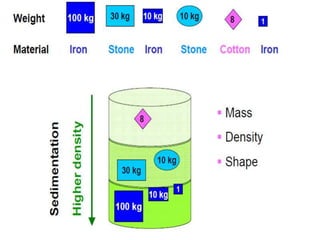
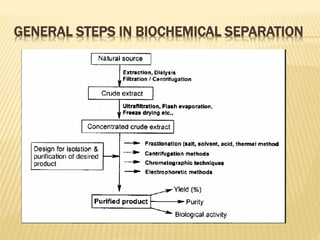
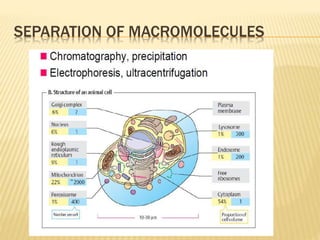
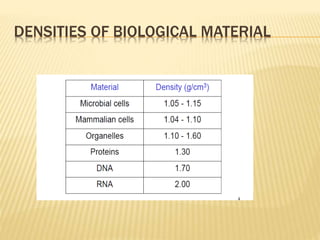
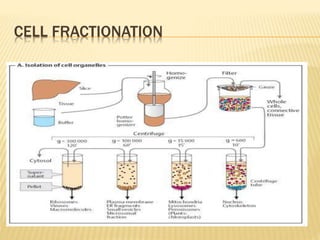
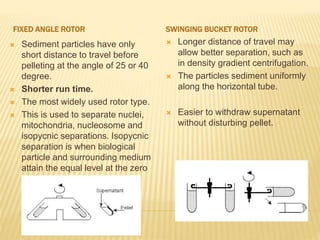
Centrifugation is a technique that uses centrifugal force to separate particles in a solution based on their size, shape, density, and other properties. A centrifuge spins the solution at high speeds, causing denser particles to sediment toward the bottom while less dense particles float to the top. This technique is commonly used to isolate cells, organelles, proteins, and other biological molecules. It works by exploiting even small differences in density between particles and the surrounding medium under artificially strong centrifugal forces.