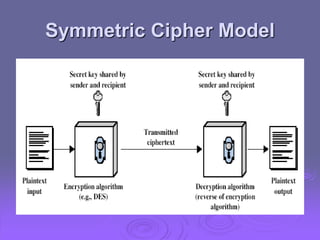
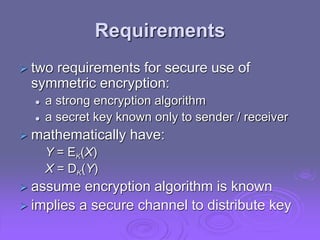
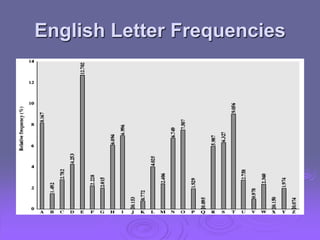
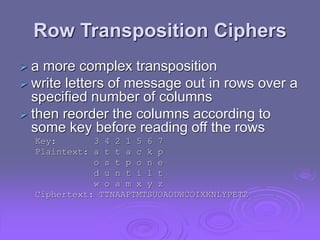
This document summarizes classical encryption techniques discussed in Chapter 2. Symmetric encryption uses a shared secret key between the sender and receiver. Techniques discussed include the Caesar cipher, which shifts letters by a fixed number; the monoalphabetic cipher, which maps each plaintext letter to a ciphertext letter; the Playfair cipher, which encrypts digrams; and the polyalphabetic Vigenère cipher, which uses multiple Caesar ciphers with a keyword as the key. The document also discusses cryptanalysis techniques like frequency analysis and the Kasiski method to help break these classical ciphers.