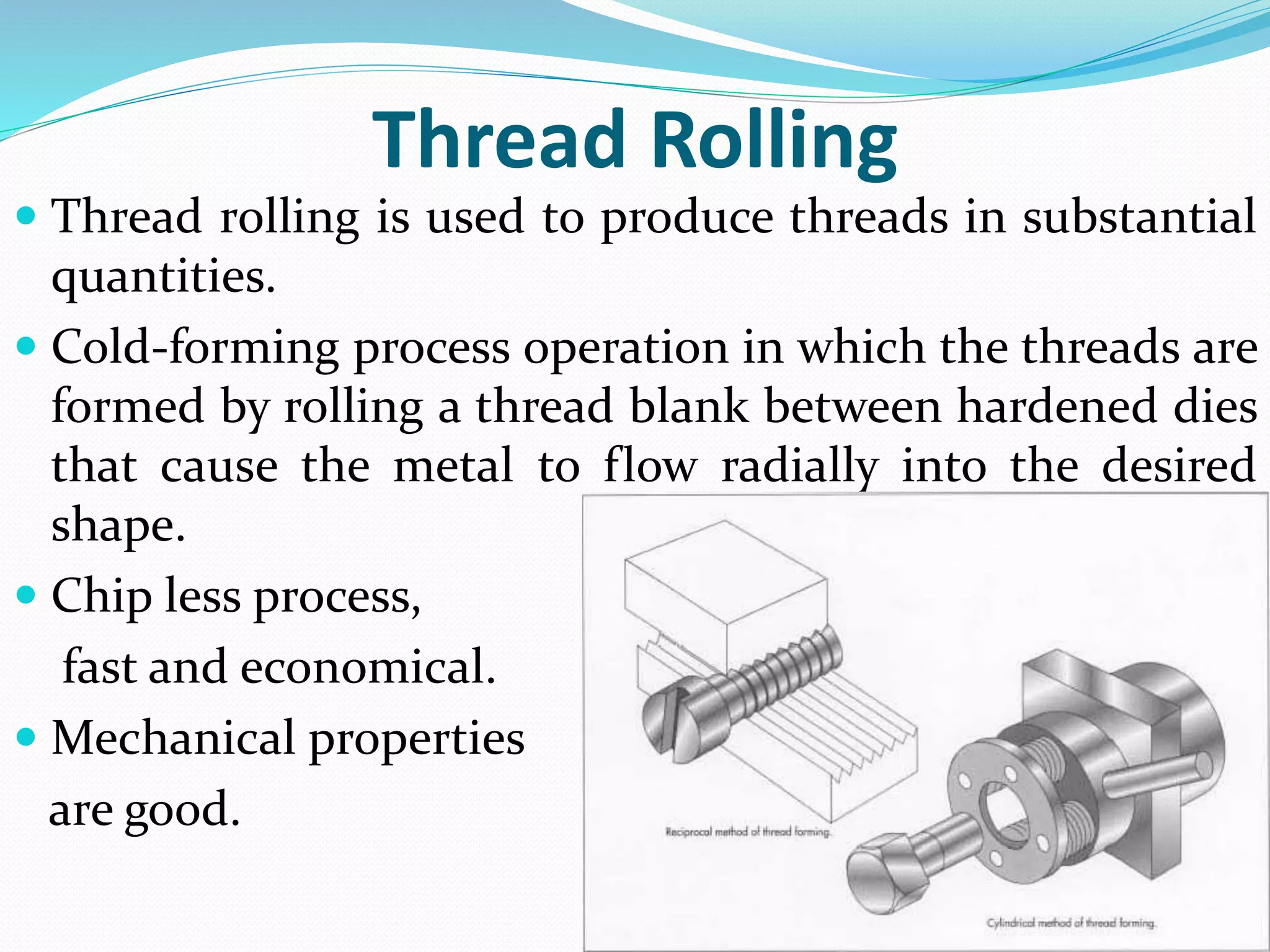
The document discusses various methods for manufacturing screw threads, including:
1) Thread cutting on lathes for both external and internal threads using tools like dies, taps, and mills.
2) Thread grinding and rolling which produce very accurate threads through forming processes.
3) Other methods like thread milling and chasing that can efficiently machine threads, especially in larger sizes.