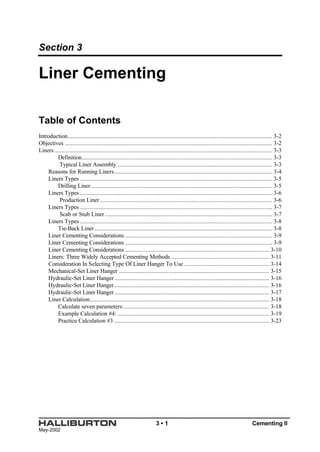
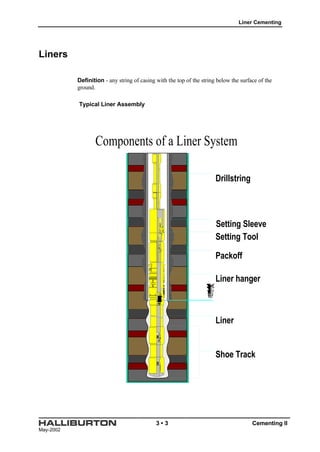
The document discusses liner cementing. It defines liners and describes typical liner assembly components. It outlines reasons for running liners such as reduced casing costs. It describes different liner types including drilling, production, scab/stub, and tie-back liners. It discusses considerations for liner cementing such as tight annular clearances and limited pump rates. It also presents widely used cementing methods and factors in selecting liner hangers. The document provides an example calculation for cementing a liner.