This document provides an overview of Ceph storage, including:
1) Ceph addresses challenges faced by traditional storage such as increasing data growth and legacy infrastructure limitations through a software-defined storage approach.
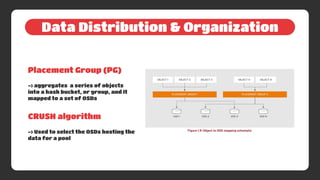
2) Ceph's architecture is based on RADOS which uses four daemons - monitors, object storage devices, managers, and metadata servers - to distribute and organize data across pools and placement groups.
3) Clients can access Ceph storage using the Ceph native API, Ceph block device, Ceph object gateway, or Ceph file system.