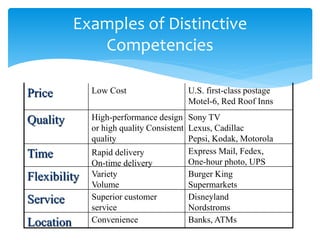
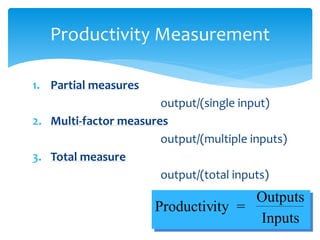
This document discusses key concepts in operations management including competitiveness, strategy, and productivity. It defines competitiveness as how well an organization meets customer needs relative to competitors. Businesses compete using marketing strategies like product design and pricing, as well as operations strategies involving factors like quality, response time, and inventory management. The document also discusses why some organizations fail due to issues like neglecting operations strategy or customer needs. It defines mission, strategy, and tactics, giving an example of how they relate for a student pursuing career goals. Distinctive competencies that give companies competitive advantages are also discussed.