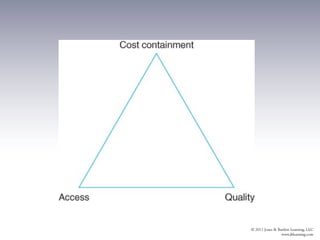
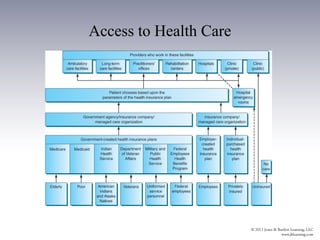
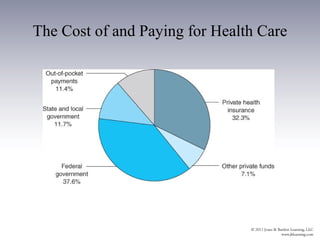
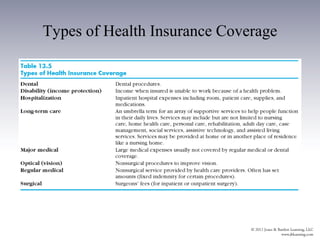
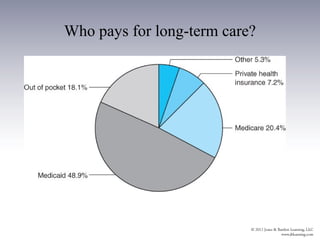
The document provides an overview of the history and structure of health care delivery in the United States. It discusses how care has shifted from patients' homes to hospitals and physicians' offices over time. It also outlines the various types of health care providers, facilities, insurance models, and ongoing efforts at reforming the system. The U.S. health care system is unique compared to other developed nations in being delivered by private providers across various settings and paid for through a mix of public and private means.