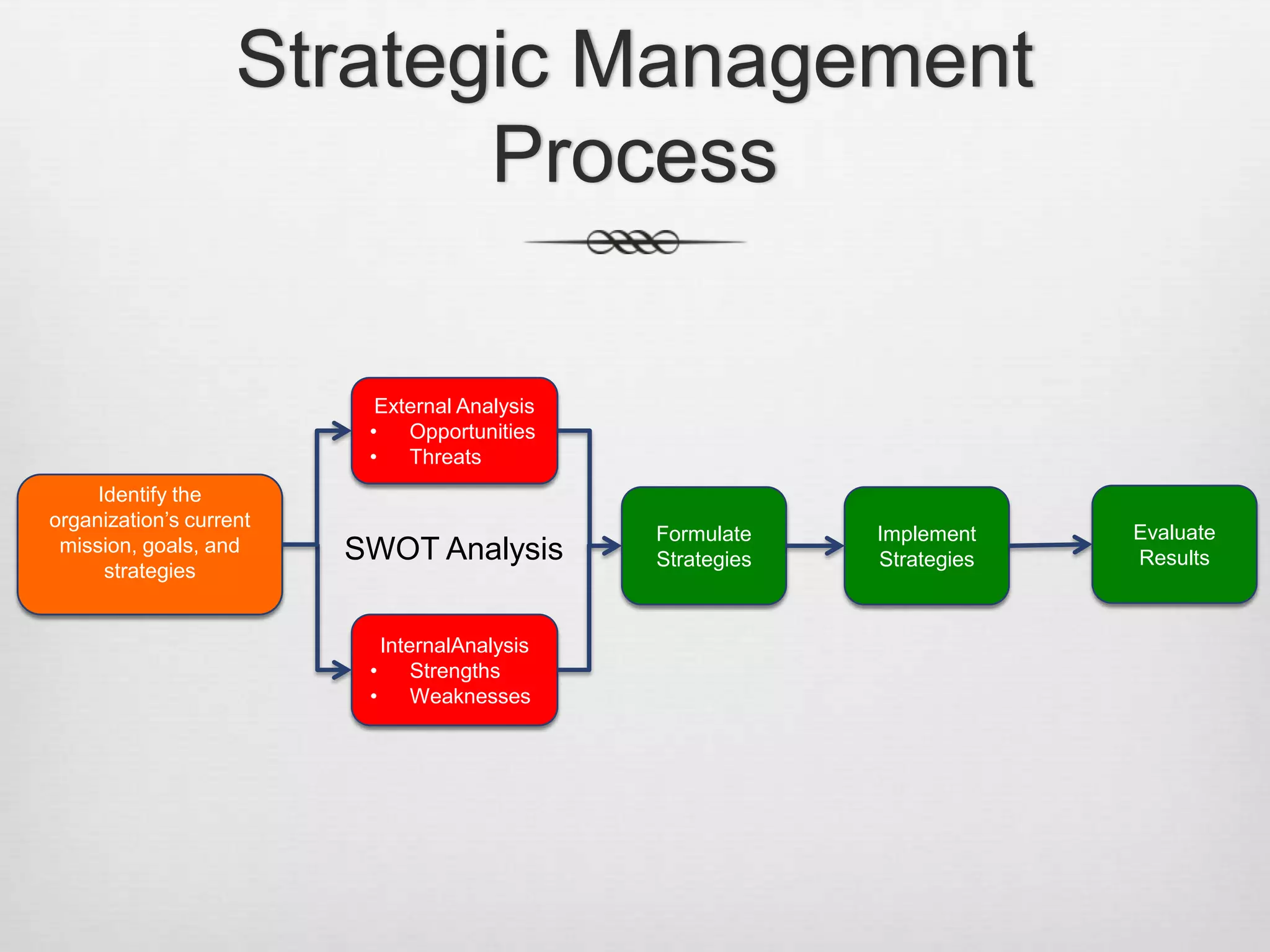
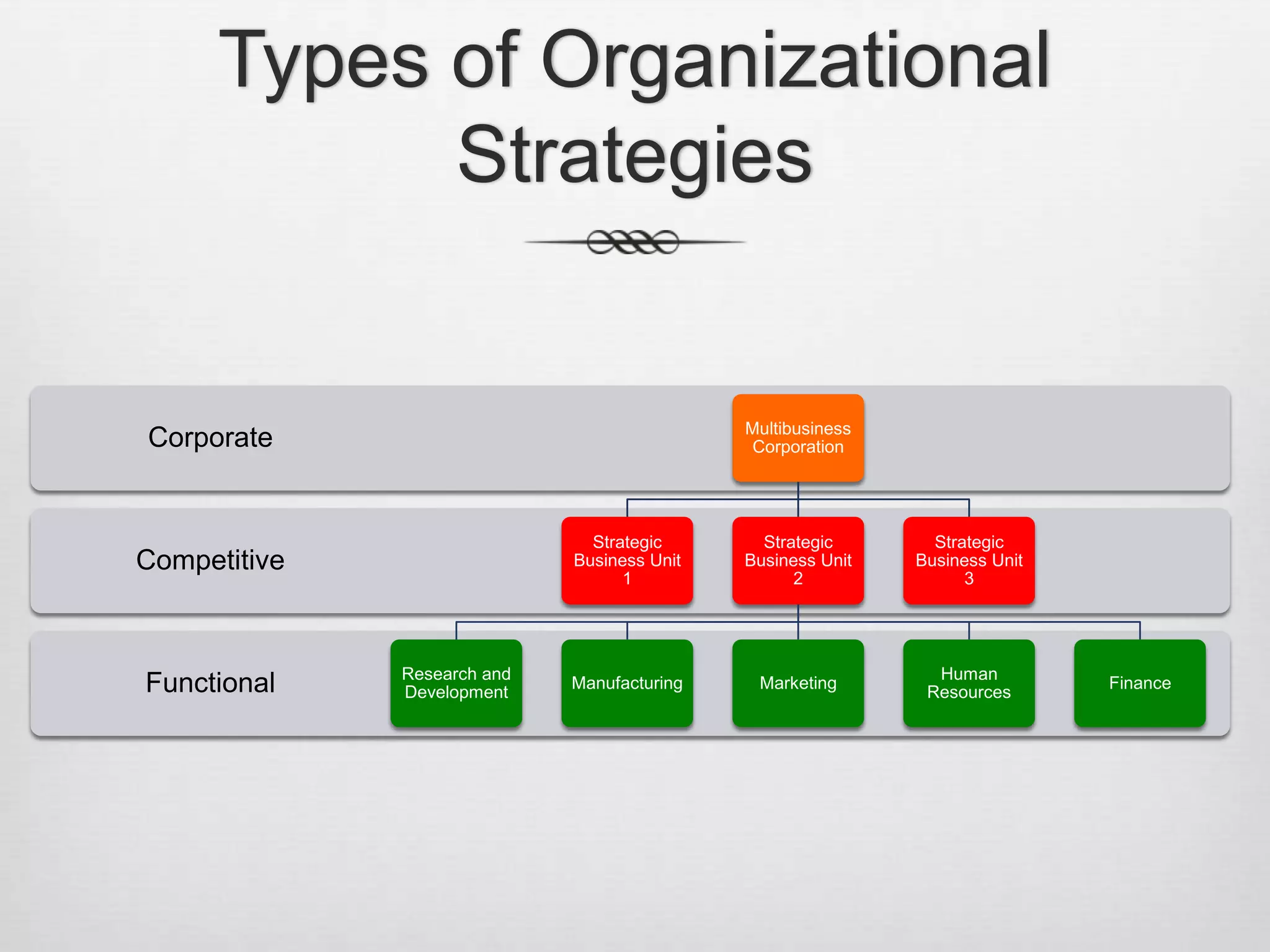
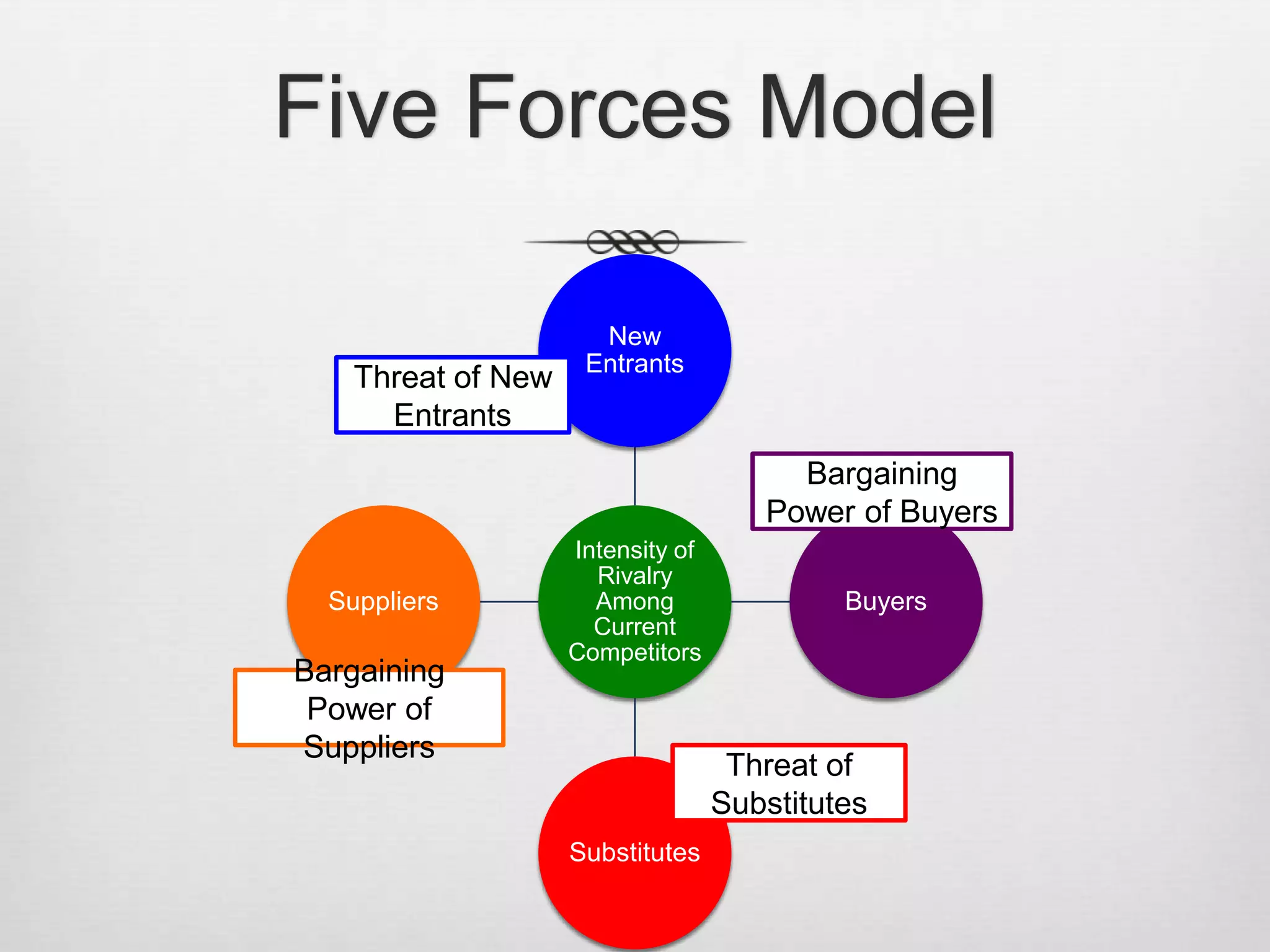
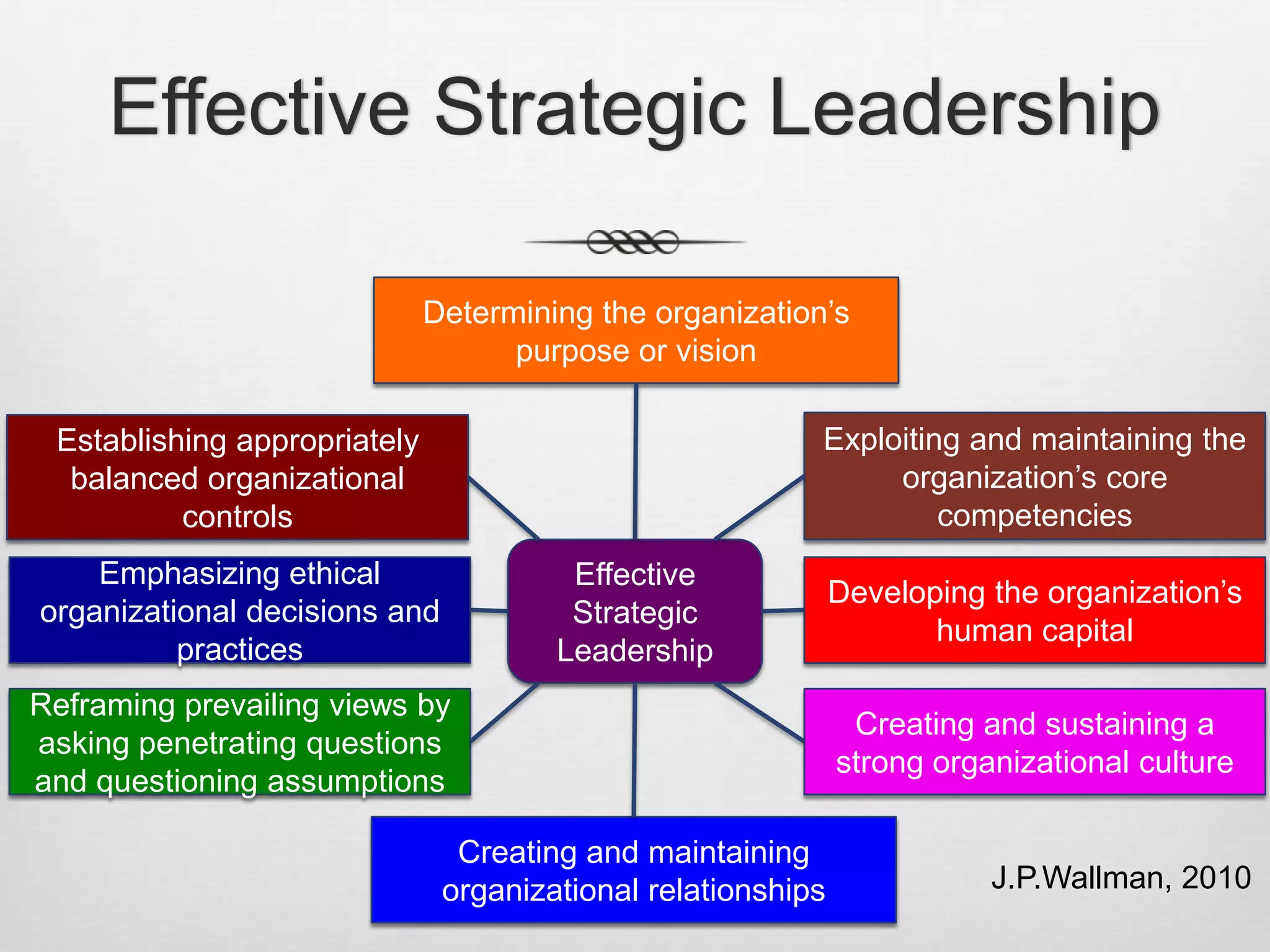
This document discusses strategic management and various related concepts. It defines strategic management as what managers do to develop organizational strategies. It then discusses why strategic management is important, outlining the strategic management process. It also summarizes various strategy types including corporate strategies, competitive strategies, and important strategies for today's environment.