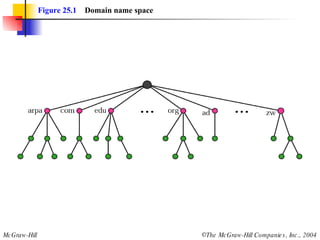
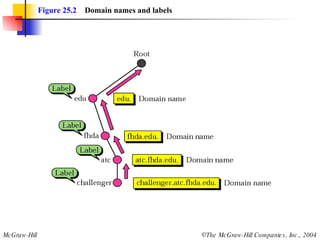
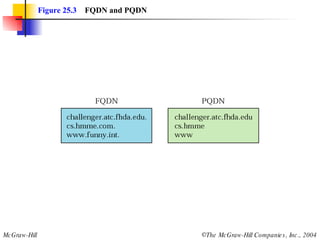
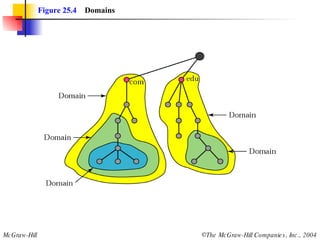
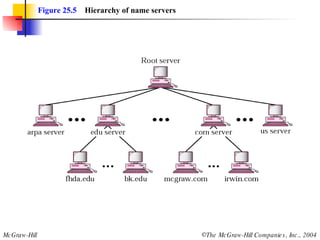
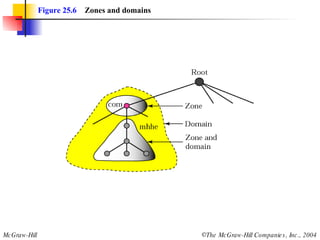
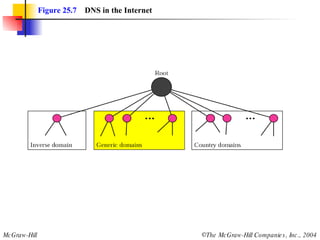
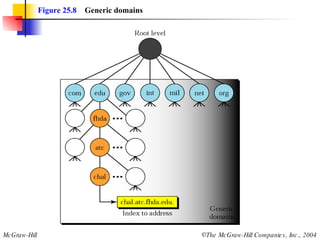
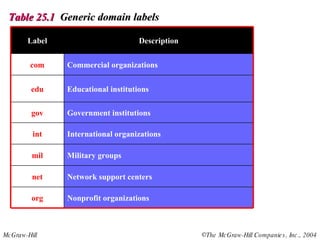
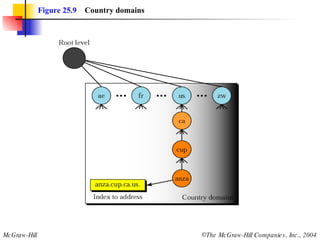
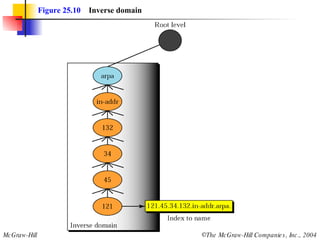
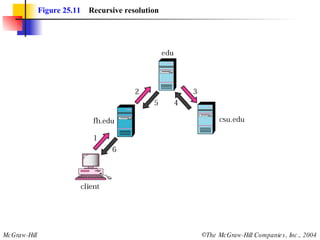
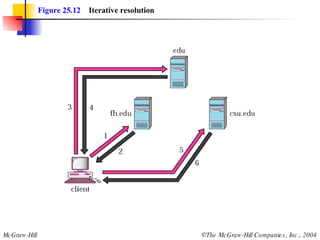
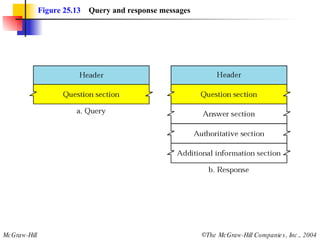
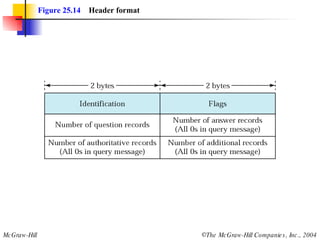
The document discusses the domain name system (DNS) which provides a hierarchical and distributed naming system that translates human-friendly domain names to IP addresses. DNS uses a system of name servers that are organized into zones to distribute the mapping of domain names to IP addresses globally. Resolvers use recursive or iterative resolution processes to map names to addresses by querying name servers in the DNS hierarchy.