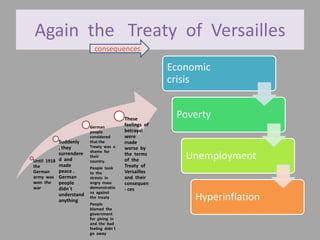
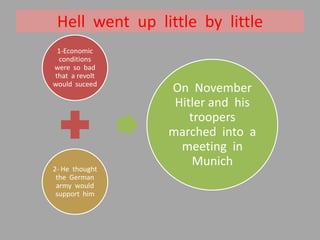
The document discusses the rise of Adolf Hitler and the Nazi party in Germany following World War 1 and the Treaty of Versailles. It describes how Germans felt betrayed by the treaty's terms, leading to economic crisis and unrest. Hitler exploited these feelings by blaming Jews and promising to return Germany to greatness. He gained popularity and used intimidation tactics to seize power legally, becoming dictator and establishing a brutal racist regime that systematically persecuted and murdered millions of Jews and others.