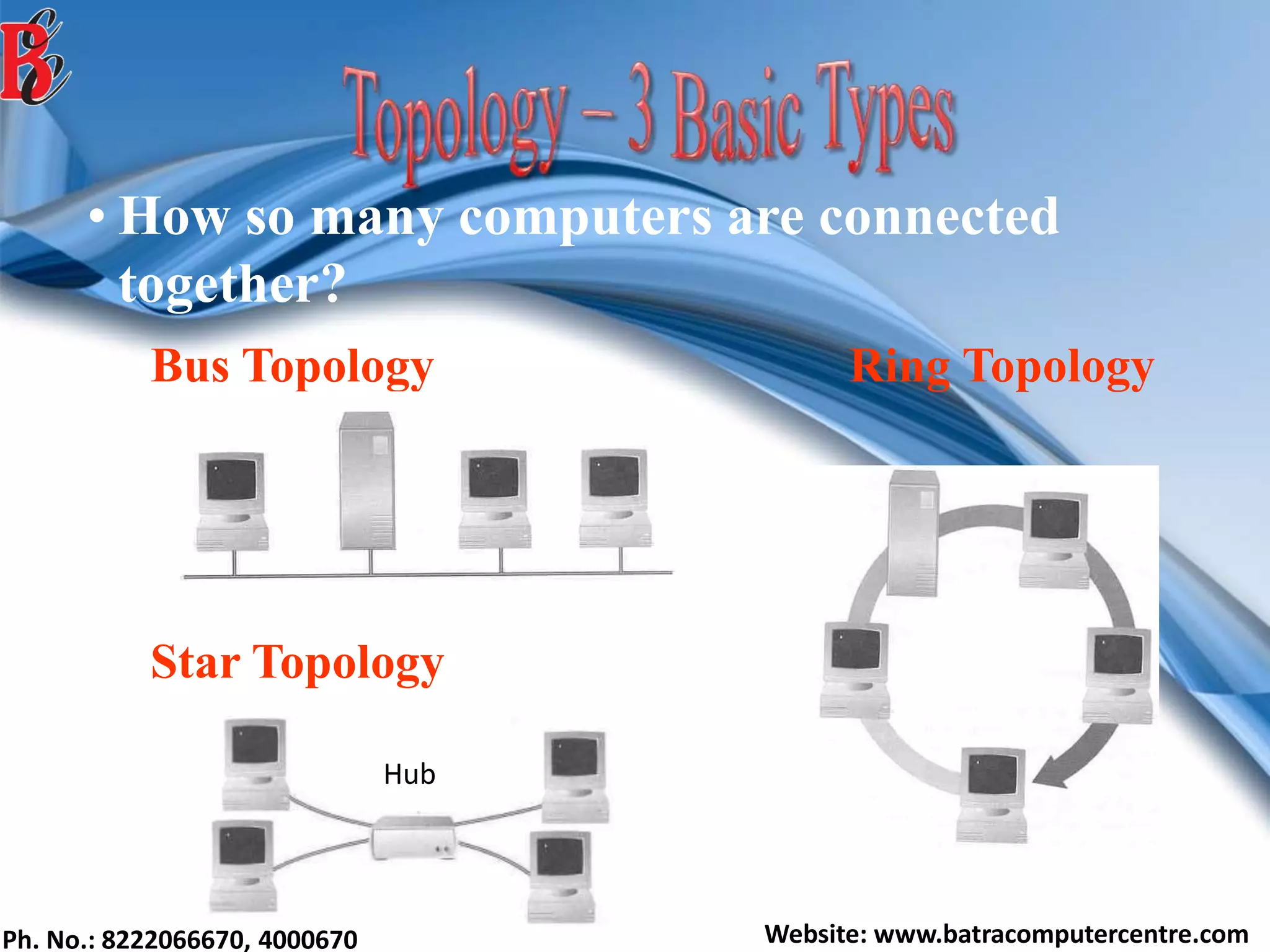
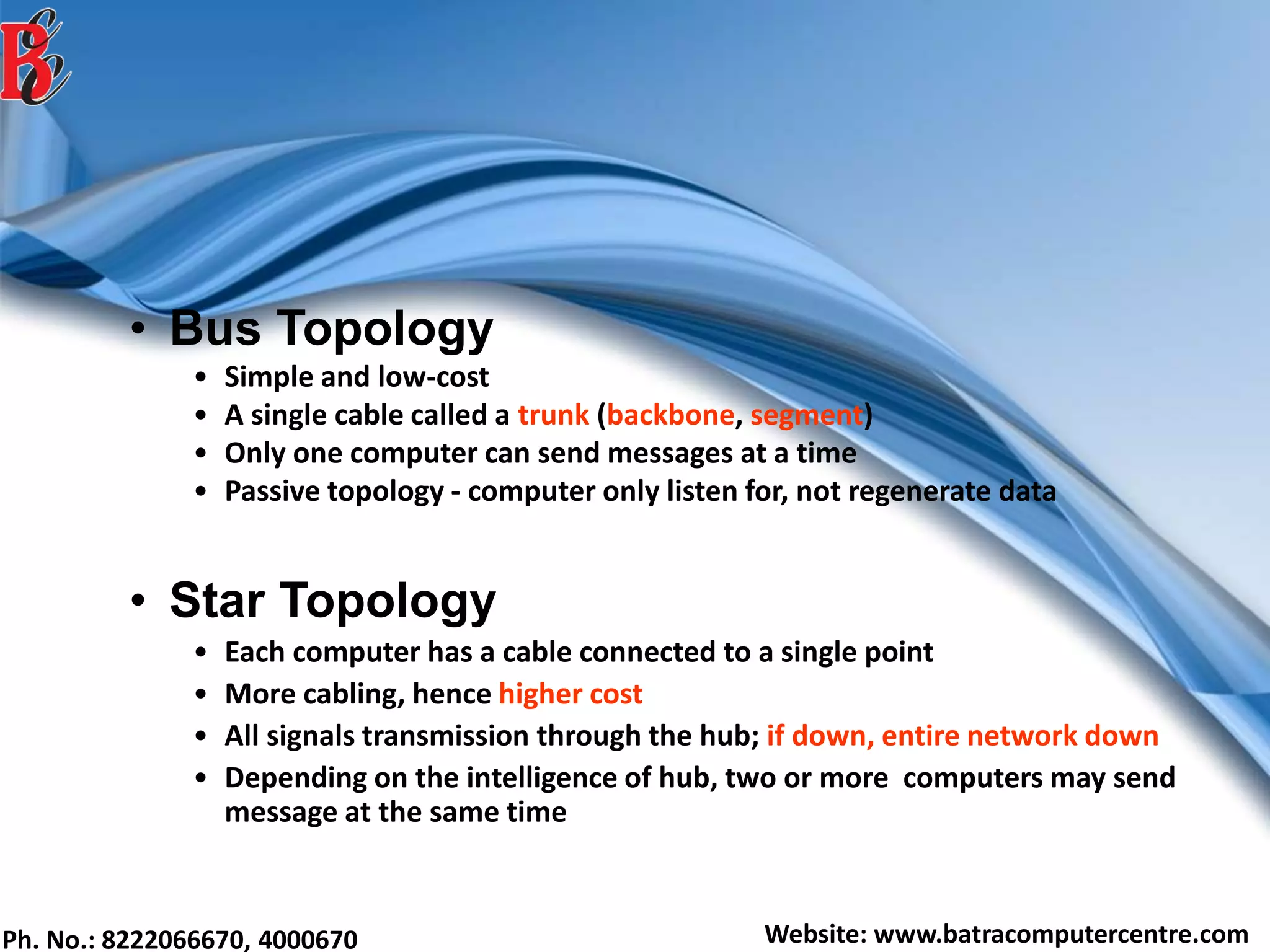
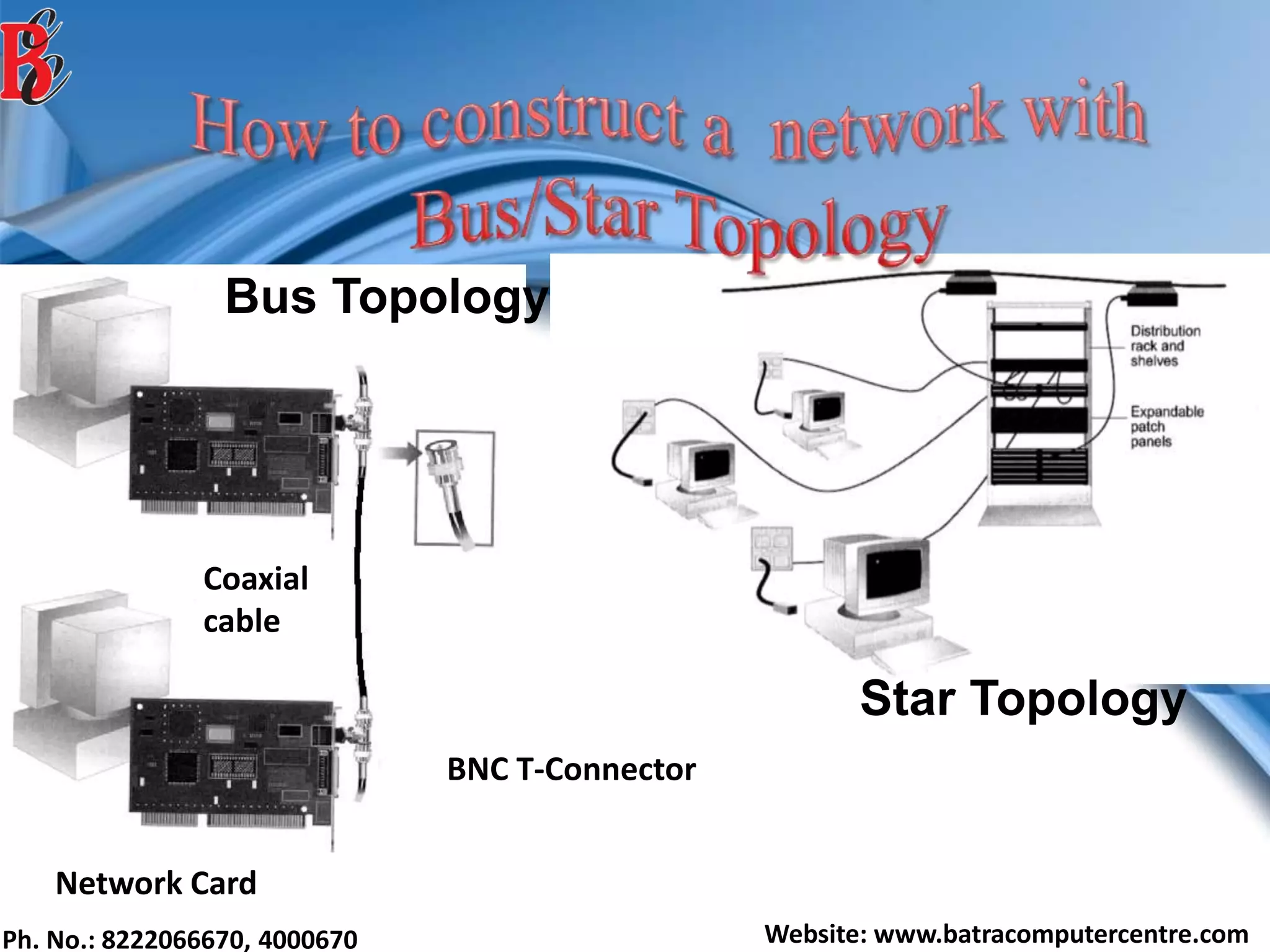
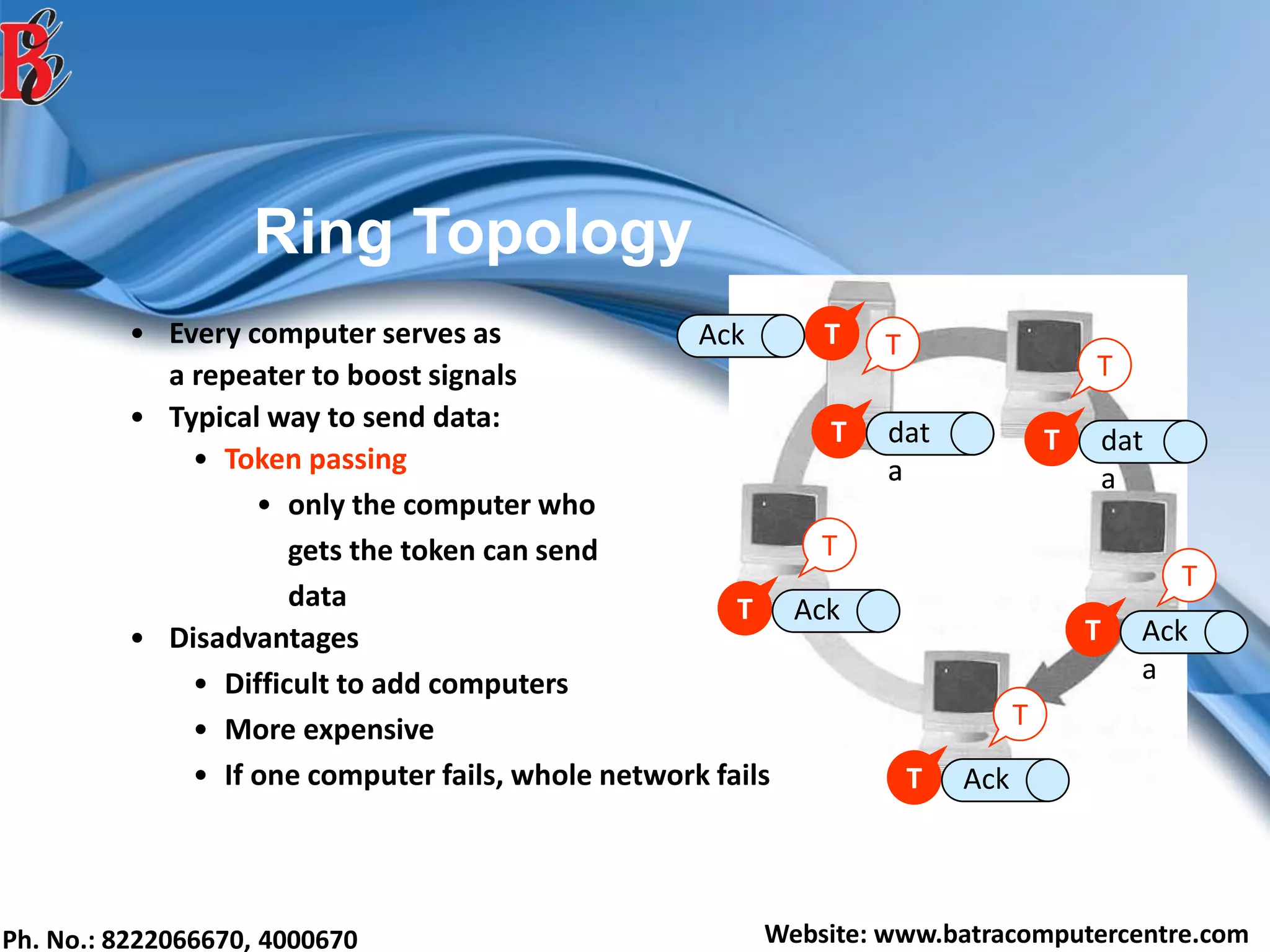
The document discusses various types of computer networks, including their classifications based on transmission media, size, management, and topology. It details different cable types such as UTP, STP, coaxial, and fiber-optic cables, along with their characteristics and applications. Additionally, it describes the differences between peer-to-peer and client/server networks, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages.