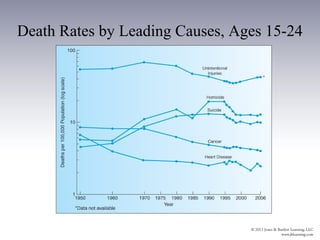
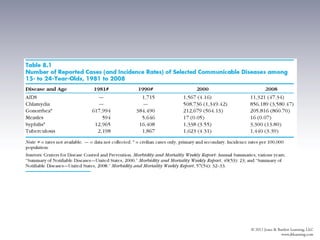
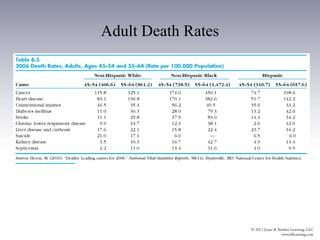
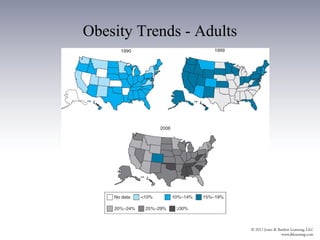
This document discusses health issues for three age groups: adolescents and young adults (15-24), adults (25-64), and older adults (65+). For adolescents and young adults, leading causes of death include injuries, homicide, and suicide. Health behaviors like risky sex, substance use, and lack of exercise are established during these years. Community strategies target these behaviors. Adults experience most chronic diseases. Leading causes of death are cancer, heart disease and behaviors like smoking, inactivity and diet impact risk. Community efforts focus on screening and managing conditions. Lifestyle changes can improve health for all age groups.