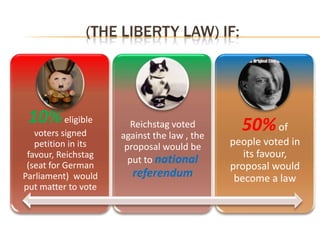
The Young Plan was proposed in 1929 to restructure German reparations payments following the failure of the Dawes Plan. It reduced Germany's total reparations to $18 billion over 37 years, with annual payments averaging $487.6 million. Some payments would be unconditional while others depended on Germany's ability to pay without harming its currency. Bonds would be issued against the unconditional portions. The plan aimed to ease Germany's burden but faced political opposition within Germany. This opposition helped bring Hitler and the Nazis into the mainstream.