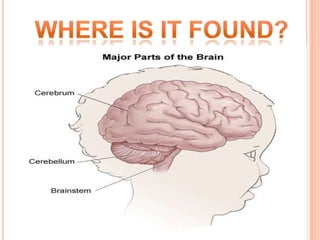
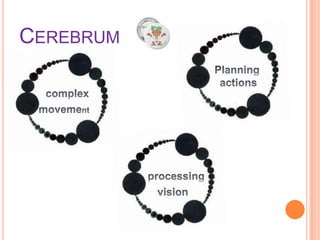
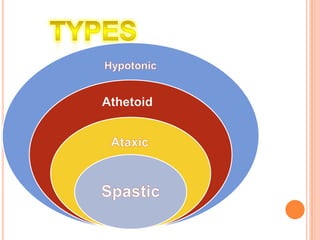
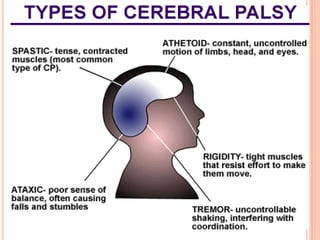
Cerebral palsy is a group of disorders that affect movement and muscle coordination. It is caused by damage to the developing brain, usually before or during birth. The most common type is spastic cerebral palsy, which causes stiff muscles and exaggerated reflexes. Other types include athetoid, ataxic, and hypotonic cerebral palsy. While there is no cure for cerebral palsy, treatment can improve capabilities and includes physical therapy, medication, and surgery. Famous people who have cerebral palsy include Christy Brown, Jerry Traylor, and Christopher Nolan.