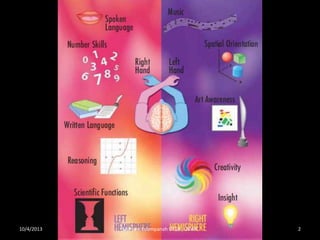
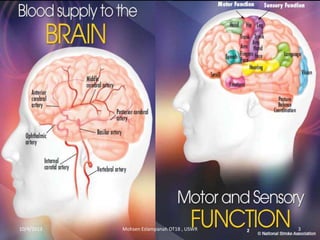
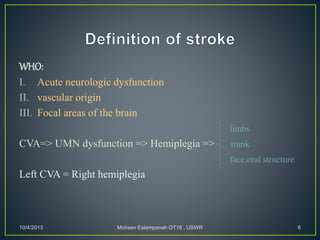
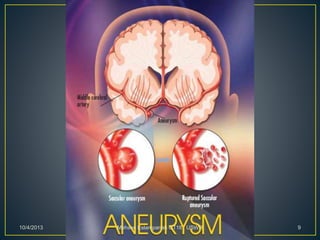
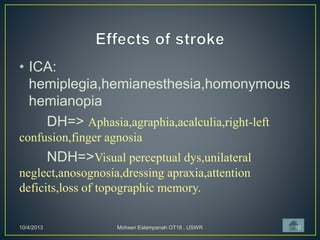
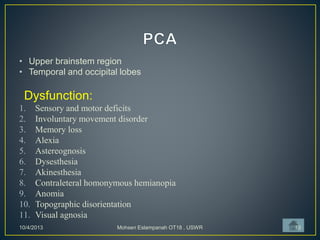
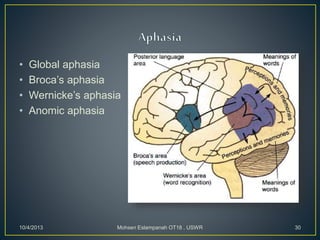
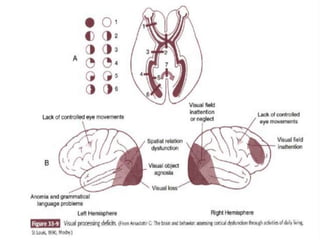
Stroke is the third leading cause of death worldwide. It is defined as acute neurologic dysfunction of vascular origin affecting focal areas of the brain. Common effects of stroke include motor paralysis, sensory disturbances, cognitive impairments, and speech or language disorders. Occupational therapists play an important role in evaluating clients after a stroke and providing intervention to improve functional limitations in areas like mobility, self-care, and upper extremity function. Treatment focuses on retraining skills and compensating for deficits through task-oriented and occupation-based approaches.