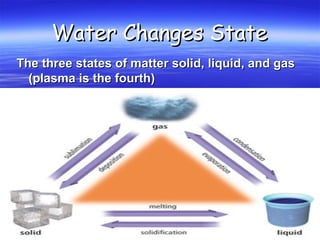
Water vapor is the most important gas in the atmosphere. Clouds form when air is cooled to its dew point. There are three main types of clouds - cirrus, cumulus, and stratus - which are classified based on their height in the atmosphere. Precipitation forms as cloud droplets grow in size, with the type of precipitation depending on temperature profiles. Common forms of precipitation include rain, snow, sleet, glaze, and hail.