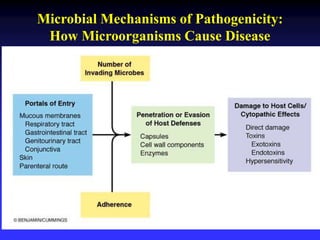
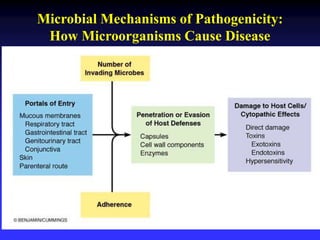
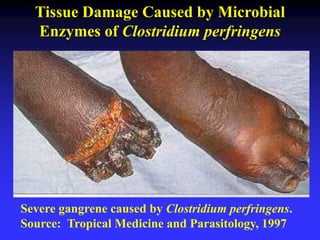
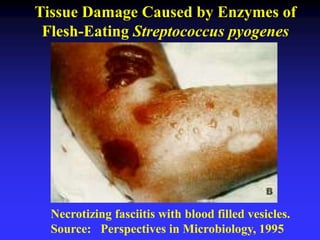
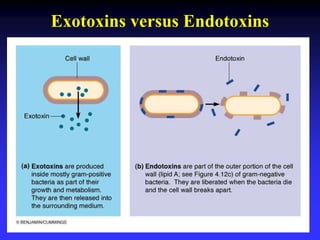
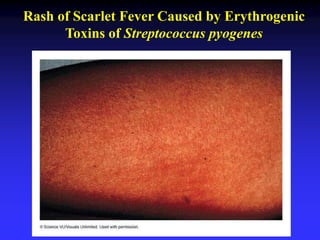
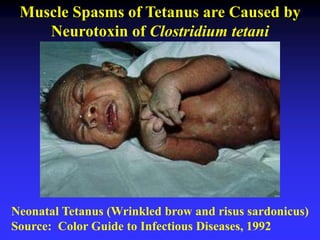
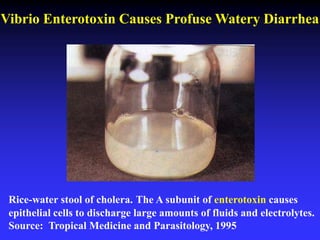
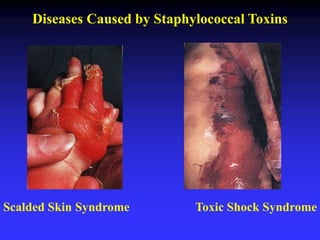
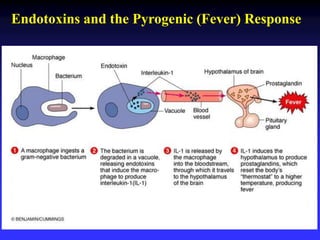
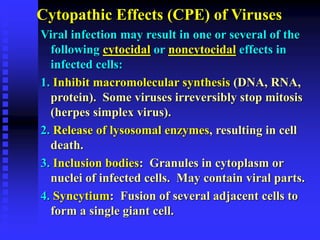
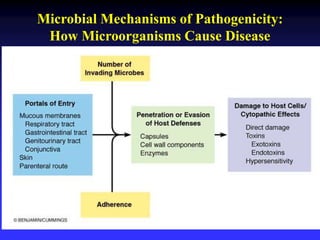
This document discusses the various mechanisms by which microorganisms cause disease in the human body. It begins by outlining the main portals of entry for pathogens, including mucous membranes, skin, and parenteral routes. It then explores specific microbial structures and products that facilitate infection, such as capsules, cell wall components, and extracellular enzymes. Pathogens can also produce toxins like exotoxins and endotoxins to damage host cells. Viruses can induce cytopathic effects through inhibition of host cell functions or metabolic changes. Overall, microbes must adhere and penetrate host barriers, avoid defenses, and damage tissues through various virulence factors to establish infection and pathogenesis.