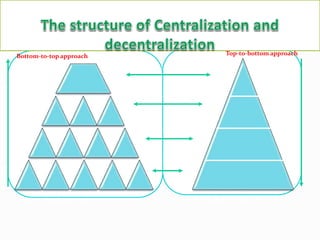
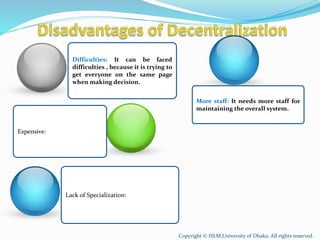
This document discusses and compares centralization and decentralization in organizational structures. Centralization refers to concentrating decision-making authority at higher levels of management, while decentralization involves dispersing authority to lower levels. The document outlines advantages and disadvantages of both approaches. Centralization can lead to delays and lack of initiative, while decentralization may cause coordination issues but improves motivation and decision making. Ultimately, the best structure depends on an organization's size, goals, and environment.