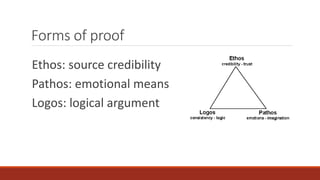
This document defines a persuasive presentation as a message designed to introduce change in the audience consistently with the presenter's purpose. It discusses goals of both immediate change and long-term impact. It also notes that asking for too much change can backfire in a "boomerang effect" where the audience likes the presenter less after hearing the presentation. The document outlines different types of arguments, evidence, proofs, and rebuttals that can be used in a persuasive presentation, including logical, emotional, and credibility-based approaches. It concludes by mentioning fear appeals and outlining Monroe's Motivated Sequence model for persuasive presentations.